LED Turning Lights on the Traction Avant
... both my cars I have electronic these flashers operated by a lever from the steering column which I use for normal driving, but I have also kept the original Scintex flashers which are still in working condition. Keeping the Scintex Flasher Replacing the light bulbs with the LED units –which is deadl ...
... both my cars I have electronic these flashers operated by a lever from the steering column which I use for normal driving, but I have also kept the original Scintex flashers which are still in working condition. Keeping the Scintex Flasher Replacing the light bulbs with the LED units –which is deadl ...
Module 27: Polarization-II Lecture 27: Polarization-II
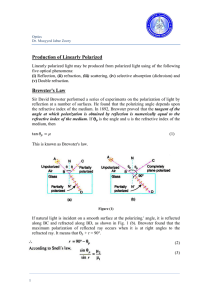
... no when E is perpendicular to the x axis. Here the x axis is referred to as the optic axis. The optical properties are the same in all directions perpendicular ~ is along the optic axis. Crystals may to the optic axis and it is different if E have more than one optic axis. Here we only consider a si ...
... no when E is perpendicular to the x axis. Here the x axis is referred to as the optic axis. The optical properties are the same in all directions perpendicular ~ is along the optic axis. Crystals may to the optic axis and it is different if E have more than one optic axis. Here we only consider a si ...
Question 10.1: Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is
... In a single slit diffraction experiment, if the width of the slit is made double the original width, then the size of the central diffraction band reduces to half and the intensity of the central diffraction band increases up to four times. The interference pattern in a double-slit experiment is mod ...
... In a single slit diffraction experiment, if the width of the slit is made double the original width, then the size of the central diffraction band reduces to half and the intensity of the central diffraction band increases up to four times. The interference pattern in a double-slit experiment is mod ...
Refraction and Lenses Learning Guide
... eyepiece produces magnified virtual image still inverted. 11. How is the refracting telescope different from the microscope? same type lenses and images, but object is farther away so longer focal lengths are used in the telescope. 12. What optical phenomenon is responsible for the creation of mirag ...
... eyepiece produces magnified virtual image still inverted. 11. How is the refracting telescope different from the microscope? same type lenses and images, but object is farther away so longer focal lengths are used in the telescope. 12. What optical phenomenon is responsible for the creation of mirag ...
Name:
... A “bit” of extra information to “byte” off about binary numbers: In any form of communication in binary signals (like a DVD, a CD, or an optical signal through an optical fiber), the smallest unit of information is a “bit” -- which would be a “one” (a light pulse) or a “zero” (no light pulse) in a g ...
... A “bit” of extra information to “byte” off about binary numbers: In any form of communication in binary signals (like a DVD, a CD, or an optical signal through an optical fiber), the smallest unit of information is a “bit” -- which would be a “one” (a light pulse) or a “zero” (no light pulse) in a g ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.