Physical Review Letters 103, 233602 (2009)
... are matter fields for atoms in j1i and j2i. [The probe laser field and c 2 may be represented by field operators (relevant for few photon pulses and quantum states) whereas the coupling laser field and the c 1 condensate component are treated as mean fields.] In the dark state, excitation amplitudes ...
... are matter fields for atoms in j1i and j2i. [The probe laser field and c 2 may be represented by field operators (relevant for few photon pulses and quantum states) whereas the coupling laser field and the c 1 condensate component are treated as mean fields.] In the dark state, excitation amplitudes ...
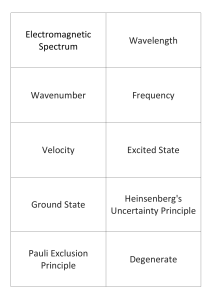
Unit 1 Inorganic Flashcards
... This is the lowest possible electronic configuration the electrons in an atom can adopt. When an electron moves down to its ground state, energy is given out. ...
... This is the lowest possible electronic configuration the electrons in an atom can adopt. When an electron moves down to its ground state, energy is given out. ...
3/27 Lecture Slides
... at a frequency of 750 MHz. This is in the radio frequency and Hz = s-1. What is the wavelength of this light? An infrared absorption band occurs at a wavenumber of 812 cm-1. What is the wavelength (in mm) and energy (J/photon) of that light? What type of light involves transitions of inner shell ele ...
... at a frequency of 750 MHz. This is in the radio frequency and Hz = s-1. What is the wavelength of this light? An infrared absorption band occurs at a wavenumber of 812 cm-1. What is the wavelength (in mm) and energy (J/photon) of that light? What type of light involves transitions of inner shell ele ...
A.Lobko, Laser acceleration of electrons and ions: principles, issues
... The laser starts to ionize the surface of the initially opaque target and successively heats more and more electrons to relativistic energies. Provided, the target is thin enough and has not blown apart under the irradiation of the laser pedestal, the laser will eventually promote all electrons with ...
... The laser starts to ionize the surface of the initially opaque target and successively heats more and more electrons to relativistic energies. Provided, the target is thin enough and has not blown apart under the irradiation of the laser pedestal, the laser will eventually promote all electrons with ...
Quantum Physics Cumulative Review
... 2. How does the law of Conservation of Energy apply to a light beam hitting an electron on a metal and knocking it off? Where is the energy before the light hits the metal and where is it afterward? 3. Helium-Neon [HeNe] lasers are very common lasers that emit 632.8 nm red light. How is it possible ...
... 2. How does the law of Conservation of Energy apply to a light beam hitting an electron on a metal and knocking it off? Where is the energy before the light hits the metal and where is it afterward? 3. Helium-Neon [HeNe] lasers are very common lasers that emit 632.8 nm red light. How is it possible ...
Wang_Project_Summery
... inferred) enters the light shack through a series of guide mirrors. Taking this visible light beam, using a series of optical devices, I will focus the beam and direct it into a light-tight box where the photo detector sits. Using a special computer to gather data from the photon counter, we will be ...
... inferred) enters the light shack through a series of guide mirrors. Taking this visible light beam, using a series of optical devices, I will focus the beam and direct it into a light-tight box where the photo detector sits. Using a special computer to gather data from the photon counter, we will be ...
laser2-broadening
... possibility of interference due to overlapping spectra. The line width ½ of an atomic absorption or emission line is defined as its width in wavelength units when measured at one half the ...
... possibility of interference due to overlapping spectra. The line width ½ of an atomic absorption or emission line is defined as its width in wavelength units when measured at one half the ...
Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani and Elite School of Optometry
... COURSE HANDOUT COURSE NO. ...
... COURSE HANDOUT COURSE NO. ...
Creation of long-term coherent optical memory via controlled nonlinear interactions
... To demonstrate that the probe light pulses are regenerated through a stimulated scattering process, we perform the following control experiment. A probe pulse is stored with the same procedure as described above except we change the magnetic field to B = 18 G. Since the ψ1 and ψ2 components can co-e ...
... To demonstrate that the probe light pulses are regenerated through a stimulated scattering process, we perform the following control experiment. A probe pulse is stored with the same procedure as described above except we change the magnetic field to B = 18 G. Since the ψ1 and ψ2 components can co-e ...
科目名稱:普通化學 期中考(I) 日期:99年10月18日 學號 姓名 I. 名詞
... a Pt atom. The density of Pt is 21.45 g/cm3 and the mass of a single Pt atom is 3.240 × 10-22 g. [The volume of a sphere of radius r is (4/3)πr3.] 10% 3. A photon of ultraviolet light possesses enough energy to mutate a strand of human DNA. What is the energy of a single UV photon and a mole of UV p ...
... a Pt atom. The density of Pt is 21.45 g/cm3 and the mass of a single Pt atom is 3.240 × 10-22 g. [The volume of a sphere of radius r is (4/3)πr3.] 10% 3. A photon of ultraviolet light possesses enough energy to mutate a strand of human DNA. What is the energy of a single UV photon and a mole of UV p ...
Time-resolved atomic inner-shell spectroscopy
... Many-body systems with excess internal energy relax towards states of lower energy by rearrangement of molecular, atomic or nuclear structure. Observing these processes in real time requires a pump pulse for initiating the microscopic dynamics and a delayed probe pulse for detecting transition state ...
... Many-body systems with excess internal energy relax towards states of lower energy by rearrangement of molecular, atomic or nuclear structure. Observing these processes in real time requires a pump pulse for initiating the microscopic dynamics and a delayed probe pulse for detecting transition state ...
Elec Structure of Atom
... an object can gain or lose is related to the frequency of the radiation: E=hv. Planck’s constant; h=6.63 x 10-34 J-s. Energy is quantized, meaning it can only have certain allowed values. Einstein proposed that that light behaves as if it consisted of quantized energy packets called photons. E ...
... an object can gain or lose is related to the frequency of the radiation: E=hv. Planck’s constant; h=6.63 x 10-34 J-s. Energy is quantized, meaning it can only have certain allowed values. Einstein proposed that that light behaves as if it consisted of quantized energy packets called photons. E ...
P316
... quantized what would the Earth’s quantum number be? How much energy would be released in a transition to the next lower quantum number? Would this amount of energy be detectable? (Earth orbit is 1.5x1011 m radius). Suppose the nucleus has charge Z(+e) and a single electron orbits it as described by ...
... quantized what would the Earth’s quantum number be? How much energy would be released in a transition to the next lower quantum number? Would this amount of energy be detectable? (Earth orbit is 1.5x1011 m radius). Suppose the nucleus has charge Z(+e) and a single electron orbits it as described by ...
Energy
... Positron Decay • Occurs with elements that have too many protons for the nucleus to be stable. ...
... Positron Decay • Occurs with elements that have too many protons for the nucleus to be stable. ...
Summary
... With the realization of coherent, laser-like atoms in the form of Bose-Einstein condensates it has become possible to explore matter-wave amplification, a process in which the number of atoms in a quantum state is amplified due to bosonic stimulation. In previous amplifiers based on superradiant Ray ...
... With the realization of coherent, laser-like atoms in the form of Bose-Einstein condensates it has become possible to explore matter-wave amplification, a process in which the number of atoms in a quantum state is amplified due to bosonic stimulation. In previous amplifiers based on superradiant Ray ...