In the diagram below, the optical train of a set of binoculars is found
... (ii) A Fabry-Perot etalon is fabricated from a 1 mm thickness of glass by silvering its two flat parallel, polished surfaces. The etalon is placed inside an oven to measure its temperature drift, by monitoring transmission of a laser beam at =500 nm. The change ...
... (ii) A Fabry-Perot etalon is fabricated from a 1 mm thickness of glass by silvering its two flat parallel, polished surfaces. The etalon is placed inside an oven to measure its temperature drift, by monitoring transmission of a laser beam at =500 nm. The change ...
Ch. 35: Reflection and Refraction of Light
... This is valid as long as the light does not change the medium through which it propagates (air, water, glass, plastic), or finds an obstacle (interface). The velocity of light in air is c c = 3x108 m/s The velocity of light in other media may be different from c (less than c). ...
... This is valid as long as the light does not change the medium through which it propagates (air, water, glass, plastic), or finds an obstacle (interface). The velocity of light in air is c c = 3x108 m/s The velocity of light in other media may be different from c (less than c). ...
lecture_three_2016
... serves as the source of spherical secondary waves also called wavelets, such that the primary wavefront at some later time is the envelope of these wavelets. Moreover, the wavelets advance with a speed and frequency equal to those of the primary wave at each point in space. This has since become kno ...
... serves as the source of spherical secondary waves also called wavelets, such that the primary wavefront at some later time is the envelope of these wavelets. Moreover, the wavelets advance with a speed and frequency equal to those of the primary wave at each point in space. This has since become kno ...
A study of reflection and transmission of
... where no and ne are the characteristic ordinary and extraordinary refractive indices of the birefringent material and φ is the waveplate rotation angle; the angle formed between the plane of incidence and the optic axis of the waveplate (this angle is analogous to β from section 1). The symbol φ was ...
... where no and ne are the characteristic ordinary and extraordinary refractive indices of the birefringent material and φ is the waveplate rotation angle; the angle formed between the plane of incidence and the optic axis of the waveplate (this angle is analogous to β from section 1). The symbol φ was ...
Mach-Zehnder interferometer
... to a statistically single photon level, so sometimes it can have 2 or even three photon together at a time. There is no antibunching (completely “single photon”) in our experiment. ...
... to a statistically single photon level, so sometimes it can have 2 or even three photon together at a time. There is no antibunching (completely “single photon”) in our experiment. ...
Understanding Polarization
... The amount of light output in each polarization state can be determined by simply breaking up the incident light into its two polarization components (s and p), and then calculating how much of each intensity is transmitted and reflected. For systems based on incoherent light, this level of detail i ...
... The amount of light output in each polarization state can be determined by simply breaking up the incident light into its two polarization components (s and p), and then calculating how much of each intensity is transmitted and reflected. For systems based on incoherent light, this level of detail i ...
Optical phase measurement emphasized
... change upon total internal reflection, which is revealed by modification of the polarization state. One can send a laser beam to a prism such that light is polarized at 45° with the horizontal. If we place and rotate a polarizer in the path of the beam right before the beam enters into the prism, we ...
... change upon total internal reflection, which is revealed by modification of the polarization state. One can send a laser beam to a prism such that light is polarized at 45° with the horizontal. If we place and rotate a polarizer in the path of the beam right before the beam enters into the prism, we ...
PDF
... Figure 2 illustrates a schematic diagram of the laser beam diffraction in which the beam is diffracted by the grooves on the disc. The grooves are periodically arranged like a diffraction grating, and thus the focused laser beam is not only reflected by the disc but is also diffracted by the grooves ...
... Figure 2 illustrates a schematic diagram of the laser beam diffraction in which the beam is diffracted by the grooves on the disc. The grooves are periodically arranged like a diffraction grating, and thus the focused laser beam is not only reflected by the disc but is also diffracted by the grooves ...
Section 9.4: Light: Wave or Particle?
... baseline array are combined to form interference patterns, which reveal information about the object under study. Another wave-like property used in interferometry is reflection. The electromagnetic radiation from the object reaches the large, parabolic radio telescope dishes, and the radio waves ar ...
... baseline array are combined to form interference patterns, which reveal information about the object under study. Another wave-like property used in interferometry is reflection. The electromagnetic radiation from the object reaches the large, parabolic radio telescope dishes, and the radio waves ar ...
Optical Microscopy Beyond the Diffraction Limit
... in glass/silica buried waveguides. We have shown that measurements of the period of the observed standing modes provides an accurate and direct measure of the effective index, which combined with the measured transverse modal shape and decay constants, determines the values of all spatial components ...
... in glass/silica buried waveguides. We have shown that measurements of the period of the observed standing modes provides an accurate and direct measure of the effective index, which combined with the measured transverse modal shape and decay constants, determines the values of all spatial components ...
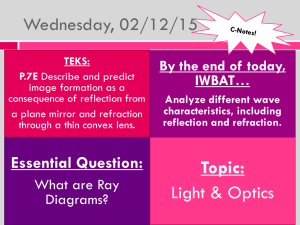
Magneto-Optic Kerr Effect
... interference” may be present.4 Since the MOKE AC signals are typically very weak, great care must be taken to eliminate or reduce these effects. Useful techniques include: 1) use of anti-reflective (AR) coatings on the PEM optical element, 2) use of a PEM with a slight wedge angle (non-parallel opti ...
... interference” may be present.4 Since the MOKE AC signals are typically very weak, great care must be taken to eliminate or reduce these effects. Useful techniques include: 1) use of anti-reflective (AR) coatings on the PEM optical element, 2) use of a PEM with a slight wedge angle (non-parallel opti ...
Optical polarization tutorial
... 1 Birefringence, or double refraction, is an optical property of certain materials, primarily crystals. Birefringent materials have anisotropic structure, such that a light wave polarized along a particular direction (called optical axis) has index of refraction which is different from waves polarize ...
... 1 Birefringence, or double refraction, is an optical property of certain materials, primarily crystals. Birefringent materials have anisotropic structure, such that a light wave polarized along a particular direction (called optical axis) has index of refraction which is different from waves polarize ...
Practical No 6
... Part B. Measurement of the speed of light in an optical fiber ATTENTION ! Laser radiation is dangerous for your eyes. Avoid any contact with the laser light! The laser light beam (electromagnetic wave of a frequency 2 MHz) generated by the source L is splitted into two beams, the first one is approa ...
... Part B. Measurement of the speed of light in an optical fiber ATTENTION ! Laser radiation is dangerous for your eyes. Avoid any contact with the laser light! The laser light beam (electromagnetic wave of a frequency 2 MHz) generated by the source L is splitted into two beams, the first one is approa ...
Biomolecular and cellular research devices.
... According to their construction, spectrophotometers can be divided into single- and double-beam types. In single-beam spectrophotometers one beam of light passes through the reference and then the measured sample (the cuvettes containing the solutions must be movable). In double-beam spectrophot ...
... According to their construction, spectrophotometers can be divided into single- and double-beam types. In single-beam spectrophotometers one beam of light passes through the reference and then the measured sample (the cuvettes containing the solutions must be movable). In double-beam spectrophot ...
r - Nano[studijní] materiály - Technical University of Liberec
... • Applied electric field E=(0,0,E) along optical axis z, perpendicular to laser beam. The values of the principal refractive indices with field E are ne(E) and no(E) • The change of refractive index causes the optical phase shift of light wave in the sample. The electric field in optical axis direct ...
... • Applied electric field E=(0,0,E) along optical axis z, perpendicular to laser beam. The values of the principal refractive indices with field E are ne(E) and no(E) • The change of refractive index causes the optical phase shift of light wave in the sample. The electric field in optical axis direct ...
Reflecting And Refracting Light
... Reflection Vocabulary • Real Image – – Image is made from “real” light rays that converge at a real focal point so the image is REAL – Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears ...
... Reflection Vocabulary • Real Image – – Image is made from “real” light rays that converge at a real focal point so the image is REAL – Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears ...
Download PDF
... the Lambert–Beer law by Eq. 共3兲 has increasing importance as the particle size decreases and becomes negligible for large particles. The reason is that the scattering cross section depends more strongly on the size parameter 2R兾 for smaller values of the particle radius R. Therefore, in this range ...
... the Lambert–Beer law by Eq. 共3兲 has increasing importance as the particle size decreases and becomes negligible for large particles. The reason is that the scattering cross section depends more strongly on the size parameter 2R兾 for smaller values of the particle radius R. Therefore, in this range ...
Fiber Optic Fundamentals
... • Brief History of Optical Fiber Technology • Multimode and Single-mode Fiber • Basic Fiber Optic Link Concepts and Applications to the Computer Industry ...
... • Brief History of Optical Fiber Technology • Multimode and Single-mode Fiber • Basic Fiber Optic Link Concepts and Applications to the Computer Industry ...
Nineteen Ways to do 3-Dimensional Imaging
... by represented in the image. That is, the image must consist of a fully populated 3-dimensional array of values. Or is it acceptable that the image only record height or distance values, say, from the “camera” to the scene. Without stepping into this discussion, I’m going to take the broader view fo ...
... by represented in the image. That is, the image must consist of a fully populated 3-dimensional array of values. Or is it acceptable that the image only record height or distance values, say, from the “camera” to the scene. Without stepping into this discussion, I’m going to take the broader view fo ...













![r - Nano[studijní] materiály - Technical University of Liberec](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007925985_1-5e55f54db686ed86c2131eb21f7dd098-300x300.png)