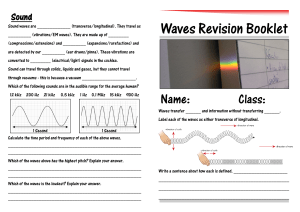
Wave Basics Reading/Study Guide
... certain point each second, basically frequency is how much a wave vibrates. The frequency of a light wave for example is what determines its color. Higher frequencies producing colors on the blue and violet end of the spectrum and lower frequencies producing colors on the red end of the spectrum. ...
... certain point each second, basically frequency is how much a wave vibrates. The frequency of a light wave for example is what determines its color. Higher frequencies producing colors on the blue and violet end of the spectrum and lower frequencies producing colors on the red end of the spectrum. ...
Controllable optical negative refraction and
... scattering. The high nonlinearity of graphene combined with its relatively low absorption makes it a very attractive optical material for two-dimensional phase conjugation. As shown in Fig. 1a, a negatively refracting lens is generated by illuminating a graphite thin film with two counter-propagatin ...
... scattering. The high nonlinearity of graphene combined with its relatively low absorption makes it a very attractive optical material for two-dimensional phase conjugation. As shown in Fig. 1a, a negatively refracting lens is generated by illuminating a graphite thin film with two counter-propagatin ...
Second-harmonic generation
... late sixties by among others Boyd [3, 4]. We will present a modest summary below (see also [1]), which should contain enough information for the present experiment. The basic idea of most theories in nonlinear optics is that the incident optical field is generally very small compared to the atomic f ...
... late sixties by among others Boyd [3, 4]. We will present a modest summary below (see also [1]), which should contain enough information for the present experiment. The basic idea of most theories in nonlinear optics is that the incident optical field is generally very small compared to the atomic f ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... In a Michelson interferometer 150 fringes cross the field of view when the movable mirror is moved through 0.0442mm. Find the wavelength of the light used. ...
... In a Michelson interferometer 150 fringes cross the field of view when the movable mirror is moved through 0.0442mm. Find the wavelength of the light used. ...
Sample Problems for Final
... Problem 4 [25 Points] A beam of green light (wavelength 532 nm) is split into two beams, with one beam going straight ahead, and the other diverging at a small angle relative to the straight-ahead beam. At a distance of 50cm the deflected beam is reflected back so that it meets the straight-ahead ...
... Problem 4 [25 Points] A beam of green light (wavelength 532 nm) is split into two beams, with one beam going straight ahead, and the other diverging at a small angle relative to the straight-ahead beam. At a distance of 50cm the deflected beam is reflected back so that it meets the straight-ahead ...
Lecture 26 - UConn Physics
... • The electric dipole antenna makes use of the basic electric force on a charged particle • Note that you can calculate the related magnetic field using Ampere’s Law. • We can also make an antenna that produces magnetic fields that look like a magnetic dipole, i.e. a loop of wire. • This loop can re ...
... • The electric dipole antenna makes use of the basic electric force on a charged particle • Note that you can calculate the related magnetic field using Ampere’s Law. • We can also make an antenna that produces magnetic fields that look like a magnetic dipole, i.e. a loop of wire. • This loop can re ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester Matthew Jones
... • The first half of the course is only concerned with the solutions to this type of differential equation. • How to solve it is not very interesting. • Of more importance is what the solutions tell us about the behavior of various physical systems. ...
... • The first half of the course is only concerned with the solutions to this type of differential equation. • How to solve it is not very interesting. • Of more importance is what the solutions tell us about the behavior of various physical systems. ...
Experiment results
... A dispersion interferometer ( D I ) is also insensitive to the mechanical vibrations. Since the measurement errors caused by the vibrations are small, the phase shift due to a plasma less than one fringe would be acceptable. Then the DI is principally free from the fringe jump error by selecting the ...
... A dispersion interferometer ( D I ) is also insensitive to the mechanical vibrations. Since the measurement errors caused by the vibrations are small, the phase shift due to a plasma less than one fringe would be acceptable. Then the DI is principally free from the fringe jump error by selecting the ...
Part 1
... + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match some initial condition for the wave function. Speed of the harmonic wave (phase velocity) ...
... + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match some initial condition for the wave function. Speed of the harmonic wave (phase velocity) ...
ppt 3.7MB - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Basis for quantum repeater protocol for long-distance quantum communication Duan, Lukin, Cirac and Zoller, Nature 414, 413 (2001) ...
... Basis for quantum repeater protocol for long-distance quantum communication Duan, Lukin, Cirac and Zoller, Nature 414, 413 (2001) ...
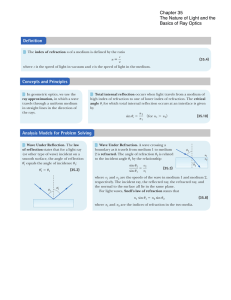
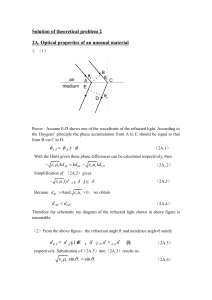
Chapter 35 Light: Reflection and Refraction
... It is natural to treat the propagation of light in terms of rays. A ray is equivalent to a very narrow beam of light, and it indicates the path along which the energy of the wave travels. Geometrical optics is the study of the behavior of straightline rays at the interference between two media by th ...
... It is natural to treat the propagation of light in terms of rays. A ray is equivalent to a very narrow beam of light, and it indicates the path along which the energy of the wave travels. Geometrical optics is the study of the behavior of straightline rays at the interference between two media by th ...