Diffraction
... suggested that the movements of heavy objects, such as black holes and dense stars, create waves that change space and time. We have a chance to detect these waves, but they need your help to do it! Einstein@Home uses computer time donated by computer owners all over the world to process data from g ...
... suggested that the movements of heavy objects, such as black holes and dense stars, create waves that change space and time. We have a chance to detect these waves, but they need your help to do it! Einstein@Home uses computer time donated by computer owners all over the world to process data from g ...
Entry Task
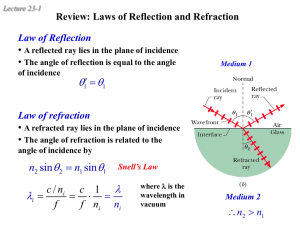
... wave will turn toward the normal. – If the medium lets the wave speed up, the wave will turn away from the normal. ...
... wave will turn toward the normal. – If the medium lets the wave speed up, the wave will turn away from the normal. ...
the measurement of the speed of the light
... the media where light is propagating. [3] Since our measurement is done in air, we should take into account the correction for refractive index obtained by L.Essen and others, [4] ng = 1 + 10 −8 (27260 + 460.8 / λ2 + 6.60 / λ4 ) We will discuss this effect later in part ÒResult and discussionÓ. ...
... the media where light is propagating. [3] Since our measurement is done in air, we should take into account the correction for refractive index obtained by L.Essen and others, [4] ng = 1 + 10 −8 (27260 + 460.8 / λ2 + 6.60 / λ4 ) We will discuss this effect later in part ÒResult and discussionÓ. ...
CHAPTER 6 Human Eye Notes FIB
... light detector to record a digital image. The image formed is ____________ and ____________. o ____________ – the opening where light enters the camera. o Wide‐angle lens – have ____________ focal lengths that produce a relatively ____________ image but have a wide field of view. o Telephoto le ...
... light detector to record a digital image. The image formed is ____________ and ____________. o ____________ – the opening where light enters the camera. o Wide‐angle lens – have ____________ focal lengths that produce a relatively ____________ image but have a wide field of view. o Telephoto le ...
Light

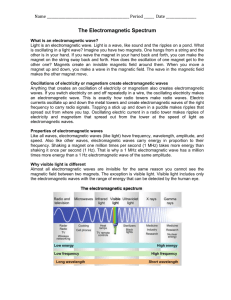
Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.