What is “magnetic reversal?”
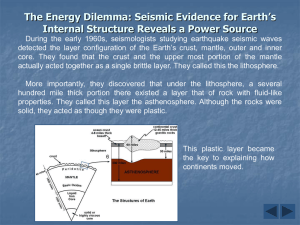
... The Energy Dilemma: Seismic Evidence for Earth’s Internal Structure Reveals a Power Source During the early 1960s, seismologists studying earthquake seismic waves detected the layer configuration of the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer and inner core. They found that the crust and the upper most portion ...
... The Energy Dilemma: Seismic Evidence for Earth’s Internal Structure Reveals a Power Source During the early 1960s, seismologists studying earthquake seismic waves detected the layer configuration of the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer and inner core. They found that the crust and the upper most portion ...
Post-‐Doctoral Research Grant in Seismology University of
... zone, and have been explained as earthquakes that occur on old, cold lithosphere that has a brittle behavior down to depths larger than usual. The study of seismogenic structures in ...
... zone, and have been explained as earthquakes that occur on old, cold lithosphere that has a brittle behavior down to depths larger than usual. The study of seismogenic structures in ...
Earth Science
... C. Seismic Waves- carry energy from Earthquake away from focus 1. P wave (primary) 1st ...
... C. Seismic Waves- carry energy from Earthquake away from focus 1. P wave (primary) 1st ...
Features of Earthquakes
... combining careful geologic studies of earthquake hazards and creative engineering in designing and protecting such important structures and lifelines. ...
... combining careful geologic studies of earthquake hazards and creative engineering in designing and protecting such important structures and lifelines. ...
Chapter 4
... • The risk that an earthquake will occur close to where you live depends on whether or not tectonic activity that causes deformation is occurring within the crust of that area. • For the U.S., the risk is greatest in the most tectonically active area, near the plate margin in the Western U.S. • The ...
... • The risk that an earthquake will occur close to where you live depends on whether or not tectonic activity that causes deformation is occurring within the crust of that area. • For the U.S., the risk is greatest in the most tectonically active area, near the plate margin in the Western U.S. • The ...
base-isolating - Madison County Schools
... hits, you should move to an open area such as a playground. You should sit on the ground so you will not be thrown to the ground when the earthquake shakes. ...
... hits, you should move to an open area such as a playground. You should sit on the ground so you will not be thrown to the ground when the earthquake shakes. ...
(1 point
... Felt by people walking; rocking of free standing objects Sleepers awakened; bells ring Trees sway, some damage from falling objects General alarm, cracking of walls Chimneys fall and some damage to building Ground crack, houses begin to collapse, pipes break ...
... Felt by people walking; rocking of free standing objects Sleepers awakened; bells ring Trees sway, some damage from falling objects General alarm, cracking of walls Chimneys fall and some damage to building Ground crack, houses begin to collapse, pipes break ...
Activity 1 quiz File
... 11) _____ Which type of seismic wave causes the most damage to buildings? a) S-waves b) P-waves c) Surface waves 12) _____ Which type of seismic wave can travel through both solid and liquid material? a) S-waves b) P-waves c) Surface waves 13) _____ The places in the interior of the earth through wh ...
... 11) _____ Which type of seismic wave causes the most damage to buildings? a) S-waves b) P-waves c) Surface waves 12) _____ Which type of seismic wave can travel through both solid and liquid material? a) S-waves b) P-waves c) Surface waves 13) _____ The places in the interior of the earth through wh ...
What are Earthquakes
... When the Earth's plates move against each other, stress is put on the lithosphere. When this stress is great enough, the lithosphere breaks or shifts Where do they occur most often? Within areas of the crust are fractures, known as faults, One block may move up while the other moves down, or ...
... When the Earth's plates move against each other, stress is put on the lithosphere. When this stress is great enough, the lithosphere breaks or shifts Where do they occur most often? Within areas of the crust are fractures, known as faults, One block may move up while the other moves down, or ...
Earthquake Damage Unit
... furniture and other objects that might topple over. Do out run outside. If you are in a car drive away from tall buildings, tunnels and power lines, bridges and stay in your car. • After an earthquake be cautious • Check for fire hazards ...
... furniture and other objects that might topple over. Do out run outside. If you are in a car drive away from tall buildings, tunnels and power lines, bridges and stay in your car. • After an earthquake be cautious • Check for fire hazards ...
EARTHQUAKES
... • Measures damage to human (man made) structures. • Intensity depends on: reporting accuracy, population, development, building codes, and enforcement. • Intensity Scale is I - XII. • Useful for all pre-instrumental events. The few seismographs operating in the early part of the last century were is ...
... • Measures damage to human (man made) structures. • Intensity depends on: reporting accuracy, population, development, building codes, and enforcement. • Intensity Scale is I - XII. • Useful for all pre-instrumental events. The few seismographs operating in the early part of the last century were is ...
simple strengthening techniques and new technologies for seismic
... Recent earthquakes in Turkey (Van 2011, Izmit 1999) and worldwide demonstrated the power of nature and the catastrophic impact of such power upon urban cities. Surveys carried out in the aftermath of several destructive earthquakes shows that many low-rise reinforced concrete buildings have suffered ...
... Recent earthquakes in Turkey (Van 2011, Izmit 1999) and worldwide demonstrated the power of nature and the catastrophic impact of such power upon urban cities. Surveys carried out in the aftermath of several destructive earthquakes shows that many low-rise reinforced concrete buildings have suffered ...
Geology 412-001: Crustal Geophysics Spring 2007
... Office hours: Mon: 1-5 PM; Tues-Thur: 2-5 PM Wed-Fri: Research days! (Warning: you may be talked into undertaking a research project if you stop by on these days!) Course Objectives: The main objective of this course is to introduce you to the techniques of geophysics and how they are used to constr ...
... Office hours: Mon: 1-5 PM; Tues-Thur: 2-5 PM Wed-Fri: Research days! (Warning: you may be talked into undertaking a research project if you stop by on these days!) Course Objectives: The main objective of this course is to introduce you to the techniques of geophysics and how they are used to constr ...
earthquake shearing deformation compression fault plateau focus
... A fault formed when rocks are pulled apart due to tension. ...
... A fault formed when rocks are pulled apart due to tension. ...
Earthquakescrossword
... 3. break in Earth’s crust along which portions of Earth’s crust move relative to one another 4. the study of earthquakes 5. point inside Earth where an earthquake begins 8. point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s starting point 10. the fastest seismic waves 11. secondary seismic wave ...
... 3. break in Earth’s crust along which portions of Earth’s crust move relative to one another 4. the study of earthquakes 5. point inside Earth where an earthquake begins 8. point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s starting point 10. the fastest seismic waves 11. secondary seismic wave ...
Finding the epicenter of an earthquake Background Information
... station after the P-waves. Each type of wave is affected by the density of the earth material in which it travels. P-waves can travel through both the solid crust and mantle and the molten outer core. S-waves can also travel through the solid parts of the earth, but not through liquid or molten mate ...
... station after the P-waves. Each type of wave is affected by the density of the earth material in which it travels. P-waves can travel through both the solid crust and mantle and the molten outer core. S-waves can also travel through the solid parts of the earth, but not through liquid or molten mate ...
Chapter 8
... What causes Quakes • The changing of rocks due to stress is called deformation • Focus is the area in the crust where the rock under stress breaks • Epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus ...
... What causes Quakes • The changing of rocks due to stress is called deformation • Focus is the area in the crust where the rock under stress breaks • Epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus ...
Earthquake engineering

Earthquake engineering or Seismic engineering is a branch of engineering that searches for ways to make structures, such as buildings and bridges, resistant to earthquake damage. Earthquake engineer, better known as a seismic engineer aim to develop building techniques that will prevent any damage in a minor quake and avoid serious damage or collapse in a major shake. It is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of both structural and geotechnical engineering. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics and finance. The main objectives of earthquake engineering are: Foresee the potential consequences of strong earthquakes on urban areas and civil infrastructure. Design, construct and maintain structures to perform at earthquake exposure up to the expectations and in compliance with building codes.A properly engineered structure does not necessarily have to be extremely strong or expensive. It has to be properly designed to withstand the seismic effects while sustaining an acceptable level of damage.