Optical properties of the human tissue
... This method includes inverse adding-doubling (IAD) method developed by Prahl et al (Prahl S.A., et al. // Appl. Opt., 1993, Vol. 32(4), P. 559-568) and inverse Monte Carlo simulations. The IAD method is widely used in tissue optics for processing the experimental data of spectrophotometry with integ ...
... This method includes inverse adding-doubling (IAD) method developed by Prahl et al (Prahl S.A., et al. // Appl. Opt., 1993, Vol. 32(4), P. 559-568) and inverse Monte Carlo simulations. The IAD method is widely used in tissue optics for processing the experimental data of spectrophotometry with integ ...
Porous Biomimetic Microlens Arrays as Multifunctional Optical
... concentration and/or thickness of the dye layer covering the lens. By using different liquids (e.g. with selective refractive index and/or including dyes that can absorb a certain wavelength) as surrounding medium between lenses40, further control over the lens focal length, numerical aperture and w ...
... concentration and/or thickness of the dye layer covering the lens. By using different liquids (e.g. with selective refractive index and/or including dyes that can absorb a certain wavelength) as surrounding medium between lenses40, further control over the lens focal length, numerical aperture and w ...
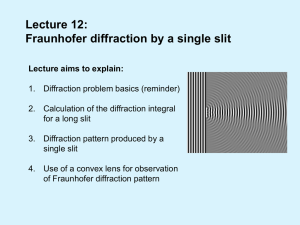
Lecture 12: Fraunhofer diffraction by a single slit
... Problem: A propagating wave encounters an obstacle (i.e. a distortion of the wave-front occurs). How will the distortion influence the propagation of the wave? Fraunhofer diffraction: the resultant wave is measured very far away from the place where the wave-front was distorted (R>>size of the obsta ...
... Problem: A propagating wave encounters an obstacle (i.e. a distortion of the wave-front occurs). How will the distortion influence the propagation of the wave? Fraunhofer diffraction: the resultant wave is measured very far away from the place where the wave-front was distorted (R>>size of the obsta ...
P1X
... Requirements for Laser action (Y&F 38.6): Theoretical laser: • We want a three level system in which the intermediate state is metastable (ie. the time for transition is much longer than the time for transition to other states). • If we can optically pump a three level system such that electrons a ...
... Requirements for Laser action (Y&F 38.6): Theoretical laser: • We want a three level system in which the intermediate state is metastable (ie. the time for transition is much longer than the time for transition to other states). • If we can optically pump a three level system such that electrons a ...
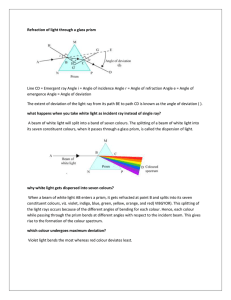
Ref. “Optical Materials”
... For a given angle c the refracted beam will be paralel to the surface (1=90o) We call this angle “critical angle” The critical angle value will be given by senc=n1/n2 For any angle 2 larger that the critical angle, light will be completely reflected to the medium. This process is what we call To ...
... For a given angle c the refracted beam will be paralel to the surface (1=90o) We call this angle “critical angle” The critical angle value will be given by senc=n1/n2 For any angle 2 larger that the critical angle, light will be completely reflected to the medium. This process is what we call To ...
Active imaging lens with real-time variable resolution and constant
... Also, although the idea of using active optics to control distortion is novel, both the idea of using active elements to enhance optical systems and the idea of controlling static distortion to adjust resolution have been used in the past. Using deformable mirrors in adaptive optics to correct the p ...
... Also, although the idea of using active optics to control distortion is novel, both the idea of using active elements to enhance optical systems and the idea of controlling static distortion to adjust resolution have been used in the past. Using deformable mirrors in adaptive optics to correct the p ...
The page, which you have just visited, was created for students of
... Many solids have a crystalline structure on microscopic scales. The molecules are arranged in a regular lattice. Usually when a liquid is cooled to below its melting point, crystals form and it solidifies. But sometimes it could become supercooled and remain liquid below, its melting point because t ...
... Many solids have a crystalline structure on microscopic scales. The molecules are arranged in a regular lattice. Usually when a liquid is cooled to below its melting point, crystals form and it solidifies. But sometimes it could become supercooled and remain liquid below, its melting point because t ...
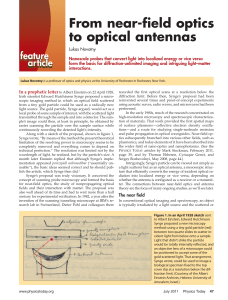
From near-field optics to optical antennas
... and allow researchers to correlate fluorescence images with simultaneously recorded topographical maps of surface molecules. Those advantages, however, come at the cost of significantly higher experimental complexity. Figure 5 shows a fluorescence image of single Nile blue molecules dispersed on a g ...
... and allow researchers to correlate fluorescence images with simultaneously recorded topographical maps of surface molecules. Those advantages, however, come at the cost of significantly higher experimental complexity. Figure 5 shows a fluorescence image of single Nile blue molecules dispersed on a g ...
1 Introduction to Optics and Photophysics - Wiley-VCH
... the scalar product of the vectors. The spatial frequency counts the number of amplitude maxima per meter in the medium in which it is traveling (Figure 1.2). The spatial position x denotes the coordinate at which we are observing. In many cases, we deal with linear optics, where all amplitudes will ...
... the scalar product of the vectors. The spatial frequency counts the number of amplitude maxima per meter in the medium in which it is traveling (Figure 1.2). The spatial position x denotes the coordinate at which we are observing. In many cases, we deal with linear optics, where all amplitudes will ...
Analysis of Optical Systems I
... and one which does not (the extraordinary wave). This phenomenon is called double refraction, and is discussed in detail in Chapter 18. If an optical system contains only planar interfaces, the path of a ray of light through the system can be easily calculated using only the law of reflection and Sn ...
... and one which does not (the extraordinary wave). This phenomenon is called double refraction, and is discussed in detail in Chapter 18. If an optical system contains only planar interfaces, the path of a ray of light through the system can be easily calculated using only the law of reflection and Sn ...
Chapter 2 Classical propagation
... The full width at half maximum of the strongest hyperfine component of the sodium D2 line at 589.0 nm is 100 MHz. A beam of light passes through a gas of sodium with an atom density of 11017 m-3. Calculate: (i) The peak absorption coefficient due to this absorption line. (ii ) The frequency at whic ...
... The full width at half maximum of the strongest hyperfine component of the sodium D2 line at 589.0 nm is 100 MHz. A beam of light passes through a gas of sodium with an atom density of 11017 m-3. Calculate: (i) The peak absorption coefficient due to this absorption line. (ii ) The frequency at whic ...
Dispersion Compensation using a Prism-pair
... The generation of ultrashort pulses [1, 2] revolutionized the field of molecular spectroscopy [3]. Not only that ultrashort pulses enable to observe molecular motion in time [4, 5, 6], but they allow also to manipulate their dynamics [7, 8, 9] by controlling the spectral properties of the pulses. Fo ...
... The generation of ultrashort pulses [1, 2] revolutionized the field of molecular spectroscopy [3]. Not only that ultrashort pulses enable to observe molecular motion in time [4, 5, 6], but they allow also to manipulate their dynamics [7, 8, 9] by controlling the spectral properties of the pulses. Fo ...
3. How to - TYC Physics Workshop Project
... Frederica that he saw. Everyone observed that the pencil was pointing well above and past the actual location of the fish, as viewed from the side. Does your ray diagram demonstrate this fact? If not, how must it be changed to correctly show the law of refraction? QUALITATIVE REASONING 1. How many r ...
... Frederica that he saw. Everyone observed that the pencil was pointing well above and past the actual location of the fish, as viewed from the side. Does your ray diagram demonstrate this fact? If not, how must it be changed to correctly show the law of refraction? QUALITATIVE REASONING 1. How many r ...
Physics II - Magnetism
... to itself, “Hey these rays all look like they’re coming from behind the mirror!” Your brain does a bit of back ray tracing is what happens. So we end up with a virtual image that is erect and magnified. ...
... to itself, “Hey these rays all look like they’re coming from behind the mirror!” Your brain does a bit of back ray tracing is what happens. So we end up with a virtual image that is erect and magnified. ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... Remove any slides attached to the slide holder. At the back focal plane we see a single focal spot. The position of the spot locates the ‘dc level’ of illumination of the beam entering the lens. Any other spots appearing on the card indicate the presence of other spatial frequencies. Remove the card ...
... Remove any slides attached to the slide holder. At the back focal plane we see a single focal spot. The position of the spot locates the ‘dc level’ of illumination of the beam entering the lens. Any other spots appearing on the card indicate the presence of other spatial frequencies. Remove the card ...
human eye and colourful world part 2
... space, the sky will appear to be dark. The least scattering red colour light finds its application in various fields. For example, in marking red light, danger signals etc. red colour is preferred because it is scattered least by fog, smoke, and dust particles present in air. 2. Sunrise and sunset A ...
... space, the sky will appear to be dark. The least scattering red colour light finds its application in various fields. For example, in marking red light, danger signals etc. red colour is preferred because it is scattered least by fog, smoke, and dust particles present in air. 2. Sunrise and sunset A ...
Refraction Practice Problems
... 9. A laser beam is incident at an angle of 30.0° to the vertical onto a solution of corn syrup in water. If the beam is refracted to 19.24° to the vertical, (a) what is the index of refraction of the syrup solution? Suppose the light is red, with wavelength 632.8 nm in a vacuum. Find its (b) wavelen ...
... 9. A laser beam is incident at an angle of 30.0° to the vertical onto a solution of corn syrup in water. If the beam is refracted to 19.24° to the vertical, (a) what is the index of refraction of the syrup solution? Suppose the light is red, with wavelength 632.8 nm in a vacuum. Find its (b) wavelen ...
PP_SSL_Modeling - LAS
... As known textbooks of lasers, beam propagation through a series of parabolic optical elements can be described by the use of ABCD matrices. In many cases the optical elements in a resonator, such as spherical mirrors and dielectric interfaces, can be approximated parabolically. The ABCD Matrices fo ...
... As known textbooks of lasers, beam propagation through a series of parabolic optical elements can be described by the use of ABCD matrices. In many cases the optical elements in a resonator, such as spherical mirrors and dielectric interfaces, can be approximated parabolically. The ABCD Matrices fo ...