Chapter 8a Wave Optics
... Example 2: two microscope slides each 7.5cm long are in contact along one pair of edges while the other edges are held apart by a piece of paper 0.012mm thick. Calculate the spacing of interference fringes under illumination by light of 632nm wavelength at near normal incidence. Solution: let the a ...
... Example 2: two microscope slides each 7.5cm long are in contact along one pair of edges while the other edges are held apart by a piece of paper 0.012mm thick. Calculate the spacing of interference fringes under illumination by light of 632nm wavelength at near normal incidence. Solution: let the a ...
Electronic Structure and Optical Quality of Nanocrystalline Y2O3
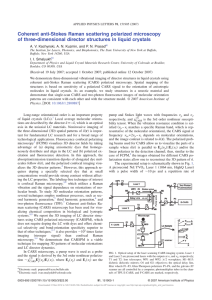
... surface/interface chemistry, Y−O bonding, and optical constants of the Y2O3 film surface and Y2O3−Si interface were evaluated by the combined use of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), depth-profiling, and spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE). XPS analyses indicate the binding energies (BEs) of the Y 3 ...
... surface/interface chemistry, Y−O bonding, and optical constants of the Y2O3 film surface and Y2O3−Si interface were evaluated by the combined use of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), depth-profiling, and spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE). XPS analyses indicate the binding energies (BEs) of the Y 3 ...
Chapter 8
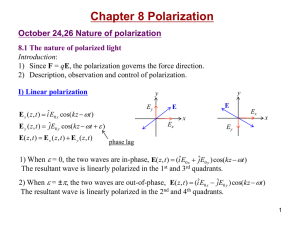
... Polarization by scattering: If the incident light is unpolarized, then 1) The scattered light in the forward direction is unpolarized. 2) The scattered light at 90º is linearly polarized. 3) The scattered light in other directions are partially polarized. ...
... Polarization by scattering: If the incident light is unpolarized, then 1) The scattered light in the forward direction is unpolarized. 2) The scattered light at 90º is linearly polarized. 3) The scattered light in other directions are partially polarized. ...
Design of a video interface controller for color sequential liquid
... through two biaxial films. The symbols that blue color represents 450nm with green color (550nm), red color (630nm) are separately express visible wavelength. The starting position is at position K, where incident light pass through linear polarizer. Then, after passing through first biaxial film, t ...
... through two biaxial films. The symbols that blue color represents 450nm with green color (550nm), red color (630nm) are separately express visible wavelength. The starting position is at position K, where incident light pass through linear polarizer. Then, after passing through first biaxial film, t ...
Resins for Optics
... As the word "optoelectronics is popular," the fields of electronics and optics now have a close relationship each other. Optical field includes precision components such as optical pickup devices, liquid crystal devices, micro lenses, prisms, and optical wave guides. The resin materials that are use ...
... As the word "optoelectronics is popular," the fields of electronics and optics now have a close relationship each other. Optical field includes precision components such as optical pickup devices, liquid crystal devices, micro lenses, prisms, and optical wave guides. The resin materials that are use ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... Fig. 3: (a) Variation of α as a function of hv and (b) optical band gap of CuO thin film deposited at various pH. 3.4 The Refractive index of CuO film The refractive index (η) is one of the fundamental properties of an optical material because of its close relationship to the electronic polarization ...
... Fig. 3: (a) Variation of α as a function of hv and (b) optical band gap of CuO thin film deposited at various pH. 3.4 The Refractive index of CuO film The refractive index (η) is one of the fundamental properties of an optical material because of its close relationship to the electronic polarization ...
Phase Change upon Reflection—CE Mungan, Spring 2008
... is analogous to a transverse wave pulse incident from a low-density to a high-density string, for which the reflected pulse is similarly inverted. Textbooks could improve their string/light wave analogy for phase reflection if they built their argument as follows: (i) A string wave is inverted when ...
... is analogous to a transverse wave pulse incident from a low-density to a high-density string, for which the reflected pulse is similarly inverted. Textbooks could improve their string/light wave analogy for phase reflection if they built their argument as follows: (i) A string wave is inverted when ...
Vol. 26. Is. 5 - Society for Experimental Mechanics
... between two path lengths, and this, indeed, is one way that interferometry is used. But, there is another way that is even more useful. Suppose that we hold one of the paths constant and call it a reference path. Then, we induce a change in the second path, taking intensity measurements before and a ...
... between two path lengths, and this, indeed, is one way that interferometry is used. But, there is another way that is even more useful. Suppose that we hold one of the paths constant and call it a reference path. Then, we induce a change in the second path, taking intensity measurements before and a ...
supplemental_material
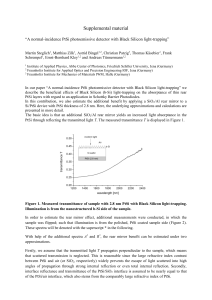
... Illumination is from the nanostructured b-Si side of the sample. In order to estimate the rear mirror effect, additional measurements were conducted, in which the sample was flipped; such that illumination is from the polished, PtSi coated sample side (Figure 2). These spectra will be denoted with t ...
... Illumination is from the nanostructured b-Si side of the sample. In order to estimate the rear mirror effect, additional measurements were conducted, in which the sample was flipped; such that illumination is from the polished, PtSi coated sample side (Figure 2). These spectra will be denoted with t ...
Slide 1
... Abstract: Acousto-optic (AO) imaging is a new dual-wave modality that combines ultrasound with diffuse light to achieve deep-tissue imaging of optical properties with the spatial resolution of ultrasound. In this technique, the sample is simultaneously insonified by an ultrasound beam and illuminate ...
... Abstract: Acousto-optic (AO) imaging is a new dual-wave modality that combines ultrasound with diffuse light to achieve deep-tissue imaging of optical properties with the spatial resolution of ultrasound. In this technique, the sample is simultaneously insonified by an ultrasound beam and illuminate ...
07 Propagation of Waves
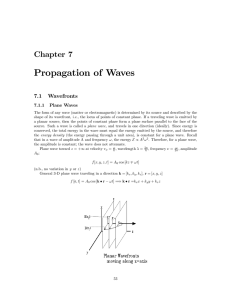
... The form of any wave (matter or electromagnetic) is determined by its source and described by the shape of its wavefront, i.e., the locus of points of constant phase. If a traveling wave is emitted by a planar source, then the points of constant phase form a plane surface parallel to the face of the ...
... The form of any wave (matter or electromagnetic) is determined by its source and described by the shape of its wavefront, i.e., the locus of points of constant phase. If a traveling wave is emitted by a planar source, then the points of constant phase form a plane surface parallel to the face of the ...
Experiment 1: Law of Geometrical Optics
... a. Record the position of the rotation stage as 0 in Table 1 below. b. Note that there are two reflections to line up as you aim the beam back onto itself. Explain these. (Why isn't there just one?) 5. Scan the angle of the mirror by turning (R) such that the laser beam is reflected onto the piece ...
... a. Record the position of the rotation stage as 0 in Table 1 below. b. Note that there are two reflections to line up as you aim the beam back onto itself. Explain these. (Why isn't there just one?) 5. Scan the angle of the mirror by turning (R) such that the laser beam is reflected onto the piece ...
1. Which of the following statement are true about "LED life" term?
... LED life refers to time duration of the charge carriers in the active region (lifetime of the carriers) LED life increase if Iforward increase 2. Which are the main parameters of an LED that are affected by temperature? Luminous intensity (brightness) ...
... LED life refers to time duration of the charge carriers in the active region (lifetime of the carriers) LED life increase if Iforward increase 2. Which are the main parameters of an LED that are affected by temperature? Luminous intensity (brightness) ...
How can I tell what the polarization axis is for a linear polarizer? The
... how does this relate to the film specifications? To achieve the phase shift designated for any given retarder, the optical thickness of the material is selected to give the desired shift at a specific wavelength. Retarders are very wavelength dependent. Wavelengths close to the design or slight thic ...
... how does this relate to the film specifications? To achieve the phase shift designated for any given retarder, the optical thickness of the material is selected to give the desired shift at a specific wavelength. Retarders are very wavelength dependent. Wavelengths close to the design or slight thic ...
LASERPULSE™ LIGHT ARM FOR PIV MODEL 610015
... in delivering the light sheet for Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) measurements or for other high energy laser applications. Featuring a beam path that can be fully enclosed from the laser to the measurement area, it is essential for safely delivering high-energy, pulsed YAG laser beams. ...
... in delivering the light sheet for Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) measurements or for other high energy laser applications. Featuring a beam path that can be fully enclosed from the laser to the measurement area, it is essential for safely delivering high-energy, pulsed YAG laser beams. ...
PDF
... the room-temperature SmA material, octylcyanobiphenyl s8CBd sAldrichd, by heating the LC to its isotropic phase s70 ° C or higherd. Some of the samples were doped by a fluorescent dye n , n8-biss2,5-di-tert-butylphenyld-3,4,9,10perylenedicarboximide sBTBPd sfor the TPF reference experimentsd at 0.01 ...
... the room-temperature SmA material, octylcyanobiphenyl s8CBd sAldrichd, by heating the LC to its isotropic phase s70 ° C or higherd. Some of the samples were doped by a fluorescent dye n , n8-biss2,5-di-tert-butylphenyld-3,4,9,10perylenedicarboximide sBTBPd sfor the TPF reference experimentsd at 0.01 ...
optical properties of dielectric mirrors, produced by large area glass
... wet coating and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating. In case of wet coating, the metal used as reflective substrate is silver. It is deposited onto the glass surface, via certain chemical process as result of chemical reaction of two chemicals. The deposited Ag is protected (covered) by Cu, and ...
... wet coating and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating. In case of wet coating, the metal used as reflective substrate is silver. It is deposited onto the glass surface, via certain chemical process as result of chemical reaction of two chemicals. The deposited Ag is protected (covered) by Cu, and ...
In the diagram below, the optical train of a set of binoculars is found
... (ii) A Fabry-Perot etalon is fabricated from a 1 mm thickness of glass by silvering its two flat parallel, polished surfaces. The etalon is placed inside an oven to measure its temperature drift, by monitoring transmission of a laser beam at =500 nm. The change ...
... (ii) A Fabry-Perot etalon is fabricated from a 1 mm thickness of glass by silvering its two flat parallel, polished surfaces. The etalon is placed inside an oven to measure its temperature drift, by monitoring transmission of a laser beam at =500 nm. The change ...