Lens Characteristics
... ratio play the major part in achieving better sunlight readability. The specially designed filters used in Oxley indicator lamps attenuate the ambient light reflected off the lens. Any reflected light from the inner surfaces of the indicator lamp that may cause spurious ON/OFF indications is also at ...
... ratio play the major part in achieving better sunlight readability. The specially designed filters used in Oxley indicator lamps attenuate the ambient light reflected off the lens. Any reflected light from the inner surfaces of the indicator lamp that may cause spurious ON/OFF indications is also at ...
Phys342_Syl.pdf
... Hunter College regards acts of academic dishonesty (e.g., plagiarism, cheating on examinations, obtaining unfair advantage, and falsification of records and official documents) as serious offenses against the values of intellectual honesty. The college is committed to enforcing the CUNY Policy on Ac ...
... Hunter College regards acts of academic dishonesty (e.g., plagiarism, cheating on examinations, obtaining unfair advantage, and falsification of records and official documents) as serious offenses against the values of intellectual honesty. The college is committed to enforcing the CUNY Policy on Ac ...
Crystal Optics with Intense Light Sources Exercise sheet #4
... (a) Think about the light you want and the light you do not want to measure. Which filter would you place behind the sample? Use the filter curves given on the next page. (1) (b) In addition, nonlinear optical processes can occur in the polarization optics before and after the light passes the sampl ...
... (a) Think about the light you want and the light you do not want to measure. Which filter would you place behind the sample? Use the filter curves given on the next page. (1) (b) In addition, nonlinear optical processes can occur in the polarization optics before and after the light passes the sampl ...
the reactions of photosynthesis that are directly dependent upon
... • Light is a form of kinetic energy called Electromagnetic radiation – Travels in waves (and particles) – Different wavelengths give the energy different properties ...
... • Light is a form of kinetic energy called Electromagnetic radiation – Travels in waves (and particles) – Different wavelengths give the energy different properties ...
diffraction glasses: what`s in a color?
... Light can be broken into component colors using a diffraction grating - waves, light, or any type of wave that goes through a narrow slit spreads out. The process that results from the wave spreading out as it goes through a narrow opening is called diffraction. When we use diffraction, it is possib ...
... Light can be broken into component colors using a diffraction grating - waves, light, or any type of wave that goes through a narrow slit spreads out. The process that results from the wave spreading out as it goes through a narrow opening is called diffraction. When we use diffraction, it is possib ...
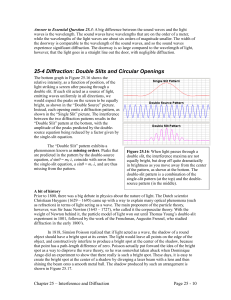
25-4 Diffraction: Double Slits and Circular Openings
... the narrower the width of the central peak in the diffraction pattern. This dependence on the diameter of the opening has implications for how close two objects can be before you cannot resolve them. For instance, when you look up at the sky at night, two stars that are very close together may appea ...
... the narrower the width of the central peak in the diffraction pattern. This dependence on the diameter of the opening has implications for how close two objects can be before you cannot resolve them. For instance, when you look up at the sky at night, two stars that are very close together may appea ...
The Photoelectric Effect
... no photoelectrons are emitted, no matter how much the intensity of the light is increased. However, when f>f0, the photocurrent increases proportionally with the intensity of the light. These observations are inconsistent with a classical wave model of light, and led Einstein to postulate in 1905 th ...
... no photoelectrons are emitted, no matter how much the intensity of the light is increased. However, when f>f0, the photocurrent increases proportionally with the intensity of the light. These observations are inconsistent with a classical wave model of light, and led Einstein to postulate in 1905 th ...
Lecture 22 - LSU Physics
... A thickness D=(m+0.5) 2.02 mm would make the waves OUT of phase. For example, 1.008 mm makes them in phase, and 1.010 mm makes them OUT of phase. ...
... A thickness D=(m+0.5) 2.02 mm would make the waves OUT of phase. For example, 1.008 mm makes them in phase, and 1.010 mm makes them OUT of phase. ...
lightandeye - Leon County Schools
... Light and the Human Eye (cont.) • The retina is a layer of special light-sensitive cells in the back of the eye. • In the retina, chemical reactions produce nerve signals that the optic nerve sends to your brain. • Rod cells and cone cells are two types of lightsensitive cells in your retina. • Rod ...
... Light and the Human Eye (cont.) • The retina is a layer of special light-sensitive cells in the back of the eye. • In the retina, chemical reactions produce nerve signals that the optic nerve sends to your brain. • Rod cells and cone cells are two types of lightsensitive cells in your retina. • Rod ...
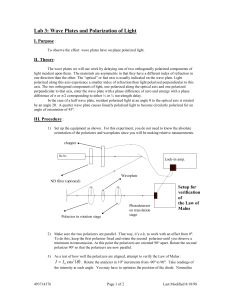
Physics 102 Lab 8: Measuring wavelengths with a
... everywhere one is positive, the other is negative by an equal amount. Although the diffraction of light waves ostensibly appears the same as the diffraction of classical waves such as water or sound waves, it is an intrinsically quantum mechanical process. Indeed, while the diffraction pattern of a ...
... everywhere one is positive, the other is negative by an equal amount. Although the diffraction of light waves ostensibly appears the same as the diffraction of classical waves such as water or sound waves, it is an intrinsically quantum mechanical process. Indeed, while the diffraction pattern of a ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.