Bessel Beam Theory - u.arizona.edu
... Diffraction is a feature of the wave nature of light. It can occur anytime a beam of light passes through an aperture that is large with respect to its wavelength1. According to the Huygens-Fresnel Principle2, every point of the wavefront that is unobstructed by the hindrance serves as a source of s ...
... Diffraction is a feature of the wave nature of light. It can occur anytime a beam of light passes through an aperture that is large with respect to its wavelength1. According to the Huygens-Fresnel Principle2, every point of the wavefront that is unobstructed by the hindrance serves as a source of s ...
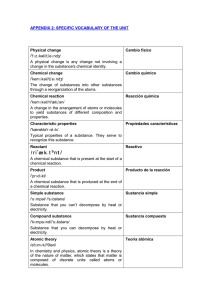
eBook AQA GCSE Chemistry Unit C2 Part 1
... Flo’s teacher heats a piece of sodium. He puts a gas jar of chlorine over it. There is a bright orange flame. Flo sees white clouds. Tiny white crystals of sodium chloride form on the sides of the gas jar. Sodium is a metal. It is in Group 1 of the periodic table, the alkali metals. Each sodium atom ...
... Flo’s teacher heats a piece of sodium. He puts a gas jar of chlorine over it. There is a bright orange flame. Flo sees white clouds. Tiny white crystals of sodium chloride form on the sides of the gas jar. Sodium is a metal. It is in Group 1 of the periodic table, the alkali metals. Each sodium atom ...
Name - mrshayden
... The amount of energy E, measured in ergs, is based on the amount of ground motion recorded by a seismograph at a known distance from the epicenter of the quake. The logarithmic function for the Richter scale assigns very large numbers for the amount of energy, E, to numbers that range from 1 to 9. A ...
... The amount of energy E, measured in ergs, is based on the amount of ground motion recorded by a seismograph at a known distance from the epicenter of the quake. The logarithmic function for the Richter scale assigns very large numbers for the amount of energy, E, to numbers that range from 1 to 9. A ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... Write down all possible terms and levels from the configuration 2p3p3d. Verify that in the coupled basis, there are 360 states. Hint: One must form all possible parent terms by coupling the inner two electrons before coupling the outer electron to each of these in turn. ...
... Write down all possible terms and levels from the configuration 2p3p3d. Verify that in the coupled basis, there are 360 states. Hint: One must form all possible parent terms by coupling the inner two electrons before coupling the outer electron to each of these in turn. ...
notes - ap unit 1 matter_meas_blank
... 2. Leading zeros are those that precede all of the non-zero digits and are never counted as significant figures. 3. Captive zeros are those that fall between non-zero digits and are always counted as significant figures. 4. Trailing zeros are those at the end of a number and are only significant if ...
... 2. Leading zeros are those that precede all of the non-zero digits and are never counted as significant figures. 3. Captive zeros are those that fall between non-zero digits and are always counted as significant figures. 4. Trailing zeros are those at the end of a number and are only significant if ...
2011 Lecture 22: Transport in Bulk Electrolytes
... uniform, neutral electrolyte, ci =constant. If concentration gradients exist, then ∇2 φ 6= 0 in a neutral electrolyte. The resolution of this paradox is that there are always some small charge fluctuations, which produce electric fields that lead to ionic fluxes that continuously neutralize the solu ...
... uniform, neutral electrolyte, ci =constant. If concentration gradients exist, then ∇2 φ 6= 0 in a neutral electrolyte. The resolution of this paradox is that there are always some small charge fluctuations, which produce electric fields that lead to ionic fluxes that continuously neutralize the solu ...
KIN1PP - Knockhardy
... such as the way reactions take place and the rate (speed) of the process. One can look at the QUALITATIVE and the QUANTITATIVE aspects of how the rate (speed) of a reaction can be changed. Chemical kinetics plays an important part in industrial chemistry because the time taken for a reaction to take ...
... such as the way reactions take place and the rate (speed) of the process. One can look at the QUALITATIVE and the QUANTITATIVE aspects of how the rate (speed) of a reaction can be changed. Chemical kinetics plays an important part in industrial chemistry because the time taken for a reaction to take ...
The Energy and Geometrical Structure of Molecules
... reach the understanding that we can use quantum theory to estimate the size of a molecule by looking at the wavelengths of the light that it absorbs. 1.2 Infrared Radiation from the Earth We will see that a spectrum of the IR emitted from the Earth, as recorded by an observation satellite, gives us ...
... reach the understanding that we can use quantum theory to estimate the size of a molecule by looking at the wavelengths of the light that it absorbs. 1.2 Infrared Radiation from the Earth We will see that a spectrum of the IR emitted from the Earth, as recorded by an observation satellite, gives us ...
Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom
... Electrons do not circle the nucleus in little planetlike orbits. The assumptions injected into the Bohr model have no basis in physical reality. BUT the model does get some of the numbers right for SIMPLE atoms… ...
... Electrons do not circle the nucleus in little planetlike orbits. The assumptions injected into the Bohr model have no basis in physical reality. BUT the model does get some of the numbers right for SIMPLE atoms… ...
Explaining Cold Fusion
... can be generated as cracks form [6-9] (called fractofusion), energetic radiation might result from unusual energy states having no relationship to CF, or energy might result on occasion from zero-point based processes[10]. As an example, claims for low-level energetic particle and neutron emission m ...
... can be generated as cracks form [6-9] (called fractofusion), energetic radiation might result from unusual energy states having no relationship to CF, or energy might result on occasion from zero-point based processes[10]. As an example, claims for low-level energetic particle and neutron emission m ...
Document
... Use the “Solubility Rules” handout (at end of notes) to determine the solubility. If the compound is soluble that means that it will remain as ions in the solution, if it is insoluble then the compound precipitated out of the reaction (it became the precipitate or solid). 2. If at least one INSOLUBL ...
... Use the “Solubility Rules” handout (at end of notes) to determine the solubility. If the compound is soluble that means that it will remain as ions in the solution, if it is insoluble then the compound precipitated out of the reaction (it became the precipitate or solid). 2. If at least one INSOLUBL ...
Lecture Notes # 3
... you have boundary conditions and want to solve for possible values of and a functional form of ...
... you have boundary conditions and want to solve for possible values of and a functional form of ...
Atomic Electron Configurations and Chapter 8 Chemical Periodicity
... Α. The electrons in a shell repel more, therefore the atom expands B. The nucleus becomes bigger in size as it has more protons and neutrons C Down the group C. group, new shells (i (i.e. e n is increased by 1) are added; each new shell is further and further away from the nucleus D. The nucleus exp ...
... Α. The electrons in a shell repel more, therefore the atom expands B. The nucleus becomes bigger in size as it has more protons and neutrons C Down the group C. group, new shells (i (i.e. e n is increased by 1) are added; each new shell is further and further away from the nucleus D. The nucleus exp ...
Inorganic Physical Methods
... groups, molecular symmetry, force constants, etc Gives precise structural information (atom positions) and some information about atomic motions. Powder studies used for fingerprinting and determining unit cell symmetry and dimensions. Detection and estimation of atomic composition of solids ...
... groups, molecular symmetry, force constants, etc Gives precise structural information (atom positions) and some information about atomic motions. Powder studies used for fingerprinting and determining unit cell symmetry and dimensions. Detection and estimation of atomic composition of solids ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... describe their significance. Use quantum designations to determine the distance away from the nucleus, the shape of the orbital, the orientation, and the spin of the electron. Determine the number of electrons that can be located in each energy level and sublevel. Define the Pauli Exclusion Pr ...
... describe their significance. Use quantum designations to determine the distance away from the nucleus, the shape of the orbital, the orientation, and the spin of the electron. Determine the number of electrons that can be located in each energy level and sublevel. Define the Pauli Exclusion Pr ...
Electro-optical photonic circuits for classical and
... any single particle and pair of distant microscopic bodies and it directly follows from first principles of quantum mechanics: the absence of entanglement between the internal degrees of freedom of two distant and initially uncorrelated systems persists, after interaction with a split single particl ...
... any single particle and pair of distant microscopic bodies and it directly follows from first principles of quantum mechanics: the absence of entanglement between the internal degrees of freedom of two distant and initially uncorrelated systems persists, after interaction with a split single particl ...
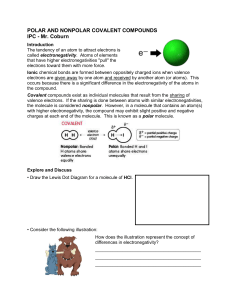
Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
... electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are given away by one atom and received by another atom (or atoms). This occurs because there is a significant difference in the electronegativity of the atoms in the compoun ...
... electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are given away by one atom and received by another atom (or atoms). This occurs because there is a significant difference in the electronegativity of the atoms in the compoun ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.