Part II - Web site of Dr. Charles Berks
... the valence shell electrons in the atom being removed. Thus the cation has a lesser number of shells of electrons than the original atom. This results in a decrease in electron repulsions. At the same time the nuclear charge is constant but the number of shells of screening electrons has been reduce ...
... the valence shell electrons in the atom being removed. Thus the cation has a lesser number of shells of electrons than the original atom. This results in a decrease in electron repulsions. At the same time the nuclear charge is constant but the number of shells of screening electrons has been reduce ...
Exploring Compton Scattering Using the Spectrum
... Although the origin of spectral features in the gamma spectrum of a pure radioisotope is a common source of confusion among beginner physics students, its explanation is simple and touches on one of the most important ideas about the nature of light. This experiment directly demonstrates the transfe ...
... Although the origin of spectral features in the gamma spectrum of a pure radioisotope is a common source of confusion among beginner physics students, its explanation is simple and touches on one of the most important ideas about the nature of light. This experiment directly demonstrates the transfe ...
Name_____________________________________ Chemistry
... An example of a chemical change is a. sanding wood. c. milk going sour. b. melting ice. d. vaporizing gasoline. ____ 12. A physical change occurs when a a. peach spoils. c. bracelet turns your wrist green. b. copper bowl tarnishes. d. glue gun melts a glue stick. ____ 13. The state of matter in whic ...
... An example of a chemical change is a. sanding wood. c. milk going sour. b. melting ice. d. vaporizing gasoline. ____ 12. A physical change occurs when a a. peach spoils. c. bracelet turns your wrist green. b. copper bowl tarnishes. d. glue gun melts a glue stick. ____ 13. The state of matter in whic ...
Spectroscopy studies of few particle effects in pyramidal quantum dots Daniel Dufåker
... In this thesis work two very similar processes have been studied both involving excitations of particles during recombination of exciton complexes in quantum dots, reducing the energy of the emitted photon. Different exciton complexes are defined according to the number of electrons and holes in the ...
... In this thesis work two very similar processes have been studied both involving excitations of particles during recombination of exciton complexes in quantum dots, reducing the energy of the emitted photon. Different exciton complexes are defined according to the number of electrons and holes in the ...
physical setting chemistry
... (1) the same molecular structures and the same properties (2) the same molecular structures and different properties (3) different molecular structures and the same properties (4) different molecular structures and different properties ...
... (1) the same molecular structures and the same properties (2) the same molecular structures and different properties (3) different molecular structures and the same properties (4) different molecular structures and different properties ...
Odd Number of Electrons
... 3. An electron dot structure can be used to show the shared pair of electrons of the covalent bond. 4. Using page 218 use electron dots to combine two Fluorine atoms then show the electron configuration for each atom. 5. Structural Formula – represents the covalent bonds by using dashes, each dash r ...
... 3. An electron dot structure can be used to show the shared pair of electrons of the covalent bond. 4. Using page 218 use electron dots to combine two Fluorine atoms then show the electron configuration for each atom. 5. Structural Formula – represents the covalent bonds by using dashes, each dash r ...
7. Atoms
... chemistry follows from solving the Schrödinger equation for some number of electrons. However, solving the Schrödinger equation for many particles is hard and there is a long path between “in principle” and “in practice”. In this section, we take the first steps down this path. 7.1 Hydrogen We’re ...
... chemistry follows from solving the Schrödinger equation for some number of electrons. However, solving the Schrödinger equation for many particles is hard and there is a long path between “in principle” and “in practice”. In this section, we take the first steps down this path. 7.1 Hydrogen We’re ...
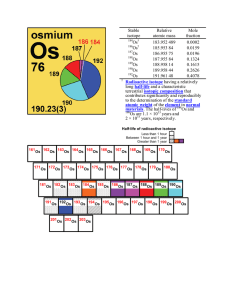
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. beta decay (β-decay) – radioactive decay process resulting in emission of a beta particle of either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric c ...
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. beta decay (β-decay) – radioactive decay process resulting in emission of a beta particle of either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric c ...
chemistry
... 5 Which list of elements consists of a metal, a metalloid, and a nonmetal? (1) Li, Na, Rb (3) Sn, Si, C (2) Cr, Mo, W (4) O, S, Te 6 At STP, which physical property of aluminum always remains the same from sample to sample? (1) mass (3) length (2) density (4) volume ...
... 5 Which list of elements consists of a metal, a metalloid, and a nonmetal? (1) Li, Na, Rb (3) Sn, Si, C (2) Cr, Mo, W (4) O, S, Te 6 At STP, which physical property of aluminum always remains the same from sample to sample? (1) mass (3) length (2) density (4) volume ...
Atoms and Materials for Engineering
... When we study electricity, we are particularly interested in the nature of the metallic bonds that form between atoms such as copper. Unlike covalent bonds, where electrons are only shared by two atoms, metal atoms joined by metallic bonding have “delocalized” electrons. That means that the outer el ...
... When we study electricity, we are particularly interested in the nature of the metallic bonds that form between atoms such as copper. Unlike covalent bonds, where electrons are only shared by two atoms, metal atoms joined by metallic bonding have “delocalized” electrons. That means that the outer el ...
3.1 Atomic Mass - Pace University Webspace
... • In nature, most elements have more than one isotope, meaning that the same element with a different number of neutrons exists. • The average atomic mass that is seen on the periodic table is the average mass of the different isotopes of an element that occur naturally. • To figure out the average ...
... • In nature, most elements have more than one isotope, meaning that the same element with a different number of neutrons exists. • The average atomic mass that is seen on the periodic table is the average mass of the different isotopes of an element that occur naturally. • To figure out the average ...
Monday, Mar. 23, 2015
... Transitions in the Hydrogen Atom • Lyman series: The atom will remain in the excited state for a short time before emitting a photon and returning to a lower stationary state. All hydrogen ...
... Transitions in the Hydrogen Atom • Lyman series: The atom will remain in the excited state for a short time before emitting a photon and returning to a lower stationary state. All hydrogen ...
Problem Set 4: De Broglies Relations, Fourier Superpositions and
... m/s and also that of an electron moving with a speed of 0.99 × 108 m/s. Be careful in your choice of formulae in the second case as it is relativistic. (b) To observe small objects, one measures the diffraction of particles whose de Broglie wavelength is comparable to objects size (or features). Fin ...
... m/s and also that of an electron moving with a speed of 0.99 × 108 m/s. Be careful in your choice of formulae in the second case as it is relativistic. (b) To observe small objects, one measures the diffraction of particles whose de Broglie wavelength is comparable to objects size (or features). Fin ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry Level
... Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X rays) ...
... Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X rays) ...
Tabletop nanometer extreme ultraviolet imaging in an
... (SEM) images, and also removes all negative effects of nonuniform illumination of the sample or imperfect knowledge of the sample position as it is scanned [17]. The result is a general and extensible imaging technique that can provide a comprehensive and definitive characterization of how light at ...
... (SEM) images, and also removes all negative effects of nonuniform illumination of the sample or imperfect knowledge of the sample position as it is scanned [17]. The result is a general and extensible imaging technique that can provide a comprehensive and definitive characterization of how light at ...
Lecture #13 - UMD | Atmospheric and Oceanic Science
... If your concern is the mass of some pollutant that is being transported through the air for biogeochemical cycles, then you want to know the mean diameter of the particles with the mass or volume. In other words, "What size particles carry the most mass?” If your concern loss of visibility then you ...
... If your concern is the mass of some pollutant that is being transported through the air for biogeochemical cycles, then you want to know the mean diameter of the particles with the mass or volume. In other words, "What size particles carry the most mass?” If your concern loss of visibility then you ...
Inhomogeneous liquid Superscript>4 Superscript>He: A density
... for "Vextthe He-He potential. 15 This gives the density distribution around a fictitious helium atom with infinite mass. 16'* We expect to obtain a radial density profile close to the radial distribution function g (r) of liquid helium. The result is shown in Fig. 2, together with g(r). 17 The profi ...
... for "Vextthe He-He potential. 15 This gives the density distribution around a fictitious helium atom with infinite mass. 16'* We expect to obtain a radial density profile close to the radial distribution function g (r) of liquid helium. The result is shown in Fig. 2, together with g(r). 17 The profi ...
Get
... we show two families of induced index patterns associated with two solitons at different saturation levels. In Fig. 1(a), a 7-mm FWHM soliton at wavelength l 苷 514 nm (Dn0 ⯝ 5.4 3 1024 , for n 苷 2.45) with an intensity ratio u0 2 苷 4 leads to three characteristic pattern regimes: For h 苷 Eext兾共V 兾L兲 ...
... we show two families of induced index patterns associated with two solitons at different saturation levels. In Fig. 1(a), a 7-mm FWHM soliton at wavelength l 苷 514 nm (Dn0 ⯝ 5.4 3 1024 , for n 苷 2.45) with an intensity ratio u0 2 苷 4 leads to three characteristic pattern regimes: For h 苷 Eext兾共V 兾L兲 ...
Second-order coupling between excited atoms and surface polaritons
... and whose amplitude decreases exponentially when moving away from the surface. They are capable of interacting and can be moved around on a surface, making them very attractive means of transporting quantum information from one point to another [9]. Upon taking advantage of the individual properties ...
... and whose amplitude decreases exponentially when moving away from the surface. They are capable of interacting and can be moved around on a surface, making them very attractive means of transporting quantum information from one point to another [9]. Upon taking advantage of the individual properties ...
Physics 316 B2 1 Revised 3/7/08 Experiment B2: Monochromatic
... holder that permits rotation of the biprism in its own plane. Accurate alignment of the edge of the biprism with the slit (S) is critical to obtain the best fringes. Align the laser, filter, slit (S) and biprism and look, by eye, for fringes. You should be able to see them, and if you use a simple m ...
... holder that permits rotation of the biprism in its own plane. Accurate alignment of the edge of the biprism with the slit (S) is critical to obtain the best fringes. Align the laser, filter, slit (S) and biprism and look, by eye, for fringes. You should be able to see them, and if you use a simple m ...
Unit 12 Worksheet Answers
... 34. Find the formula mass for each of the following (include units): a) magnesium phosphide b) sodium sulfate 134.9 g/mol 142 g/mol 35. In a bag full of pennies, you may have 2.15 moles of copper. How many grams do you have? 137 g 36. Experiments performed to reveal the structure of atoms led scient ...
... 34. Find the formula mass for each of the following (include units): a) magnesium phosphide b) sodium sulfate 134.9 g/mol 142 g/mol 35. In a bag full of pennies, you may have 2.15 moles of copper. How many grams do you have? 137 g 36. Experiments performed to reveal the structure of atoms led scient ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed All atoms of a given element are identical Atoms combined chemically in definite whole-number ratios to form compounds Atoms of different elements have different ...
... Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed All atoms of a given element are identical Atoms combined chemically in definite whole-number ratios to form compounds Atoms of different elements have different ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.