Lecture 1
... Lecture today: Chapter 20 (included in exam 1) 1) Entropy 2) Second Law of Thermodynamics 3) Statistical View of Entropy ...
... Lecture today: Chapter 20 (included in exam 1) 1) Entropy 2) Second Law of Thermodynamics 3) Statistical View of Entropy ...
Lecture 11 - Laws of Thermodynamics
... An ideal gas is slowly compressed at a constant pressure of 2.0 atm from 10.0 L to 2.0 L. (In this process, some heat flows out of the gas and the temperature drops.) Heat is then added to the gas, holding the volume constant, and the pressure and temperature are allowed to rise (line DA) until the ...
... An ideal gas is slowly compressed at a constant pressure of 2.0 atm from 10.0 L to 2.0 L. (In this process, some heat flows out of the gas and the temperature drops.) Heat is then added to the gas, holding the volume constant, and the pressure and temperature are allowed to rise (line DA) until the ...
thermochemistry - Pace University Webspace
... • Gibbs Free Energy is a measure of nonpV work that must go into a reaction to make it occur (when G is positive) or work that a reaction can do (when negative). It can be shown that the change of Gibbs Free Energy over temperature in a reaction is the change of the total entropy of the reacting sys ...
... • Gibbs Free Energy is a measure of nonpV work that must go into a reaction to make it occur (when G is positive) or work that a reaction can do (when negative). It can be shown that the change of Gibbs Free Energy over temperature in a reaction is the change of the total entropy of the reacting sys ...
HeatTransfer
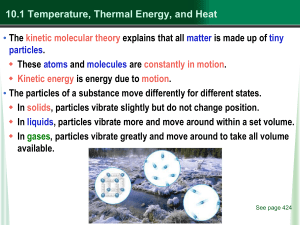
... Heat moves from higher temperature (higher kinetic energy) particles to lower temperature particles (lower kinetic energy.) e.g.: a cold spoon warms when placed in a cup of hot coffee. Thermal conductors transfer heat easily, while insulators do not. • Convection is the transfer of heat in flu ...
... Heat moves from higher temperature (higher kinetic energy) particles to lower temperature particles (lower kinetic energy.) e.g.: a cold spoon warms when placed in a cup of hot coffee. Thermal conductors transfer heat easily, while insulators do not. • Convection is the transfer of heat in flu ...
Entropy
... the energy of the system does not change. If there is no net loss of energy when these processes operate in the forward or natural direction, it would not require any expenditure of energy for them to operate in reverse. In other words, contrary to the common sense, ...
... the energy of the system does not change. If there is no net loss of energy when these processes operate in the forward or natural direction, it would not require any expenditure of energy for them to operate in reverse. In other words, contrary to the common sense, ...
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS
... Ans. If for a given state, there is a definite volume for each property then the property is known as a point function. The differentials of point function are exact differentials. For e.g. pressure temperature volume entropy and enthalpy etc. These type of thermodynamic properties only depend on en ...
... Ans. If for a given state, there is a definite volume for each property then the property is known as a point function. The differentials of point function are exact differentials. For e.g. pressure temperature volume entropy and enthalpy etc. These type of thermodynamic properties only depend on en ...
The First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19
... V1 = 10"2 m 3 ,V2 = 3x10"2 m 3 ,n = 2 moles of monatomic ideal gas Evaluate #U,W ,Q,and #T for the path 1- > 3- > 2 and compare with the isothermal process 1 - > 2 Let P1 = 3x10 5 ...
... V1 = 10"2 m 3 ,V2 = 3x10"2 m 3 ,n = 2 moles of monatomic ideal gas Evaluate #U,W ,Q,and #T for the path 1- > 3- > 2 and compare with the isothermal process 1 - > 2 Let P1 = 3x10 5 ...
First Law Of Thermodynamics
... In biological system If the capacity to do work is represented by the symbol “W” and “H” stands for enthalpy (or heat content), then the firat law can be expressed as: ΔH = Q - W ...
... In biological system If the capacity to do work is represented by the symbol “W” and “H” stands for enthalpy (or heat content), then the firat law can be expressed as: ΔH = Q - W ...
Energy
... A system does 130. J of work on its surroundings while 70. J of heat are added to the system. What is the internal energy change for the system? ...
... A system does 130. J of work on its surroundings while 70. J of heat are added to the system. What is the internal energy change for the system? ...