A General Look at Feedback and Oscillations
... 2. lies in the wave length region where the gain factor is sufficiently large. While the first condition would still allow many wave lengths, the second conditions normally admits just one. But why? Simply because any two mirrors at any distance define a resonant structure and that is why such a sys ...
... 2. lies in the wave length region where the gain factor is sufficiently large. While the first condition would still allow many wave lengths, the second conditions normally admits just one. But why? Simply because any two mirrors at any distance define a resonant structure and that is why such a sys ...
Theory of relativistic harmonic generation
... Wlcm’,) that relativistic effects are expected to be important. The harmonic radiation is found to be emitted in a narrow cone (of radius 5.6 degrees) in the near forward direction, with a reasonably large (2 x lo-*) conversion efficiency. Perhaps most surprisingly they found that the intensity of t ...
... Wlcm’,) that relativistic effects are expected to be important. The harmonic radiation is found to be emitted in a narrow cone (of radius 5.6 degrees) in the near forward direction, with a reasonably large (2 x lo-*) conversion efficiency. Perhaps most surprisingly they found that the intensity of t ...
Experimental observation of the far field diffraction patterns of
... A large number of spatial effects can be observed when an intense light beam interacts with a nonlinear medium [1-7]. In particular, concentric ring intensity distribution pattern can be induced in the far field of a beam after propagation through a nonlinear material. This effect of spatial phase-m ...
... A large number of spatial effects can be observed when an intense light beam interacts with a nonlinear medium [1-7]. In particular, concentric ring intensity distribution pattern can be induced in the far field of a beam after propagation through a nonlinear material. This effect of spatial phase-m ...
Communications Employing Binary Polarization Shift Keying (2PolSK)
... AM Disadvantages Requires adaptive thresholding scheme to perform optimally in the presence of turbulence [1]; PM Disadvantages Highly sensitive to the phase noise; Requires a complex synchronization [2]; FM Disadvantages Bandwidth inefficient; Inferior BER performance compared to PM in the add ...
... AM Disadvantages Requires adaptive thresholding scheme to perform optimally in the presence of turbulence [1]; PM Disadvantages Highly sensitive to the phase noise; Requires a complex synchronization [2]; FM Disadvantages Bandwidth inefficient; Inferior BER performance compared to PM in the add ...
Comment on ""Electromagnetic Wave Dynamics in Matter- Wave Superradiant Scattering" Please share
... The Letter by Deng et al. [1] presents an analytic theoretical description of matter-wave superradiance [2] which claims to go beyond previous theoretical frameworks. I show here that the theory presented in this Letter is not a description of superradiance per se, but rather an elegant perturbative ...
... The Letter by Deng et al. [1] presents an analytic theoretical description of matter-wave superradiance [2] which claims to go beyond previous theoretical frameworks. I show here that the theory presented in this Letter is not a description of superradiance per se, but rather an elegant perturbative ...
QIM 2013 Verifying Entanglement poster final
... (a) Bi-photons produced in a first non-linear (NL) crystal via spontaneous parametric down conversion (SPDC) enter an identical second NL crystal together with the original pump, and are either enhanced by further down conversion (DC), or up-converted back to the pump, depending on the relative phas ...
... (a) Bi-photons produced in a first non-linear (NL) crystal via spontaneous parametric down conversion (SPDC) enter an identical second NL crystal together with the original pump, and are either enhanced by further down conversion (DC), or up-converted back to the pump, depending on the relative phas ...
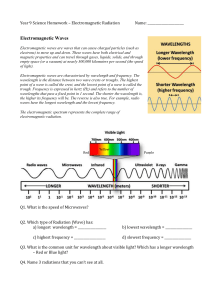
Light+and+Sound.+RM1
... surface of an object. The normal is a line perpendicular to the surface at the point of reflection. The angle of incident is the angle formed by the incident ray and the normal. The angle of reflection is the angle formed by the reflection ray and the normal. ...
... surface of an object. The normal is a line perpendicular to the surface at the point of reflection. The angle of incident is the angle formed by the incident ray and the normal. The angle of reflection is the angle formed by the reflection ray and the normal. ...
High Resolution Biomedical Imaging with Light and Sound
... illuminates tissue, where optical absorption and transient thermal expansion leads to ultrasound emission. Image contrast is based on the naturally occurring (endogenous) optical absorption in tissue. Spatial resolution and penetration depth are determined by the ultrasonic properties of tissue. Per ...
... illuminates tissue, where optical absorption and transient thermal expansion leads to ultrasound emission. Image contrast is based on the naturally occurring (endogenous) optical absorption in tissue. Spatial resolution and penetration depth are determined by the ultrasonic properties of tissue. Per ...
Types of polarization
... propagates differently in the material according to the direction taken. When light passes through a medium it is slowed down to a velocity v with respect to its velocity in a vacuum c and it is usual to denote this by the refractive index ...
... propagates differently in the material according to the direction taken. When light passes through a medium it is slowed down to a velocity v with respect to its velocity in a vacuum c and it is usual to denote this by the refractive index ...
three-dimensional solutions in media with spatial dependence of
... susceptibility of such material. The spatial dependance of χ(3) can be reached by diffusion effects in semiconductor technology [22] also. The oldest method for realizing such local nonlinearity variation using additional optical field was presented in [23]. In this paper, we analyze a nonparaxial v ...
... susceptibility of such material. The spatial dependance of χ(3) can be reached by diffusion effects in semiconductor technology [22] also. The oldest method for realizing such local nonlinearity variation using additional optical field was presented in [23]. In this paper, we analyze a nonparaxial v ...
Laser beam shaping in industrial applications Wei-Yuen Tan 84717925
... Optical path length condition 1/2 • Optical path length along axis of system: ...
... Optical path length condition 1/2 • Optical path length along axis of system: ...
tire
... 1. The most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation. 2. Short for "picture element" and is one square in a grid of light sensing elements. 3. A spectrum that contains only bright emission lines. 4. The distance from a lens or mirror to where the converging light rays meet. 5. Hotter stars emit m ...
... 1. The most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation. 2. Short for "picture element" and is one square in a grid of light sensing elements. 3. A spectrum that contains only bright emission lines. 4. The distance from a lens or mirror to where the converging light rays meet. 5. Hotter stars emit m ...