Assigning Hybridization: A Tutorial
... It is a common misconception that only the number of attachments to that atom controls hybridization of an atom. Instead, hybridization is controlled by what gives the molecule the lowest energy. This lowest energy includes not only a minimization of electron repulsion, but also accommodates electro ...
... It is a common misconception that only the number of attachments to that atom controls hybridization of an atom. Instead, hybridization is controlled by what gives the molecule the lowest energy. This lowest energy includes not only a minimization of electron repulsion, but also accommodates electro ...
p15_11_6.pdf
... action along the trajectory[5–10]; in this way semiclassical methods can capture essential quantum phenomena such as interference, zero-point energy effects, and to some extent tunneling. We present some results from an approach that uses semiclassical electron dynamics to evaluate the correlation t ...
... action along the trajectory[5–10]; in this way semiclassical methods can capture essential quantum phenomena such as interference, zero-point energy effects, and to some extent tunneling. We present some results from an approach that uses semiclassical electron dynamics to evaluate the correlation t ...
Molecular Structure and Orbitals - Blackboard
... – Usually atomic orbitals are half-filled before bonding – Spins of the electrons are paired once bond is formed • Overlapping orbitals are on adjacent atoms and are either – Standard atomic orbitals (s, p, d, f) – Hybridized atomic orbitals made by combining individual atomic orbitals. • Each bonde ...
... – Usually atomic orbitals are half-filled before bonding – Spins of the electrons are paired once bond is formed • Overlapping orbitals are on adjacent atoms and are either – Standard atomic orbitals (s, p, d, f) – Hybridized atomic orbitals made by combining individual atomic orbitals. • Each bonde ...
Numerical Methods for strongly correlated electrons
... insulating behavior when the number of electron per unit cell is odd. There are several examples of such ”Mott insulators”, expecially within the transition metal oxides, like MnO. Ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism, also, cannot be fully understood within a single particle formulation. One of th ...
... insulating behavior when the number of electron per unit cell is odd. There are several examples of such ”Mott insulators”, expecially within the transition metal oxides, like MnO. Ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism, also, cannot be fully understood within a single particle formulation. One of th ...
Chemical Reactivity as Described by Quantum Chemical Methods
... "modern" quantum mechanics around 1925 due to the work of Schrödinger, Heisenberg, Born, … Schrödinger's equation occupied a central position in this new theory and, although later on complemented by its relativistic analogue by Dirac, stood the test of time and has been for now 75 years the central ...
... "modern" quantum mechanics around 1925 due to the work of Schrödinger, Heisenberg, Born, … Schrödinger's equation occupied a central position in this new theory and, although later on complemented by its relativistic analogue by Dirac, stood the test of time and has been for now 75 years the central ...
Chapter 10
... How do we account for 4 C—H sigma bonds 109o apart? Need to use 4 atomic orbitals — s, px, py, and pz — to form 4 new hybrid orbitals pointing in the correct direction. Dr. S. M. Condren ...
... How do we account for 4 C—H sigma bonds 109o apart? Need to use 4 atomic orbitals — s, px, py, and pz — to form 4 new hybrid orbitals pointing in the correct direction. Dr. S. M. Condren ...
Doubly excited nonautoionizing P, D, and F states of helium with
... of helium in the field of synchrotron radiation 关1兴. With the advanced experimental techniques 关2,3兴, it becomes challenging to theoreticians to come up with more accurate results. Due to angular-momentum and parity conservation rules, the autoionization of doubly excited states below N = 2 threshol ...
... of helium in the field of synchrotron radiation 关1兴. With the advanced experimental techniques 关2,3兴, it becomes challenging to theoreticians to come up with more accurate results. Due to angular-momentum and parity conservation rules, the autoionization of doubly excited states below N = 2 threshol ...
Computer simulation by quantum mechanical time dependent wave
... Control over wave packet processes is the foundation of laser control of chemical reaction dynamics. The critical stage in a chemical reaction occurs within ...
... Control over wave packet processes is the foundation of laser control of chemical reaction dynamics. The critical stage in a chemical reaction occurs within ...
Implementation of the SCC-DFTB Method for
... approximation) and refers to the leading matrix element of the Hamiltonian, Ĥ0. The Kohn-Sham molecular orbitals ψi are expanded in a minimal basis set of Slater-type confined atomic orbitals, i.e., ψi ) ∑νcνiφν as described by Eschrig and Bergert,39 which is determined by solving the atomic Kohn-S ...
... approximation) and refers to the leading matrix element of the Hamiltonian, Ĥ0. The Kohn-Sham molecular orbitals ψi are expanded in a minimal basis set of Slater-type confined atomic orbitals, i.e., ψi ) ∑νcνiφν as described by Eschrig and Bergert,39 which is determined by solving the atomic Kohn-S ...
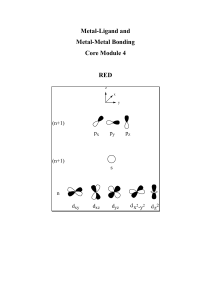
Metal-Ligand and Metal-Metal Bonding Lecture Notes
... The trends observed in 1 and 2 are a result of the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) that is a consequence of shielding and penetration. s > p > d > f The relatively very poor shielding of an electron in an f-orbital results in a steady decrease in the radii of the lanthanides (approximately 25%). Thi ...
... The trends observed in 1 and 2 are a result of the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) that is a consequence of shielding and penetration. s > p > d > f The relatively very poor shielding of an electron in an f-orbital results in a steady decrease in the radii of the lanthanides (approximately 25%). Thi ...
Theoretical modeling of x-ray and vibrational spectroscopies applied to liquid
... simple substance it is not easily understood. In fact, water has many anomalies like a very high boiling point, a density maximum at 4 degrees C, an unusually high compressibility etc.[1] These anomalies can be traced back to the properties of the hydrogen bond (H-bond), which in strength is between ...
... simple substance it is not easily understood. In fact, water has many anomalies like a very high boiling point, a density maximum at 4 degrees C, an unusually high compressibility etc.[1] These anomalies can be traced back to the properties of the hydrogen bond (H-bond), which in strength is between ...
Molecular Orbitals Chapter 5 : Molecular Orbitals
... In contrast to LE, molecular orbitals describe how electrons spread over all the atoms in a molecule and bind them together, which can give correct views of • concept of resonance. • paramagnetic properties. • bond energy. Fact: O2 is paramagnetic! ...
... In contrast to LE, molecular orbitals describe how electrons spread over all the atoms in a molecule and bind them together, which can give correct views of • concept of resonance. • paramagnetic properties. • bond energy. Fact: O2 is paramagnetic! ...
Third-order optical response of intermediate
... than on individual electrons and holes). We therefore refer to an electron– hole pair as a particle. We then derive the commutation relations of the particle operators that show their nonboson statistics, and we express the Hamiltonian in terms of them. Applying the equation of motion technique,8,19 ...
... than on individual electrons and holes). We therefore refer to an electron– hole pair as a particle. We then derive the commutation relations of the particle operators that show their nonboson statistics, and we express the Hamiltonian in terms of them. Applying the equation of motion technique,8,19 ...
First Principles Calculations of Off-Normal LEEM
... Our method: Find self-consistent potential and scattering states with DFT packages for solids Introduce a supercell Match incoming and outgoing plane waves to Bloch solutions at interfaces Quantum ESPRESSO (plane wave basis) Specular reflection only; lowest energy range Focus on Free-Standing Gr ...
... Our method: Find self-consistent potential and scattering states with DFT packages for solids Introduce a supercell Match incoming and outgoing plane waves to Bloch solutions at interfaces Quantum ESPRESSO (plane wave basis) Specular reflection only; lowest energy range Focus on Free-Standing Gr ...
The origin of the phase in the interference of Bose
... description of this phenomenon involves the introduction of a condensate wave function with a definite phase. We investigate the origin of this phase and the theoretical basis of treating interference. It is possible to construct a phase state for which the particle number is uncertain, but the phas ...
... description of this phenomenon involves the introduction of a condensate wave function with a definite phase. We investigate the origin of this phase and the theoretical basis of treating interference. It is possible to construct a phase state for which the particle number is uncertain, but the phas ...
The Mean-Field Limit for the Dynamics of Large Particle
... positrons, protons, neutrons etc... are fermions. That the wave function of a system of N fermions is skew-symmetric implies Pauli’s exclusion principle: two (or more) fermions cannot find themselves in the same quantum state. This apparently innocuous statement has far-reaching physical consequence ...
... positrons, protons, neutrons etc... are fermions. That the wave function of a system of N fermions is skew-symmetric implies Pauli’s exclusion principle: two (or more) fermions cannot find themselves in the same quantum state. This apparently innocuous statement has far-reaching physical consequence ...
chapter 7 multielectron atoms outline
... Consider the 3 electrons in a lithium atom, which has the electron configuration: 1s22s1. (a) Write the Hamiltonian for the electrons in a Lithium atom in (i) MKS (SI) units and (ii) in atomic units. (b) Use the “Independent Particle Model” (i.e. ignore interelectronic repulsions) to calculate the e ...
... Consider the 3 electrons in a lithium atom, which has the electron configuration: 1s22s1. (a) Write the Hamiltonian for the electrons in a Lithium atom in (i) MKS (SI) units and (ii) in atomic units. (b) Use the “Independent Particle Model” (i.e. ignore interelectronic repulsions) to calculate the e ...
The role of radial nodes of atomic orbitals for
... nodes will move the outermost maximum further away from the nucleus. This will be essential for the discussion in this article. When turning to multielectron atoms, the energetic degeneracy of different angular momentum for a given n is lifted by electron–electron interactions, but the spherical sym ...
... nodes will move the outermost maximum further away from the nucleus. This will be essential for the discussion in this article. When turning to multielectron atoms, the energetic degeneracy of different angular momentum for a given n is lifted by electron–electron interactions, but the spherical sym ...
art 1. Background Material
... The Bohr formula for energy levels did not agree as well with the observed pattern of emission spectra for species containing more than a single electron. However, it does give a reasonable fit, for example, to the Na atom spectra if one examines only transitions involving only the single valence el ...
... The Bohr formula for energy levels did not agree as well with the observed pattern of emission spectra for species containing more than a single electron. However, it does give a reasonable fit, for example, to the Na atom spectra if one examines only transitions involving only the single valence el ...
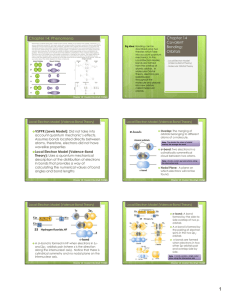
Chapter 14: Phenomena Chapter 14 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
... Phenomena: Scientists knew that in order to form a bond, orbitals on two atoms must overlap. However, px, py, and pz orbitals are located 90˚ from each other and compounds like CH4 (which would form bonds using their p orbitals) do not have bond angles of 90˚. Therefore, scientists had to explain th ...
... Phenomena: Scientists knew that in order to form a bond, orbitals on two atoms must overlap. However, px, py, and pz orbitals are located 90˚ from each other and compounds like CH4 (which would form bonds using their p orbitals) do not have bond angles of 90˚. Therefore, scientists had to explain th ...
E. Waltersson, On the role of the electron
... standard choice for the confining potential. Still, this is indeed an approximation and some efforts have been made to use a more realistic description of the whole physical situation, see e.g. Refs. [10, 14–17]. If one assumes this simplified view of the confining potential, theoretical quantum dot ...
... standard choice for the confining potential. Still, this is indeed an approximation and some efforts have been made to use a more realistic description of the whole physical situation, see e.g. Refs. [10, 14–17]. If one assumes this simplified view of the confining potential, theoretical quantum dot ...
A practical guide to density matrix embedding
... eigenvalues of Dkl (kl ∈ B) can lie arbitrarily close to 0 or 1 (or to 0 or 2 when a spin-summed restricted Slater determinant is used as the low-level wavefunction). It can happen for very large basis sets (Nocc < LA ), or when the occupied core orbitals of neighbouring atoms are in practice unenta ...
... eigenvalues of Dkl (kl ∈ B) can lie arbitrarily close to 0 or 1 (or to 0 or 2 when a spin-summed restricted Slater determinant is used as the low-level wavefunction). It can happen for very large basis sets (Nocc < LA ), or when the occupied core orbitals of neighbouring atoms are in practice unenta ...
A Theoretical Study of Atomic Trimers in the Critical Stability Region
... a harder task than bound state calculations. From a computational perspective such threshold states are difficult to obtain, since they lead to representations having very small and very large eigenvalues. As such, calculations of atomic halos and vdW trimers provide a challenge for any formal/numer ...
... a harder task than bound state calculations. From a computational perspective such threshold states are difficult to obtain, since they lead to representations having very small and very large eigenvalues. As such, calculations of atomic halos and vdW trimers provide a challenge for any formal/numer ...
Interacting Fock spaces: central limit theorems and quantum
... some important properties are exposed. In particular we present the rules of commutations, namely canonical commutation relations (CCR), canonical anticommutation relations (CAR) and free commutation relations of these operators respectively in boson, fermion and free case. In the second chapter int ...
... some important properties are exposed. In particular we present the rules of commutations, namely canonical commutation relations (CCR), canonical anticommutation relations (CAR) and free commutation relations of these operators respectively in boson, fermion and free case. In the second chapter int ...
Breaking Multiple Covalent Bonds with Hartree-Fock-based
... We enhance the recently proposed Optimized-orbital Quasi-Variational Coupled Cluster Doubles (OQVCCD) method for the calculation of ground-state molecular electronic structure by augmenting it with the standard perturbative (T) correction for the effects of connected triple excitations. We demonstra ...
... We enhance the recently proposed Optimized-orbital Quasi-Variational Coupled Cluster Doubles (OQVCCD) method for the calculation of ground-state molecular electronic structure by augmenting it with the standard perturbative (T) correction for the effects of connected triple excitations. We demonstra ...