From a flat mirror, designer light — Harvard School of Engineering
... Fellow in Electrical Engineering at SEAS. "Our discovery carries optics into new territory and opens the door to exciting developments in photonics technology." It has been recognized since ancient times that light travels at different speeds through different media. Reflection and refraction occur ...
... Fellow in Electrical Engineering at SEAS. "Our discovery carries optics into new territory and opens the door to exciting developments in photonics technology." It has been recognized since ancient times that light travels at different speeds through different media. Reflection and refraction occur ...
Chapter 23: Electromagnetic waves What will we learn in this chapter?
... The radiation pressure of sunlight on an absorbing surface is approximately 4.7x10-6 Pa (this can be measured!). Theoretically, one could use the pressure of the sun’s EM waves to power spacecrafts–so called sun sails. Some projects are currently being explored. Tails of comets always face away from ...
... The radiation pressure of sunlight on an absorbing surface is approximately 4.7x10-6 Pa (this can be measured!). Theoretically, one could use the pressure of the sun’s EM waves to power spacecrafts–so called sun sails. Some projects are currently being explored. Tails of comets always face away from ...
Chapter 7
... • Newton tried to explain the energy in a light beam as the KE of a particle stream, and failed. • About 1800, some experiments proved that light acts like waves. • About 1900, other experiments proved that light acts like particles. • Present idea: sometimes like waves, sometimes like particles. ...
... • Newton tried to explain the energy in a light beam as the KE of a particle stream, and failed. • About 1800, some experiments proved that light acts like waves. • About 1900, other experiments proved that light acts like particles. • Present idea: sometimes like waves, sometimes like particles. ...
Length poster
... Although the iodine-stabilised helium-neon laser provides a very stable optical frequency (or vacuum wavelength), it is already possible to build lasers with an optical frequency that is known around ten thousand times more accurately. The iodinestabilised laser is limited because the iodine molecul ...
... Although the iodine-stabilised helium-neon laser provides a very stable optical frequency (or vacuum wavelength), it is already possible to build lasers with an optical frequency that is known around ten thousand times more accurately. The iodinestabilised laser is limited because the iodine molecul ...
Atomic_spectra
... the midst of the rainbow of colors was a series of black lines. These dark lines were later determined to be the result of the absorption of selected frequencies of the electromagnetic radiation by an atom or molecule. ...
... the midst of the rainbow of colors was a series of black lines. These dark lines were later determined to be the result of the absorption of selected frequencies of the electromagnetic radiation by an atom or molecule. ...
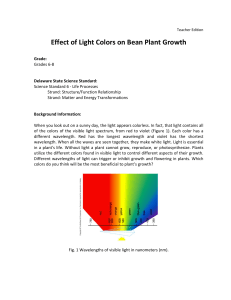
Effect of Light Colors on Bean Plant Growth
... indicates the wavelengths of light. Explain what is meant by “wavelength” and that a nanometer is 0.000000001 meter in length. Show the students how white light is separated into colors using a prism, and that colors of objects are due to the reflection of specific wavelengths, while other wavelengt ...
... indicates the wavelengths of light. Explain what is meant by “wavelength” and that a nanometer is 0.000000001 meter in length. Show the students how white light is separated into colors using a prism, and that colors of objects are due to the reflection of specific wavelengths, while other wavelengt ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.