Notes - RCSD
... Group 18 is called the Noble Gases. These gases are completely unreactive (they do not make compounds with any other elements). The large block of elements in the middle of the Periodic Table is called the Transition Metals. These metals are very good conductors and are not very reactive, which ...
... Group 18 is called the Noble Gases. These gases are completely unreactive (they do not make compounds with any other elements). The large block of elements in the middle of the Periodic Table is called the Transition Metals. These metals are very good conductors and are not very reactive, which ...
More Chemistry!
... Mendeleev grouped elements that had similar chemical and physical properties. Within these groups, he listed the elements top to bottom by their atomic masses; The elements also line up in rows across the table by bonding power; this is the number of chemical bonds an element can form by attachi ...
... Mendeleev grouped elements that had similar chemical and physical properties. Within these groups, he listed the elements top to bottom by their atomic masses; The elements also line up in rows across the table by bonding power; this is the number of chemical bonds an element can form by attachi ...
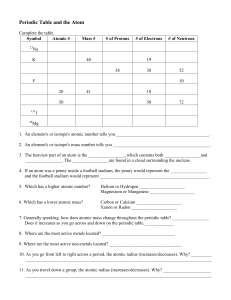
3.08_Periodic Table and the Atom
... 22. Elements of Groups 17 are called ________________________________. 23. The most active element in Group 17 is ________________________________. 24. Elements of Groups 18 are called ________________________________. 25. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Metals? ________________ 26. ...
... 22. Elements of Groups 17 are called ________________________________. 23. The most active element in Group 17 is ________________________________. 24. Elements of Groups 18 are called ________________________________. 25. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Metals? ________________ 26. ...
Questions on Chapter 7
... 1) In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) O, S, Se B) N, O, F C) Na, Mg, K D) S, Se, Si E) Ne, Na, Mg 2) In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) P, Se, I B) Cl, Br, Na C) Si, As, ...
... 1) In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) O, S, Se B) N, O, F C) Na, Mg, K D) S, Se, Si E) Ne, Na, Mg 2) In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) P, Se, I B) Cl, Br, Na C) Si, As, ...
Chem A Week 5 Periodic Table Notes and Coloring
... Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. What makes an element reactive? An incomplete valence electron level. All atoms (except hydrogen) want to have 8 electrons in their very outermost energy level (This is called the rule of octet.) Atoms bond until this level is comple ...
... Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. What makes an element reactive? An incomplete valence electron level. All atoms (except hydrogen) want to have 8 electrons in their very outermost energy level (This is called the rule of octet.) Atoms bond until this level is comple ...
Element Review
... These do not conduct heat or electricity, they are not shiny or malleable. Non-metals ...
... These do not conduct heat or electricity, they are not shiny or malleable. Non-metals ...
Ch. 13 Notes---Electrons in Atoms
... – Also, moving across a period takes us from metals to anions nonmetals. Since nonmetals generally form _________, they gain tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. Noble __________ gases – ___________ are not listed ...
... – Also, moving across a period takes us from metals to anions nonmetals. Since nonmetals generally form _________, they gain tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. Noble __________ gases – ___________ are not listed ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... 2. After you paste the pictures on the back of the cards, cut the cards out. 3. Try to match the vocabulary word with the correct definition. You will know if you’re correct if the ...
... 2. After you paste the pictures on the back of the cards, cut the cards out. 3. Try to match the vocabulary word with the correct definition. You will know if you’re correct if the ...
Slide 1 - Herricks
... Electronegativity- The ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound As you move across a period EN increases because nuclear charge increases and shielding effect remains constant so the nucleus is able to attract electrons better. As you move down a group EN decreases be ...
... Electronegativity- The ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound As you move across a period EN increases because nuclear charge increases and shielding effect remains constant so the nucleus is able to attract electrons better. As you move down a group EN decreases be ...
Periodic Table – Organizing the Elements
... within a group (compare Li and Na)? –The electron to be removed from Na is further from the nucleus than Lithium’s electron. –Sodium’s electron is held more loosely and therefore easier (less energy) to remove. ...
... within a group (compare Li and Na)? –The electron to be removed from Na is further from the nucleus than Lithium’s electron. –Sodium’s electron is held more loosely and therefore easier (less energy) to remove. ...
Ch 5
... as the compounds they formed, which was very difficult. At that time, there was no accurate way to determine the atomic mass or the # of atoms of an element in a particular compound. Different chemists used different atomic masses for the same element, which made it impossible to compare results. ...
... as the compounds they formed, which was very difficult. At that time, there was no accurate way to determine the atomic mass or the # of atoms of an element in a particular compound. Different chemists used different atomic masses for the same element, which made it impossible to compare results. ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Alkali metals
... elementary particles that make up all known matter. Sentence- The electric charge of elements before a reaction, are all generally zero. ...
... elementary particles that make up all known matter. Sentence- The electric charge of elements before a reaction, are all generally zero. ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Tuesday February 26th - seys
... Element- a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance by ordinary chemical change changes, consists of atoms of only one type Chemical formula- an expression that shows the numbers and types of atoms joined in a compound (H2O) Compound- two different types of atoms bonded together ...
... Element- a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance by ordinary chemical change changes, consists of atoms of only one type Chemical formula- an expression that shows the numbers and types of atoms joined in a compound (H2O) Compound- two different types of atoms bonded together ...
The Periodic Table - Ms. Dormer
... First periodic table 63 known elements at the time Mendeleev’s table contains gaps that unknown elements should fill He predicted the properties of these unknown elements & gave them names ...
... First periodic table 63 known elements at the time Mendeleev’s table contains gaps that unknown elements should fill He predicted the properties of these unknown elements & gave them names ...
Test Review
... Alkali Metals- Group 1, most reactive metals on the periodic table. Form +1 ions, losing 1 electron to look like a noble gas. Too reactive to exist in nature freely. Must be stored in mineral oil. Alkaline Earth Metals – Group 2, not as reactive as alkali metals. Form +2 ions, losing 2 electrons to ...
... Alkali Metals- Group 1, most reactive metals on the periodic table. Form +1 ions, losing 1 electron to look like a noble gas. Too reactive to exist in nature freely. Must be stored in mineral oil. Alkaline Earth Metals – Group 2, not as reactive as alkali metals. Form +2 ions, losing 2 electrons to ...
Questions on The Periodic Table
... 2. How did Newlands classify the elements and how was it initially received? 3. Why did his method fail beyond the element calcium and would it work today for the first 20 elements? 4. How did Mendeleev and Meyer organize the elements? were their periodic tables the same? ...
... 2. How did Newlands classify the elements and how was it initially received? 3. Why did his method fail beyond the element calcium and would it work today for the first 20 elements? 4. How did Mendeleev and Meyer organize the elements? were their periodic tables the same? ...
Chemistry Summative Exam Part 2 Study Guide Answer Key
... What elements are the most reactive and where are they located on the periodic table? The most reactive elements are the alkali metals located in the first family of the periodic table of elements. The column all the way to the left of the periodic table. 18. What elements are the least reactive and ...
... What elements are the most reactive and where are they located on the periodic table? The most reactive elements are the alkali metals located in the first family of the periodic table of elements. The column all the way to the left of the periodic table. 18. What elements are the least reactive and ...
Activity 16 Elements and the Periodic Table
... Do you see another of the patterns that Mendeleev and other scientists recognized? ___________ Neutral atoms contain equal numbers of protons (+) and electrons (-). Because of this, you know that neutral atoms of lithium, beryllium, boron and carbon also have 3, 4, 5, and 6 electrons respectively. W ...
... Do you see another of the patterns that Mendeleev and other scientists recognized? ___________ Neutral atoms contain equal numbers of protons (+) and electrons (-). Because of this, you know that neutral atoms of lithium, beryllium, boron and carbon also have 3, 4, 5, and 6 electrons respectively. W ...
The Periodic Table
... Identifying the Staircase • Notice the “zigzag” line on the table. Elements to the LEFT of the line are “METALS”. Elements to the RIGHT of the line are “NON-METALS”. Elements that are right next to the line are often ...
... Identifying the Staircase • Notice the “zigzag” line on the table. Elements to the LEFT of the line are “METALS”. Elements to the RIGHT of the line are “NON-METALS”. Elements that are right next to the line are often ...
Periodic Table
... noble gases. They do not ordinarily form compounds because atoms of noble gases do not usually gain, lose, or share electrons. They have 8 valence e-, except helium which only has 2. They are odorless and colorless. Remember from a previous discussion, the noble gases are used in neon lights. Highly ...
... noble gases. They do not ordinarily form compounds because atoms of noble gases do not usually gain, lose, or share electrons. They have 8 valence e-, except helium which only has 2. They are odorless and colorless. Remember from a previous discussion, the noble gases are used in neon lights. Highly ...
helium
... The compounds of transition metals are usually brightly colored and are often used to color paints. Transition elements have 1 or 2 valence electrons, which they lose when they form bonds with other atoms. Some transition elements can lose electrons in their next-to-outermost level. ...
... The compounds of transition metals are usually brightly colored and are often used to color paints. Transition elements have 1 or 2 valence electrons, which they lose when they form bonds with other atoms. Some transition elements can lose electrons in their next-to-outermost level. ...
Properties of Elements
... Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. What makes an element reactive? ...
... Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. What makes an element reactive? ...
Noble gas

The noble gases make a group of chemical elements with similar properties. Under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six noble gases that occur naturally are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn).For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18 of the periodic table.It is possible that due to relativistic effects, the group 14 element flerovium exhibits some noble-gas-like properties, instead of the group 18 element ununoctium. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when under particular extreme conditions. The inertness of noble gases makes them very suitable in applications where reactions are not wanted. For example: argon is used in lightbulbs to prevent the hot tungsten filament from oxidizing; also, helium is breathed by deep-sea divers to prevent oxygen and nitrogen toxicity.The properties of the noble gases can be well explained by modern theories of atomic structure: their outer shell of valence electrons is considered to be ""full"", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions, and it has been possible to prepare only a few hundred noble gas compounds. The melting and boiling points for a given noble gas are close together, differing by less than 10 °C (18 °F); that is, they are liquids over only a small temperature range.Neon, argon, krypton, and xenon are obtained from air in an air separation unit using the methods of liquefaction of gases and fractional distillation. Helium is sourced from natural gas fields which have high concentrations of helium in the natural gas, using cryogenic gas separation techniques, and radon is usually isolated from the radioactive decay of dissolved radium, thorium, or uranium compounds (since those compounds give off alpha particles). Noble gases have several important applications in industries such as lighting, welding, and space exploration. A helium-oxygen breathing gas is often used by deep-sea divers at depths of seawater over 55 m (180 ft) to keep the diver from experiencing oxygen toxemia, the lethal effect of high-pressure oxygen, and nitrogen narcosis, the distracting narcotic effect of the nitrogen in air beyond this partial-pressure threshold. After the risks caused by the flammability of hydrogen became apparent, it was replaced with helium in blimps and balloons.