Chemistry Mid-Term Review: 2015-2016
... 5. What distinguishes the atoms of one element from the atoms of another? 6. What equation tells you how to calculate the number of neutrons in an atom? 7. What is the charge- positive or negative, of the nucleus of every atom? 8. Why is an atom electrically neutral? 9. What does the atomic number o ...
... 5. What distinguishes the atoms of one element from the atoms of another? 6. What equation tells you how to calculate the number of neutrons in an atom? 7. What is the charge- positive or negative, of the nucleus of every atom? 8. Why is an atom electrically neutral? 9. What does the atomic number o ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
Chapter1 - WilsonChemWiki
... or shells). Energy levels are labeled (n). The first energy level that is closer to the nucleus has n=1 (holds a maximum of 2 electrons) and the next has n=2, (holds a maximum of 8 electrons….Maximum number of electrons in an energy level is 2n2. Energy levels are subdivided to orbital, where each o ...
... or shells). Energy levels are labeled (n). The first energy level that is closer to the nucleus has n=1 (holds a maximum of 2 electrons) and the next has n=2, (holds a maximum of 8 electrons….Maximum number of electrons in an energy level is 2n2. Energy levels are subdivided to orbital, where each o ...
Acid-Base Reactions
... normally in the range of 3 to 6 M. The NaOH is analyzed periodically. In one such analysis, 45.7 mL of 0.500 M H2SO4 is required to neutralize a 20.0-mL sample of NaOH solution. What is the concentration of the NaOH solution? ...
... normally in the range of 3 to 6 M. The NaOH is analyzed periodically. In one such analysis, 45.7 mL of 0.500 M H2SO4 is required to neutralize a 20.0-mL sample of NaOH solution. What is the concentration of the NaOH solution? ...
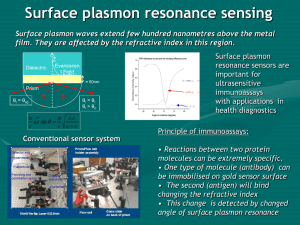
Surface plasmon resonance sensing
... 1. Prism for coupling to SP, 2. Thin metal layer(s), 3. Self Assembled Monolayer (typically 1,6-hexanedithiol or 2mercaptoethylamine, 4. Attached metal colloids (typically Au or Ag, between 10 nm and 50 nm diameter) [11] ...
... 1. Prism for coupling to SP, 2. Thin metal layer(s), 3. Self Assembled Monolayer (typically 1,6-hexanedithiol or 2mercaptoethylamine, 4. Attached metal colloids (typically Au or Ag, between 10 nm and 50 nm diameter) [11] ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE 2.1 THE ATOM
... gain two electrons to form the O2– ion. An atom, especially of a metal, may also lose electrons to form a positive ion (or cation), because there are now more protons than electrons. The ion will have one positive charge for each electron lost. For example aluminium tends to lose three electrons to ...
... gain two electrons to form the O2– ion. An atom, especially of a metal, may also lose electrons to form a positive ion (or cation), because there are now more protons than electrons. The ion will have one positive charge for each electron lost. For example aluminium tends to lose three electrons to ...
Prof. Jeffery Lang (EECS) - MIT Sea Grant
... “Simple sensor systems that are capable of operating without drift for long periods of time and that are sufficiently selective and sensitive are not yet available…” ...
... “Simple sensor systems that are capable of operating without drift for long periods of time and that are sufficiently selective and sensitive are not yet available…” ...
Practice exam - Dynamic Science
... The smallest particle of matter. The smallest possible sugar crystal. The smallest particle of water. The energy given off during a chemical reaction. ...
... The smallest particle of matter. The smallest possible sugar crystal. The smallest particle of water. The energy given off during a chemical reaction. ...
Thermo Chemistry Ch 9 Notes
... reaction, the temperature increased from 23.0oC to 45.5oC. Assuming the solution in the calorimeter has the same heat capacity as water, determine the heat of reaction per mole of magnesium. ...
... reaction, the temperature increased from 23.0oC to 45.5oC. Assuming the solution in the calorimeter has the same heat capacity as water, determine the heat of reaction per mole of magnesium. ...
chap3 (WP)
... Now, these observations did not agree with what one expected from the theory of electromagnetism as it was known in 1900. In the classical theory of electromagnetism, the force that an electromagnetic wave could exert on a charged object depended on the intensity of the light, not its colour or freq ...
... Now, these observations did not agree with what one expected from the theory of electromagnetism as it was known in 1900. In the classical theory of electromagnetism, the force that an electromagnetic wave could exert on a charged object depended on the intensity of the light, not its colour or freq ...
molecular modeling and electronic structure calculations
... What are the major differences between the input geometry, based on average bond lengths and VSEPR, and the optimized geometry (aka: How do bond lengths, angles, etc. change from what you were expecting)? What accounts for these differences? PROBLEM 3: Ozone Oxygen is a paramagnetic compound, which ...
... What are the major differences between the input geometry, based on average bond lengths and VSEPR, and the optimized geometry (aka: How do bond lengths, angles, etc. change from what you were expecting)? What accounts for these differences? PROBLEM 3: Ozone Oxygen is a paramagnetic compound, which ...
5.62 Physical Chemistry II
... infinite number of positive, non-zero terms in qelect? Hint: 〈r〉n = a0n2. What about the nuclear partition function qnuc? 2I + 1. Nuclear spin degeneracy? Excited states of nucleus? Changing the nuclear state generally requires huge energies, so as for the electronic case there is only one nuclear e ...
... infinite number of positive, non-zero terms in qelect? Hint: 〈r〉n = a0n2. What about the nuclear partition function qnuc? 2I + 1. Nuclear spin degeneracy? Excited states of nucleus? Changing the nuclear state generally requires huge energies, so as for the electronic case there is only one nuclear e ...
Geant4: Electromagnetic Processes 1
... Dielectric - Dielectric Depending on the photon’s wave length, angle of incidence, (linear) polarization, and refractive index on both sides of the boundary: ...
... Dielectric - Dielectric Depending on the photon’s wave length, angle of incidence, (linear) polarization, and refractive index on both sides of the boundary: ...
Chemistry I
... b. electromagnetic radiation more energetic than X-rays c. electrons which move at tremendous speeds d. particles with the same mass as an electron but has a positive charge 55. Given the diagram representing a reaction: ...
... b. electromagnetic radiation more energetic than X-rays c. electrons which move at tremendous speeds d. particles with the same mass as an electron but has a positive charge 55. Given the diagram representing a reaction: ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
Chapter 1 Assignment Section 1.1 1. Why is air classified as matter
... 1. When powdered iron is left exposed to air, it will rust. Explain why the mass of the rust will be greater than the mass of the iron. 2. A chemical change can be indicated by the production/appearance of an odor. Describe two situations that you might be able to detect such a change in odor in a k ...
... 1. When powdered iron is left exposed to air, it will rust. Explain why the mass of the rust will be greater than the mass of the iron. 2. A chemical change can be indicated by the production/appearance of an odor. Describe two situations that you might be able to detect such a change in odor in a k ...
The Periodic table
... quantum mechanics could be used to characterize the motion of electrons. A quantized property is a property that can have only certain values. The energy of an electron is quantized, only certain behavior patterns are allowed. ...
... quantum mechanics could be used to characterize the motion of electrons. A quantized property is a property that can have only certain values. The energy of an electron is quantized, only certain behavior patterns are allowed. ...
Download PDF
... allows testing of the medium with a collimated beam over a large area, providing a better average across the sample. Note also that the alignment and position of the sample under test are not critical for this geometry. To prove the potential of this technique for ballistic light measurement, we per ...
... allows testing of the medium with a collimated beam over a large area, providing a better average across the sample. Note also that the alignment and position of the sample under test are not critical for this geometry. To prove the potential of this technique for ballistic light measurement, we per ...
Entangled states of trapped ions allow measuring the magnetic field
... even though no special care had been taken by, e.g., magnetic shielding [23]. The reason for this striking property comes from the advantages of decoherence-free subspaces: the linear Zeeman shift of the two ions leads to phase shifts acting in opposite directions, and since the ions are very close ...
... even though no special care had been taken by, e.g., magnetic shielding [23]. The reason for this striking property comes from the advantages of decoherence-free subspaces: the linear Zeeman shift of the two ions leads to phase shifts acting in opposite directions, and since the ions are very close ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.