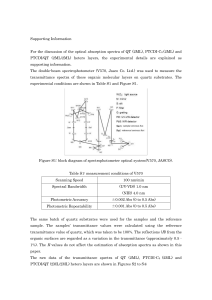
Supporting Information For the discussion of the optical absorption
... In contrast, the HOMO level is located around 5.9 eV, estimated by UPS measurements carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT HOMO level drops to a lower level or the optical band-gap expands after exposure to air. In an ...
... In contrast, the HOMO level is located around 5.9 eV, estimated by UPS measurements carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT HOMO level drops to a lower level or the optical band-gap expands after exposure to air. In an ...
Discussion 8
... Both diagrams and graphs are used in chemistry to help represent physical phenomena. The most common graphs show the relationship of two variables, such as distance and time, or frequency and wavelength. Diagrams, however, are a bit tricker. Diagrams can come in a number of different structures and ...
... Both diagrams and graphs are used in chemistry to help represent physical phenomena. The most common graphs show the relationship of two variables, such as distance and time, or frequency and wavelength. Diagrams, however, are a bit tricker. Diagrams can come in a number of different structures and ...
Unit #7 Take Home Test
... b. The proportion by mass of elements combined in potassium chlorate varies. c. Potassium chlorate is composed of four elements. d. Potassium chlorate is composed of five elements. 25. If a chemical equation is balanced properly, both sides of the equation must have the same number of a. atoms b. co ...
... b. The proportion by mass of elements combined in potassium chlorate varies. c. Potassium chlorate is composed of four elements. d. Potassium chlorate is composed of five elements. 25. If a chemical equation is balanced properly, both sides of the equation must have the same number of a. atoms b. co ...
Atomic physics: Atomic Spectra: Thomson`s plum
... Drawbacks of Rutherford’s model is that the atom as a whole cannot be stable. because, according to Rutherford that the electrons are in circular motion, the centripetal force would provided by electrostatic attraction. But uniform rotation is an accelerated motion and according to the classical el ...
... Drawbacks of Rutherford’s model is that the atom as a whole cannot be stable. because, according to Rutherford that the electrons are in circular motion, the centripetal force would provided by electrostatic attraction. But uniform rotation is an accelerated motion and according to the classical el ...
Chapter 8 Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions
... CH3CH2OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O Synthesis Reactions • In a synthesis reaction a single compound forms from two or more reactants. • Two elements form a binary compound C + O2 CO2 2C + O2 2CO • Two compounds form a ternary compound CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(s) CO2(g) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) Decompositio ...
... CH3CH2OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O Synthesis Reactions • In a synthesis reaction a single compound forms from two or more reactants. • Two elements form a binary compound C + O2 CO2 2C + O2 2CO • Two compounds form a ternary compound CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(s) CO2(g) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) Decompositio ...
View PDF
... (magnetization and crystal structure) A light wave with high intensity can probe non-linear light-matter interactions (anti-ferromagnetic symmetry) ...
... (magnetization and crystal structure) A light wave with high intensity can probe non-linear light-matter interactions (anti-ferromagnetic symmetry) ...
Exam 2
... A. be harder and have a smaller atomic radius. B. have a higher melting temperature and a larger atomic radius. ...
... A. be harder and have a smaller atomic radius. B. have a higher melting temperature and a larger atomic radius. ...
1 Alpha Decay T e 2KL Alpha Decay T e 2KL
... inside the nucleus with some speed v presumably related to its energy. [This needs quite a leap of the imagination but it turns out that you don’t need to know v accurately at all.] ...
... inside the nucleus with some speed v presumably related to its energy. [This needs quite a leap of the imagination but it turns out that you don’t need to know v accurately at all.] ...
Optical Spectra and Atomic Structure
... lowest level, called the ground state, is taken as the zero of energy. Thus we see that 13.60 ev of energy must be delivered to a neutral hydrogen atom, in its ground state, to ionize the atom. This is called the ionization potential, for if hydrogen is placed in a gaseous discharge tube which is pr ...
... lowest level, called the ground state, is taken as the zero of energy. Thus we see that 13.60 ev of energy must be delivered to a neutral hydrogen atom, in its ground state, to ionize the atom. This is called the ionization potential, for if hydrogen is placed in a gaseous discharge tube which is pr ...
Energy and Reactions
... Energy level diagram for an exothermic chemical reaction with Energy level diagram for an exothermic chemical reaction without showing the activation energy. It could also be seen as quite zero activation energy, but reactions between two ions of opposite charge usually has a very low activation en ...
... Energy level diagram for an exothermic chemical reaction with Energy level diagram for an exothermic chemical reaction without showing the activation energy. It could also be seen as quite zero activation energy, but reactions between two ions of opposite charge usually has a very low activation en ...
1. The compound which could act both as oxidising as well as
... Radiation is emitted when a hydrogen atom goes from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The wavelength of one line in visible region of atomic spectrum of hydrogen is 6.5 × 10–7 m. Energy difference between the two states is (a) 3.0 × 10– 19 J (b) 1.0 × 10– 18 J ...
... Radiation is emitted when a hydrogen atom goes from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The wavelength of one line in visible region of atomic spectrum of hydrogen is 6.5 × 10–7 m. Energy difference between the two states is (a) 3.0 × 10– 19 J (b) 1.0 × 10– 18 J ...
Chemistry Review
... Atomic radius – increases going down, decreases going across Electronegativity – decreases going down, increases going across Ionization energy – decreases going down, increases going across ...
... Atomic radius – increases going down, decreases going across Electronegativity – decreases going down, increases going across Ionization energy – decreases going down, increases going across ...
- ANU Repository
... In Fig. 2 we show the scattering efficiency spectra (SES) for incident p-wave, including the total scattering efficiency and the contributions from ap0 (MD) and ap1 (single channel, ED). Firstly we study a single-layered nanowire (r1 = 0, r2 = 145 nm) and the SES is shown in Fig. 2(a). It is clear that ...
... In Fig. 2 we show the scattering efficiency spectra (SES) for incident p-wave, including the total scattering efficiency and the contributions from ap0 (MD) and ap1 (single channel, ED). Firstly we study a single-layered nanowire (r1 = 0, r2 = 145 nm) and the SES is shown in Fig. 2(a). It is clear that ...
CHEM 101 Final (Term 151)
... 6. The concentrated sulfuric acid used in the chemical laboratory is 98.0% H2SO4 by mass. Calculate the molality of this acid solution. (The density of the acid solution is 1.83 g/mL). A) 500. m B) 200. m C) 99.9 m D) 999 m E) 345 m ...
... 6. The concentrated sulfuric acid used in the chemical laboratory is 98.0% H2SO4 by mass. Calculate the molality of this acid solution. (The density of the acid solution is 1.83 g/mL). A) 500. m B) 200. m C) 99.9 m D) 999 m E) 345 m ...
paper - Center for Ultracold Atoms
... many-body system, which may facilitate the study of more exotic situations10. Two-particle correlation analysis is an increasingly important method for studying complex quantum phases of ultracold atoms7–13. It goes back to the discovery, by Hanbury Brown and Twiss1, that photons emitted by a chaoti ...
... many-body system, which may facilitate the study of more exotic situations10. Two-particle correlation analysis is an increasingly important method for studying complex quantum phases of ultracold atoms7–13. It goes back to the discovery, by Hanbury Brown and Twiss1, that photons emitted by a chaoti ...
Chapter 10 Notes
... particular frequency can be illustrated with a graph of the radiation intensity versus ...
... particular frequency can be illustrated with a graph of the radiation intensity versus ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.























