Phys 322 Optics - Purdue Physics
... "It's of no use whatsoever,“ "This is just an experiment that proves Maestro Maxwell was right - we just have these mysterious electromagnetic waves that we cannot see with the naked eye. But they are there.“ ...
... "It's of no use whatsoever,“ "This is just an experiment that proves Maestro Maxwell was right - we just have these mysterious electromagnetic waves that we cannot see with the naked eye. But they are there.“ ...
Basic Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation.
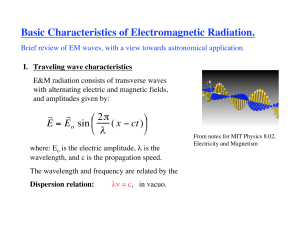
... Basic Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation. Brief review of EM waves, with a view towards astronomical application. I. Traveling wave characteristics E&M radiation consists of transverse waves with alternating electric and magnetic fields, and amplitudes given by: ...
... Basic Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation. Brief review of EM waves, with a view towards astronomical application. I. Traveling wave characteristics E&M radiation consists of transverse waves with alternating electric and magnetic fields, and amplitudes given by: ...
The University of Georgia Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Mach-Zender interferometer shown in the figure. Light from a infrared laser (λ = 1.00µm) is split into two waves that travel equal distances around the arms of the interferometer. One arm passes through an electro-optic crystal, a transparent material that can change its index of refraction in respo ...
... Mach-Zender interferometer shown in the figure. Light from a infrared laser (λ = 1.00µm) is split into two waves that travel equal distances around the arms of the interferometer. One arm passes through an electro-optic crystal, a transparent material that can change its index of refraction in respo ...
Slide - Journal of Vision
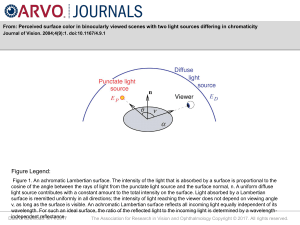
... Figure 1. An achromatic Lambertian surface. The intensity of the light that is absorbed by a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle between the rays of light from the punctate light source and the surface normal, n. A uniform diffuse light source contributes with a constant amount to the ...
... Figure 1. An achromatic Lambertian surface. The intensity of the light that is absorbed by a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle between the rays of light from the punctate light source and the surface normal, n. A uniform diffuse light source contributes with a constant amount to the ...
Homework Questions - science
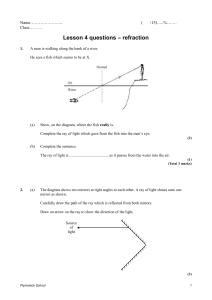
... When the light waves pass from glass into the air they change ................................ This causes a change in direction called ................................ Light waves are ................................ waves. ...
... When the light waves pass from glass into the air they change ................................ This causes a change in direction called ................................ Light waves are ................................ waves. ...
Electromagnetic Radiation Name
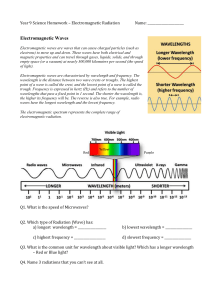
... Electromagnetic waves are waves that can cause charged particles (such as electrons) to move up and down. These waves have both electrical and magnetic properties and can travel through gases, liquids, solids, and through empty space (or a vacuum) at nearly 300,000 kilometers per second (the speed o ...
... Electromagnetic waves are waves that can cause charged particles (such as electrons) to move up and down. These waves have both electrical and magnetic properties and can travel through gases, liquids, solids, and through empty space (or a vacuum) at nearly 300,000 kilometers per second (the speed o ...
Chem 115 - Waves, Radiation and Spectroscopy (lecture 16) 3/31
... If you shine light of a particular wavelength onto metal you can get the electrons to come off of the metal if the light has high enough frequency (thus energy). The minimum threshold energy where electrons begin to come off the metal is called the “work function”. Photoelectric effect is an example ...
... If you shine light of a particular wavelength onto metal you can get the electrons to come off of the metal if the light has high enough frequency (thus energy). The minimum threshold energy where electrons begin to come off the metal is called the “work function”. Photoelectric effect is an example ...
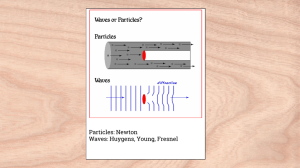
tutorial #10 [wave nature of light] .quiz
... that form a thin wedge of air as shown in fig. 1. An observer looking down through the glass plate sees the fringe pattern shown in the lower part of the drawing, with the dark fringes at the ends A and B. The wavelength of the light is 520 nm. Using the fringe pattern shown in the drawing, determin ...
... that form a thin wedge of air as shown in fig. 1. An observer looking down through the glass plate sees the fringe pattern shown in the lower part of the drawing, with the dark fringes at the ends A and B. The wavelength of the light is 520 nm. Using the fringe pattern shown in the drawing, determin ...
Light Problems Quiz: Name___________________ SHOW ALL
... into miles (1000m = 1km and 1mi = 1.6km). ...
... into miles (1000m = 1km and 1mi = 1.6km). ...
Light

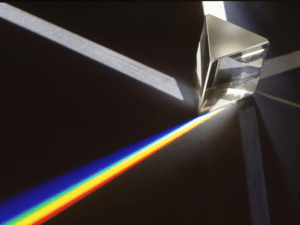
Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.










![tutorial #10 [wave nature of light] .quiz](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/020410144_1-db052accb2aa8cded167524d89755606-300x300.png)