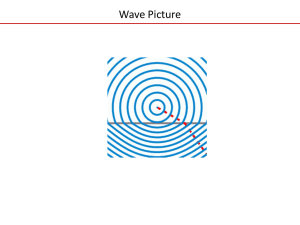
Wave Picture
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
1051-733-20092 Homework #1 Due 12/09/2000 (W)
... (b) Show that the two-dimensional sinusoidal part of this function contributions ALL of the volume and that the cosine part contributes none. 6. Consider propagation over the distance z1 and then over the distance z2 , where both distances satisfy the conditions for Fresnel diffraction. Show that a s ...
... (b) Show that the two-dimensional sinusoidal part of this function contributions ALL of the volume and that the cosine part contributes none. 6. Consider propagation over the distance z1 and then over the distance z2 , where both distances satisfy the conditions for Fresnel diffraction. Show that a s ...
Light Hits Near Infinite Speed in Silver-Coated Glass
... The new material contains a nano-scale structure that guides light waves through the metal-coated glass. It is the first with a refractive index below 0.1, which means that light passes through it at almost infinite speed, says Albert Polman at the FOM Institute AMOLF in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. ...
... The new material contains a nano-scale structure that guides light waves through the metal-coated glass. It is the first with a refractive index below 0.1, which means that light passes through it at almost infinite speed, says Albert Polman at the FOM Institute AMOLF in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. ...
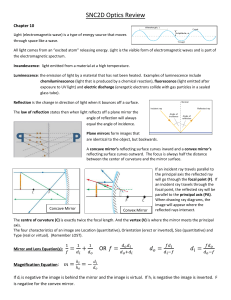
Chapter 35 Light: Reflection and Refraction
... Chapter 35 Light: Reflection and Refraction 35.1 Ray Optics It is natural to treat the propagation of light in terms of rays. A ray is equivalent to a very narrow beam of light, and it indicates the path along which the energy of the wave travels. Geometrical optics is the study of the behavior of s ...
... Chapter 35 Light: Reflection and Refraction 35.1 Ray Optics It is natural to treat the propagation of light in terms of rays. A ray is equivalent to a very narrow beam of light, and it indicates the path along which the energy of the wave travels. Geometrical optics is the study of the behavior of s ...
Light T
... that is being _______reflected__________. *The primary colors of pigments are _______cyan____, _______yellow________ and _______magenta___________. *The secondary colors of pigments are ___red_______, ________green____, and ________blue______. ...
... that is being _______reflected__________. *The primary colors of pigments are _______cyan____, _______yellow________ and _______magenta___________. *The secondary colors of pigments are ___red_______, ________green____, and ________blue______. ...
SNC2D Optics Review
... Light (electromagnetic wave) is a type of energy source that moves through space like a wave. All light comes from an “excited atom” releasing energy. Light is the visible form of electromagnetic waves and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Incandescence: light emitted from a material at a hig ...
... Light (electromagnetic wave) is a type of energy source that moves through space like a wave. All light comes from an “excited atom” releasing energy. Light is the visible form of electromagnetic waves and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Incandescence: light emitted from a material at a hig ...
n - LSU Physics
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). • How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg ...
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). • How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg ...
Waves Revision Booklet
... Complete the above table using the equation you have just completed. Use the space below for your calculations. ...
... Complete the above table using the equation you have just completed. Use the space below for your calculations. ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.