Quantum Renormalization of the Spin Hall Effect
... scale competes with the Coulomb energy U between the electrons in the d orbitals, which is also of the order of eV. The latter tends to produce the spin moment, while the former induces quantum fluctuation of that spin moment, leading to the spin singlet. The competition between these two interactio ...
... scale competes with the Coulomb energy U between the electrons in the d orbitals, which is also of the order of eV. The latter tends to produce the spin moment, while the former induces quantum fluctuation of that spin moment, leading to the spin singlet. The competition between these two interactio ...
BODY PERTURBATIVE AND GREEN`S
... bitals are assumed to be frozen. This implies that the effect of ’relaxation’ is neglected – an effect which for inner-shell ionization can be quite appreciable. A simple and popular way of including the relaxation effect in an approximate way is to perform separate self-consistent-field calculation ...
... bitals are assumed to be frozen. This implies that the effect of ’relaxation’ is neglected – an effect which for inner-shell ionization can be quite appreciable. A simple and popular way of including the relaxation effect in an approximate way is to perform separate self-consistent-field calculation ...
Dissociation energy of the water dimer from Quantum Monte Carlo
... The hydrogen bond in the water dimer has been the subject of many electronic structure studies [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] since it represents the prototype of all hydrogen-bonded systems. In recent years the water dimer has been studied using high-level quantum chemistry techniques, such as second-ord ...
... The hydrogen bond in the water dimer has been the subject of many electronic structure studies [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] since it represents the prototype of all hydrogen-bonded systems. In recent years the water dimer has been studied using high-level quantum chemistry techniques, such as second-ord ...
3 center 4 electron bond article
... be an exceedingly difficult problem [1e]. Recently, this author has proposed [2] that in phosphorus pentahalides, PX5 (X = F, Cl), a three-center, four-electron bond is formed in the axial positions via the overlap of the unhybridized p orbital on the central atom and the two axial ligand orbitals. ...
... be an exceedingly difficult problem [1e]. Recently, this author has proposed [2] that in phosphorus pentahalides, PX5 (X = F, Cl), a three-center, four-electron bond is formed in the axial positions via the overlap of the unhybridized p orbital on the central atom and the two axial ligand orbitals. ...
The Shadow Path integral Ground State method
... The study of condensed phases of 4He has played a very important role in the context of modern condensed matter Physics, both providing an extremely interesting experimental scenario, allowing one to see quantum effects in a macroscopic system, and being a constant test case of many body-theories an ...
... The study of condensed phases of 4He has played a very important role in the context of modern condensed matter Physics, both providing an extremely interesting experimental scenario, allowing one to see quantum effects in a macroscopic system, and being a constant test case of many body-theories an ...
"Effects of quantum chemistry models for bound electrons on positron annihilation spectra for atoms and small molecules" New J. Phys. , 14 , 085022 (2012). F. Wang, X. Ma, L. Selvam, G. F. Gribakin, and C. M Surko (PDF)
... also started appearing in the recent literature [12–15]. In particular, we have developed and explored a low-energy plane-wave positron (LEPWP) approximation for estimating the Doppler-shift spectra of annihilation γ-rays and tested it for noble gas atoms [12] and small molecules [13–15]. In this ap ...
... also started appearing in the recent literature [12–15]. In particular, we have developed and explored a low-energy plane-wave positron (LEPWP) approximation for estimating the Doppler-shift spectra of annihilation γ-rays and tested it for noble gas atoms [12] and small molecules [13–15]. In this ap ...
Prediction of new inorganic molecules with quantum chemical
... the predictions were remarkably improved if the exchangecorrelation functional went beyond the local-density approximation (LDA) and included some dependence on the gradient of the electron density. His second paper [27] told us how to evaluate accurately the matrix elements of these DFT functionals ...
... the predictions were remarkably improved if the exchangecorrelation functional went beyond the local-density approximation (LDA) and included some dependence on the gradient of the electron density. His second paper [27] told us how to evaluate accurately the matrix elements of these DFT functionals ...
Valence Bond theory
... For H2, we begin with the two 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms. There are two ways in which these can be combined, corresponding to two molecular orbitals. One molecular orbital lowers the energy and therefore corresponds to a bonding orbital, while the other molecular orbital raises the ener ...
... For H2, we begin with the two 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms. There are two ways in which these can be combined, corresponding to two molecular orbitals. One molecular orbital lowers the energy and therefore corresponds to a bonding orbital, while the other molecular orbital raises the ener ...
Variational approach to the Davydov soliton
... and Lomdahl. (ii) In the limit that (no exciton transport), the new equations of motion for the parameters in ~D, & are exact and lead to the correct state at all times, while the equation of motion suggested by Davydov yields incorrect results in this limit. (iii) In the limit of no exciton-phonon ...
... and Lomdahl. (ii) In the limit that (no exciton transport), the new equations of motion for the parameters in ~D, & are exact and lead to the correct state at all times, while the equation of motion suggested by Davydov yields incorrect results in this limit. (iii) In the limit of no exciton-phonon ...
International Journal of Quantum Chemistry 114:1041
... Atomic orbitals (AOs) represent an important concept in the theory of atomic and molecular physics. Historically, they first appeared as exact solutions of the Schrödinger equation of the free hydrogen atom, then they have been obtained as solutions in the Hartree-Fock (HF) approximation for the fr ...
... Atomic orbitals (AOs) represent an important concept in the theory of atomic and molecular physics. Historically, they first appeared as exact solutions of the Schrödinger equation of the free hydrogen atom, then they have been obtained as solutions in the Hartree-Fock (HF) approximation for the fr ...
Lecture 19: The Aufbau Principle
... • This is an approximation (and it is surprising how well it actually works). ...
... • This is an approximation (and it is surprising how well it actually works). ...
Chem 310 Lectures by: Dr. Muhammad D. Bala Office: Block H, 3
... Degenerate orbitals are filled according to Hund's rules: • One electron is added to each of the degenerate orbitals in a subshell before a second electron is added to any orbital in the subshell Î lowest energy subshell filled in first. • Electrons are added to a subshell with the same value of the ...
... Degenerate orbitals are filled according to Hund's rules: • One electron is added to each of the degenerate orbitals in a subshell before a second electron is added to any orbital in the subshell Î lowest energy subshell filled in first. • Electrons are added to a subshell with the same value of the ...
Self-consistent approach for calculations of exciton binding energy
... asymmetric quantum wells, and also allows incorporating external electric and magnetic fields, stress, and disordered potential acting on electrons and holes in QW because of inherent inhomogeneities of structure. All these effects, which modify the single particle part of the Hamiltonian, appear aut ...
... asymmetric quantum wells, and also allows incorporating external electric and magnetic fields, stress, and disordered potential acting on electrons and holes in QW because of inherent inhomogeneities of structure. All these effects, which modify the single particle part of the Hamiltonian, appear aut ...
Real-time, real-space implementation of the linear response time
... Calculations of the optical response with linear response TDDFT have been first achieved in early 80’s for spherical systems, atoms [19] and metallic clusters [20]. Because the independent-particle response function χ 0 defined by Eq. (13) is a scalar integral kernel for spherical systems, Eq. (12) ...
... Calculations of the optical response with linear response TDDFT have been first achieved in early 80’s for spherical systems, atoms [19] and metallic clusters [20]. Because the independent-particle response function χ 0 defined by Eq. (13) is a scalar integral kernel for spherical systems, Eq. (12) ...
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
... This will result in two non-equivalent Be-Cl bonds. However, experiments suggest that the two Be-Cl bonds are equivalent in every respect. Thus, the 2s and the 2p orbitals in the Be-atom must be hybridized to form two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals. The two hybrid orbitals lie on the same axi ...
... This will result in two non-equivalent Be-Cl bonds. However, experiments suggest that the two Be-Cl bonds are equivalent in every respect. Thus, the 2s and the 2p orbitals in the Be-atom must be hybridized to form two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals. The two hybrid orbitals lie on the same axi ...
Generalized variational principle for excited states using nodes of
... This allows one to optimize a trial wave function by minimizing the expectation value of the energy. This approach is also trivially generalized to excited states, so that given a trial wave function of a certain symmetry, one can compute an upper bound to the lowest-energy level of that symmetry. I ...
... This allows one to optimize a trial wave function by minimizing the expectation value of the energy. This approach is also trivially generalized to excited states, so that given a trial wave function of a certain symmetry, one can compute an upper bound to the lowest-energy level of that symmetry. I ...
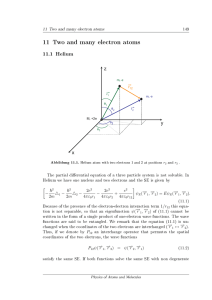
11 Two and many electron atoms - FU Berlin
... distinguished by their paths of sharp trajectories, this is not possible in quantum mechanics, if the particles are found in the same regions of space such as their interaction region. Let us consider a quantum mechanical system of N identical particles. The Hamiltonian and all observables correspon ...
... distinguished by their paths of sharp trajectories, this is not possible in quantum mechanics, if the particles are found in the same regions of space such as their interaction region. Let us consider a quantum mechanical system of N identical particles. The Hamiltonian and all observables correspon ...
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY AND BONDING NOTES
... of the nuclear attraction and the average repulsion of all other electrons.” It has the same formulation as an atomic orbital does in a many electron atom. It has an energy associated with it which gives the energy of an electron with such a wavefunction in the field of the nucleus and the other ele ...
... of the nuclear attraction and the average repulsion of all other electrons.” It has the same formulation as an atomic orbital does in a many electron atom. It has an energy associated with it which gives the energy of an electron with such a wavefunction in the field of the nucleus and the other ele ...
molecular geometry
... For H2, we begin with the two 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms. There are two ways in which these can be combined, corresponding to two molecular orbitals. One molecular orbital lowers the energy and therefore corresponds to a bonding orbital, while the other molecular orbital raises the ener ...
... For H2, we begin with the two 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms. There are two ways in which these can be combined, corresponding to two molecular orbitals. One molecular orbital lowers the energy and therefore corresponds to a bonding orbital, while the other molecular orbital raises the ener ...
fulltext
... [32, 57], and computations with millions of nuclei are made routinely. However, not all the physics of molecular dynamics can be explained by classical mechanics, which does not take phenomena like the uncertainty principle, tunnelling or zero-point energy into account. Chemical reactions are partic ...
... [32, 57], and computations with millions of nuclei are made routinely. However, not all the physics of molecular dynamics can be explained by classical mechanics, which does not take phenomena like the uncertainty principle, tunnelling or zero-point energy into account. Chemical reactions are partic ...
Calculation of C Operator in PT -Symmetric Quantum
... T pT −1 = −p, T xT −1 = x, and T iT −1 = −i. The non-Hermitian Hamiltonian H in (1) is not symmetric under P or T separately, but it is invariant under their combined operation; such Hamiltonians are said to possess space-time reflection symmetry (PT symmetry). We say that the PT symmetry of a Hamil ...
... T pT −1 = −p, T xT −1 = x, and T iT −1 = −i. The non-Hermitian Hamiltonian H in (1) is not symmetric under P or T separately, but it is invariant under their combined operation; such Hamiltonians are said to possess space-time reflection symmetry (PT symmetry). We say that the PT symmetry of a Hamil ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... of the wave function from its true form, and so the expectation value of the energy for an approximate wave function can be a very good estimate of the corresponding energy Eigen value. By using an approximate wave function that depends on some small set of parameters and minimizing its energy with ...
... of the wave function from its true form, and so the expectation value of the energy for an approximate wave function can be a very good estimate of the corresponding energy Eigen value. By using an approximate wave function that depends on some small set of parameters and minimizing its energy with ...
Molecular structure: Diatomic molecules in the rigid rotor and
... The nuclear Schrödinger equation describes both the motion of the molecule as a whole through space and relative motion—vibrations and rotations—of the atoms that make up the molecule. The way to separate the motions through space from the internal motion is to reexpress the coordinates of each atom ...
... The nuclear Schrödinger equation describes both the motion of the molecule as a whole through space and relative motion—vibrations and rotations—of the atoms that make up the molecule. The way to separate the motions through space from the internal motion is to reexpress the coordinates of each atom ...
Wednesday, Mar. 26, 2014
... 3) For finite potentials, the wave function and its derivatives must be continuous. This is required because the second-order derivative term in the wave equation must be single valued. (There are exceptions to this rule when V is infinite.) 4) In order to normalize the wave functions, they must app ...
... 3) For finite potentials, the wave function and its derivatives must be continuous. This is required because the second-order derivative term in the wave equation must be single valued. (There are exceptions to this rule when V is infinite.) 4) In order to normalize the wave functions, they must app ...