The Dual Nature of the Electron
... and describe the quantum mechanics model of the electron as a wave that changes into a particle. Wave–particle duality is deeply embedded into the foundations of quantum mechanics, so well that modern practitioners rarely discuss it as such. In the formalism of the theory, all the information about ...
... and describe the quantum mechanics model of the electron as a wave that changes into a particle. Wave–particle duality is deeply embedded into the foundations of quantum mechanics, so well that modern practitioners rarely discuss it as such. In the formalism of the theory, all the information about ...
Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work
... point, the coordinates of which, in an abstract space with N dimensions called the configuration space, are the N degrees of freedom. For such a system, the program of rational mechanics consists in determining, using the equations of motion and the initial conditions, the trajectory of the point re ...
... point, the coordinates of which, in an abstract space with N dimensions called the configuration space, are the N degrees of freedom. For such a system, the program of rational mechanics consists in determining, using the equations of motion and the initial conditions, the trajectory of the point re ...
TT 61: Correlated Electrons: (General) Theory 2 - DPG
... Würzburg, Deutschland — 2 Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Stuttgart, Deutschland — 3 Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel ...
... Würzburg, Deutschland — 2 Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Stuttgart, Deutschland — 3 Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel ...
AI Principles, Semester 2, Week 2, Lecture 5 Propositional Logic
... (ii) NEGATION, if Φ is a wff, then the expression denoted by ¬Φ is also a wff (iii) CONJUNCTION, if Φ and Ψ are both wffs, then the expression denoted by ( Φ ∧ Ψ) is a wff (iv) DISJUNCTION if Φ and Ψ are both wffs, then the expression denoted by (Φ ∨ Ψ) is a wff (v) CONDITIONAL (with ANTECEDENT and ...
... (ii) NEGATION, if Φ is a wff, then the expression denoted by ¬Φ is also a wff (iii) CONJUNCTION, if Φ and Ψ are both wffs, then the expression denoted by ( Φ ∧ Ψ) is a wff (iv) DISJUNCTION if Φ and Ψ are both wffs, then the expression denoted by (Φ ∨ Ψ) is a wff (v) CONDITIONAL (with ANTECEDENT and ...
PPT2
... probability P(q) shown right. With increasing pulse duraction the region of excitation is narrowed down. All momenta q except those with q¼0 are excited. By using Blackman pulses a more box like (inverted Fermi profile) of excitation probabilities can be obtained. ...
... probability P(q) shown right. With increasing pulse duraction the region of excitation is narrowed down. All momenta q except those with q¼0 are excited. By using Blackman pulses a more box like (inverted Fermi profile) of excitation probabilities can be obtained. ...
ENTROPY FOR SU(3) QUARK STATES
... a finite constant term could appear in the entropy. In particular, for a system with 2N states making up the ground state of a system of N particles one should expect a ground state entropy of N ln 2. We can now understand his result in terms of the SU(2) symmetry for the N particles. In this sense ...
... a finite constant term could appear in the entropy. In particular, for a system with 2N states making up the ground state of a system of N particles one should expect a ground state entropy of N ln 2. We can now understand his result in terms of the SU(2) symmetry for the N particles. In this sense ...
Lec 2 Notes
... self-explanatory, like counting, and to explain everything else in terms of these concepts. Let us look at some of these concepts and their laws, as they illustrate the principles of evidence construction quite well. (2) Why evidence could you give for 0=0? There is not much that one can say here. I ...
... self-explanatory, like counting, and to explain everything else in terms of these concepts. Let us look at some of these concepts and their laws, as they illustrate the principles of evidence construction quite well. (2) Why evidence could you give for 0=0? There is not much that one can say here. I ...
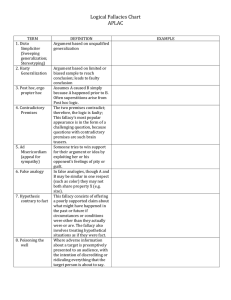
Logical Fallacies Chart APLAC TERM DEFINITION EXAMPLE 1
... Someone tries to win support for their argument or idea by exploiting her or his opponent's feelings of pity or guilt. In false analogies, though A and B may be similar in one respect (such as color) they may not both share property X (e.g. size). This fallacy consists of offering a poorly supported ...
... Someone tries to win support for their argument or idea by exploiting her or his opponent's feelings of pity or guilt. In false analogies, though A and B may be similar in one respect (such as color) they may not both share property X (e.g. size). This fallacy consists of offering a poorly supported ...
theoretical physics in crisis
... cannot provide an answer to the most important question: “What is the basic structural unit of matter (space, time, energy) and how is the universe constructed of these elementary units?” The reason for this situation is explained below. Also shown, is the way to find answers to these basic question ...
... cannot provide an answer to the most important question: “What is the basic structural unit of matter (space, time, energy) and how is the universe constructed of these elementary units?” The reason for this situation is explained below. Also shown, is the way to find answers to these basic question ...
Quantum Theory of Solid State Plasma Dielectric Response
... and sums over them are denoted by ∑i. • Mutual independence of the continuum of variables at all points x (for a fixed time t): (δ symbolizes variation for members of a continuum of variables as does ∂ for a discrete set of variables), ...
... and sums over them are denoted by ∑i. • Mutual independence of the continuum of variables at all points x (for a fixed time t): (δ symbolizes variation for members of a continuum of variables as does ∂ for a discrete set of variables), ...
Effects of scattering centers on the energy spectrum of a quantum dot
... in Fig. 2~b!. As expected, there is no degeneracy at B50 T. Clear energy level repulsion can also be seen in this case. We have made a detailed analysis of how the energy levels shown in Fig. 2~a! are changed as the impurity is moved away from the center of the dot. Just like the single-electron ene ...
... in Fig. 2~b!. As expected, there is no degeneracy at B50 T. Clear energy level repulsion can also be seen in this case. We have made a detailed analysis of how the energy levels shown in Fig. 2~a! are changed as the impurity is moved away from the center of the dot. Just like the single-electron ene ...
Logic - Decision Procedures
... Recall the question: what is the minimal set of operators necessary? A: Through such equivalences all Boolean operators can be written with a single operator (NAND). ...
... Recall the question: what is the minimal set of operators necessary? A: Through such equivalences all Boolean operators can be written with a single operator (NAND). ...
Second order logic or set theory?
... and use proofs as evidence. – Second order logic and set theory capture mathema;cal concepts such as natural and real numbers to the same extent of categoricity. – Second order logic and set th ...
... and use proofs as evidence. – Second order logic and set theory capture mathema;cal concepts such as natural and real numbers to the same extent of categoricity. – Second order logic and set th ...
to the whole? - Vasil Penchev
... The simplest special case is then when the vector space is “flat”: the vector space coincides with its conjugate space (for example Riesz ...
... The simplest special case is then when the vector space is “flat”: the vector space coincides with its conjugate space (for example Riesz ...
x - WordPress.com
... processing of uncertain and vague information. In our earlier work, a fuzzy logic with similarity was proposed and the soundness and completeness were proved (Jiabing Wang et al. 2002). In this paper, some properties of fuzzy inference based on the resolution principle and paramodulation are discuss ...
... processing of uncertain and vague information. In our earlier work, a fuzzy logic with similarity was proposed and the soundness and completeness were proved (Jiabing Wang et al. 2002). In this paper, some properties of fuzzy inference based on the resolution principle and paramodulation are discuss ...
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
... Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers) ...
... Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers) ...
pdf
... development and reinforcement of a realist perspective in many students as a result of instruction in classical physics. Such a perspective can be viewed within a resources framework[7] as dynamic, emerging in a given context in the minds of students from the coordinated activation of finer-grained ...
... development and reinforcement of a realist perspective in many students as a result of instruction in classical physics. Such a perspective can be viewed within a resources framework[7] as dynamic, emerging in a given context in the minds of students from the coordinated activation of finer-grained ...