Unit 7 Study Guide
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
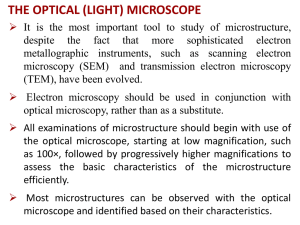
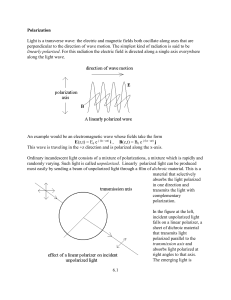
6.1 Polarization Light is a transverse wave: the electric and magnetic
... have their fast axes parallel (This is the same as a single half wave plate). The incident light is polarized at 45( to these axes. Describe the polarization state of the transmitted light. Problem 6: Linearly polarized light enters two sequential half-wave plates. The two plates have their fast axe ...
... have their fast axes parallel (This is the same as a single half wave plate). The incident light is polarized at 45( to these axes. Describe the polarization state of the transmitted light. Problem 6: Linearly polarized light enters two sequential half-wave plates. The two plates have their fast axe ...
Polarized light and polarizers
... metallic wires, placed in a plane perpendicular to the incident beam. Electromagnetic waves with electric fields aligned parallel to the wires induce the movement of electrons along the length of the wires. Since the electrons are free to move, the polarizer behaves in a similar manner as the surfac ...
... metallic wires, placed in a plane perpendicular to the incident beam. Electromagnetic waves with electric fields aligned parallel to the wires induce the movement of electrons along the length of the wires. Since the electrons are free to move, the polarizer behaves in a similar manner as the surfac ...
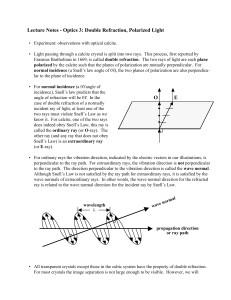
Lecture Notes - Optics 3: Double Refraction, Polarized Light E O
... observe other optical properties that result from the double refraction. For hexagonal and tetragonal crystals, there will be one O-ray and one E-ray. For orthorhombic, monoclinic, and triclinic crystals, there will be two E-rays. In general, the refractive indices for non-cubic crystals depend on v ...
... observe other optical properties that result from the double refraction. For hexagonal and tetragonal crystals, there will be one O-ray and one E-ray. For orthorhombic, monoclinic, and triclinic crystals, there will be two E-rays. In general, the refractive indices for non-cubic crystals depend on v ...
Review ! a
... ! The interferometer consists of a light source in the form of a laser emitting coherent light with wavelength ! = 632.8 nm ! The light passes through a de-focusing lens to spread out the normally very narrowly focused laser beam ! The light then passes through a half-silvered mirror m1 ...
... ! The interferometer consists of a light source in the form of a laser emitting coherent light with wavelength ! = 632.8 nm ! The light passes through a de-focusing lens to spread out the normally very narrowly focused laser beam ! The light then passes through a half-silvered mirror m1 ...
Wang Lecture - math550mathsciencetechnology
... the polarization states of light. They are made from one or more pieces of birefringent crystals. Each wave plate has a fast axis and a slow axis. Inside the crystal, the incident light is separated into two lights, each has refractive indices no and ne, and is polarized parallel to the fast or slow ...
... the polarization states of light. They are made from one or more pieces of birefringent crystals. Each wave plate has a fast axis and a slow axis. Inside the crystal, the incident light is separated into two lights, each has refractive indices no and ne, and is polarized parallel to the fast or slow ...
Background: Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of
... b) Racemic mixture is not found in biological system (for example, when alanine is isolated from biological sample only one of the two isomers is present, but when alanine is synthesized in lab, a mixture of two isomers is produced) this property is used to detect the presence of life on other plane ...
... b) Racemic mixture is not found in biological system (for example, when alanine is isolated from biological sample only one of the two isomers is present, but when alanine is synthesized in lab, a mixture of two isomers is produced) this property is used to detect the presence of life on other plane ...
Photoelectric Effect Lab
... predict the answer to every experiment that has been tried, history tells us that the correct answer to these questions is probably still not known. Future experiments will probably demonstrate that our present theories are only approximations of the true answers to nature’s questions. One of the mo ...
... predict the answer to every experiment that has been tried, history tells us that the correct answer to these questions is probably still not known. Future experiments will probably demonstrate that our present theories are only approximations of the true answers to nature’s questions. One of the mo ...
Three models of light
... coming from it enters our eyes. • Our eyes identify a point as being on an object when rays traced back converge at that point. ...
... coming from it enters our eyes. • Our eyes identify a point as being on an object when rays traced back converge at that point. ...
Select Safety Light Curtain Terms
... (transmitter) and receiver during installation. For long-range sensing, or when using deflecting mirrors, an external alignment aid (such as a laser aligning tool) may be used during installation. ...
... (transmitter) and receiver during installation. For long-range sensing, or when using deflecting mirrors, an external alignment aid (such as a laser aligning tool) may be used during installation. ...
CraveTheWaveTestQuestions-Cobra2016
... 8. If the amplitude of a wave is increased by 3 times, then the energy of the wave a. Decreased by 3 times b. Increased by 3 times c. Decreased by 6 times d. Increased by 9 times ...
... 8. If the amplitude of a wave is increased by 3 times, then the energy of the wave a. Decreased by 3 times b. Increased by 3 times c. Decreased by 6 times d. Increased by 9 times ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.