ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
... proportional to the frequency of the light. Thus radiant energy was quantized. This explains the difference in effect between xrays(high frequency, high energy) vs radio waves ( low frequency, low energy) Radiation composed of one wave length is called monochromatic. When white light is separate ...
... proportional to the frequency of the light. Thus radiant energy was quantized. This explains the difference in effect between xrays(high frequency, high energy) vs radio waves ( low frequency, low energy) Radiation composed of one wave length is called monochromatic. When white light is separate ...
I Laser A laser is a device that emits light (electromagnetic radiation
... ("excited") quantum states. Particles can interact with light by either absorbing or emitting photons. Emission can be spontaneous or stimulated. In the latter case, the photon is emitted in the same direction as the light that is passing by. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds ...
... ("excited") quantum states. Particles can interact with light by either absorbing or emitting photons. Emission can be spontaneous or stimulated. In the latter case, the photon is emitted in the same direction as the light that is passing by. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds ...
Midterm Exam
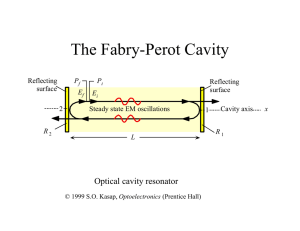
... b. Pick one of these stable resonators (choose numbers that satisfy the condition for part a) and solve for the mode of this cavity. Specifically, plot the spotsize, w(z), and the radius of curvature, R(z), of the mode everywhere in the cavity. c. Put a focusing lens immediately after the output cou ...
... b. Pick one of these stable resonators (choose numbers that satisfy the condition for part a) and solve for the mode of this cavity. Specifically, plot the spotsize, w(z), and the radius of curvature, R(z), of the mode everywhere in the cavity. c. Put a focusing lens immediately after the output cou ...
OSA journals template (MSWORD) - HAL
... a fiber-coupled spectrometer (Ocean Optics HR4000). We compensate the spectral phase using a set of chirped mirrors with total group delay dispersion of ~-300 fs2 and third order dispersion of ~-290 fs3. We measure the compressed intensity and phase of the pulse using a single-shot FROG capable of m ...
... a fiber-coupled spectrometer (Ocean Optics HR4000). We compensate the spectral phase using a set of chirped mirrors with total group delay dispersion of ~-300 fs2 and third order dispersion of ~-290 fs3. We measure the compressed intensity and phase of the pulse using a single-shot FROG capable of m ...
Reports of optical fiber communication systems 2011-2012
... When data rates were in the low gigabit range and transmission distances were less than 100 km or so, most fiber optic transmitters used directly modulated lasers. However, as data rates and span lengths grew, waveguide chirp, caused by turning a laser on and off, limited data rates. Dispersion prob ...
... When data rates were in the low gigabit range and transmission distances were less than 100 km or so, most fiber optic transmitters used directly modulated lasers. However, as data rates and span lengths grew, waveguide chirp, caused by turning a laser on and off, limited data rates. Dispersion prob ...
Single-shot Detection of Wavepacket Evolution
... atoms are excited to the 4s4p level using a nsec dye laser. A 500 fsec, 392 nm laser pulse then drives the 4s4p - 4snd transition producing a Rydberg wavepacket centered near n = 25. A second, identical 392 nm pulse enters the laser/atom interaction region nearly co-linearly with the first psec pulse ...
... atoms are excited to the 4s4p level using a nsec dye laser. A 500 fsec, 392 nm laser pulse then drives the 4s4p - 4snd transition producing a Rydberg wavepacket centered near n = 25. A second, identical 392 nm pulse enters the laser/atom interaction region nearly co-linearly with the first psec pulse ...
slicing and dicing photons - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... dynamics have not been reported for silicon NCs, perhaps owing to measurement complications associated with the indirect bandgap in the electronic structure of silicon. However, in the characterization of cooling dynamics for several other types of NCs such as InP, CdSe and PbSe, the cooling times f ...
... dynamics have not been reported for silicon NCs, perhaps owing to measurement complications associated with the indirect bandgap in the electronic structure of silicon. However, in the characterization of cooling dynamics for several other types of NCs such as InP, CdSe and PbSe, the cooling times f ...
6.1.1
... the system of “Classical Physics” slowly emerged with these fundamental ideas at its core… – Newton’s Laws define mechanics – Light is a WAVE – Atoms make up matter and are indivisible ...
... the system of “Classical Physics” slowly emerged with these fundamental ideas at its core… – Newton’s Laws define mechanics – Light is a WAVE – Atoms make up matter and are indivisible ...
November 18
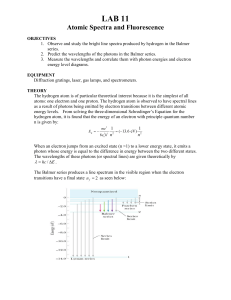
... C(speed of light 3x 108 m/s)=(lambda[wavelength in meters])(frequency in Hertz) Energy in Joules = h (plank’s constant 6.6 x 10-34) x frequency Example problem: Given that red light has a wavelength of 700 x 10-9 meters, what is the frequency and how much energy does it have? To find frequency, use ...
... C(speed of light 3x 108 m/s)=(lambda[wavelength in meters])(frequency in Hertz) Energy in Joules = h (plank’s constant 6.6 x 10-34) x frequency Example problem: Given that red light has a wavelength of 700 x 10-9 meters, what is the frequency and how much energy does it have? To find frequency, use ...
Feb20_modified
... – Why? Is it because the photons are losing energy? – No – the light is simply spreading out as it travels from its source to its destination – The farther from the source you are, the dimmer the light seems – We say that the object’s brightness, or amount of light received from a source, is ...
... – Why? Is it because the photons are losing energy? – No – the light is simply spreading out as it travels from its source to its destination – The farther from the source you are, the dimmer the light seems – We say that the object’s brightness, or amount of light received from a source, is ...