Chapter 9
... Covalent bonds are usually formed between elements close to each other on the periodic table and nonmetallic elements. ...
... Covalent bonds are usually formed between elements close to each other on the periodic table and nonmetallic elements. ...
CHAPTER 9 : CHEMICAL BONDING I
... 9.79 Give an example of an ion or molecule containing Al that (a) obeys the octet rule, (b) has an expanded octet, and (c) has an incomplete octet. 9.82 Attempts to prepare the compounds listed below as stable species under atmospheric conditions have failed. Suggest possible reasons for the failure ...
... 9.79 Give an example of an ion or molecule containing Al that (a) obeys the octet rule, (b) has an expanded octet, and (c) has an incomplete octet. 9.82 Attempts to prepare the compounds listed below as stable species under atmospheric conditions have failed. Suggest possible reasons for the failure ...
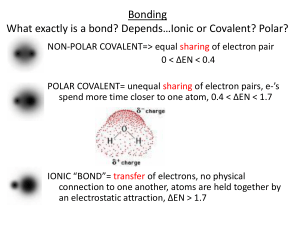
Recall: What exactly is a bond? Depends*Ionic or Covalent? Polar?
... • state • solubility in water • electrical conductivity as a solid • electrical conductivity in aqueous solution • melting point • boiling point ...
... • state • solubility in water • electrical conductivity as a solid • electrical conductivity in aqueous solution • melting point • boiling point ...
download
... important in plastics and polymers. These materials are made up of a long string molecules consisting of carbon atoms covalently bonded with other atoms, such as hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine. The covalent bonds within the molecules are very strong and rupture only under extreme conditions. T ...
... important in plastics and polymers. These materials are made up of a long string molecules consisting of carbon atoms covalently bonded with other atoms, such as hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine. The covalent bonds within the molecules are very strong and rupture only under extreme conditions. T ...
Hydrogen Bonding
... of nitrogen and oxygen compounds. Nitrogen and oxygen are more electronegative than hydrogen Covalent N—H and O—H bonds are polar bonds, the H atoms in these bonds can participate in hydrogen bonding. Amino (—NH2) and hydroxyl (—OH) groups Two atomic groups that often engage in hydrogen bonding ...
... of nitrogen and oxygen compounds. Nitrogen and oxygen are more electronegative than hydrogen Covalent N—H and O—H bonds are polar bonds, the H atoms in these bonds can participate in hydrogen bonding. Amino (—NH2) and hydroxyl (—OH) groups Two atomic groups that often engage in hydrogen bonding ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS 1 CHAPTER TWO
... d. Water (H2O) is always 1 g hydrogen for every 8 g of O present, while H2O2 is always 1 g hydrogen for every 16 g of O present. These are distinctly different compounds, each with its own unique relative number and types of atoms present. e. A chemical equation involves a reorganization of the atom ...
... d. Water (H2O) is always 1 g hydrogen for every 8 g of O present, while H2O2 is always 1 g hydrogen for every 16 g of O present. These are distinctly different compounds, each with its own unique relative number and types of atoms present. e. A chemical equation involves a reorganization of the atom ...
How are Molecules Depicted? - Belle Vernon Area School District
... E level of an atom and determines the chemical properties Lewis Structure = a structure in which e- are represented by dots: dot pairs or dashes b/t 2 atomic symbols represents pairs in covalent bonds ...
... E level of an atom and determines the chemical properties Lewis Structure = a structure in which e- are represented by dots: dot pairs or dashes b/t 2 atomic symbols represents pairs in covalent bonds ...
Chemistry Fall Final Review 2012-2013 Alchemy Unit
... 25. Are the following molecules polar or nonpolar molecules? Explain a). SiF4 b). PI3 a). SiF4 is nonpolar. The bonding between Si and F is polar covalent. The tetrahedral shape of the molecule is symmetrical which cancels out the partial charges. The resulting molecule is nonpolar. b). PI3 is polar ...
... 25. Are the following molecules polar or nonpolar molecules? Explain a). SiF4 b). PI3 a). SiF4 is nonpolar. The bonding between Si and F is polar covalent. The tetrahedral shape of the molecule is symmetrical which cancels out the partial charges. The resulting molecule is nonpolar. b). PI3 is polar ...
Chapter 2 Study Guides
... 7. Before a chemical reaction can start, ____________________ must be absorbed by the reactants. The amount that must be absorbed to start the reaction is called the ...
... 7. Before a chemical reaction can start, ____________________ must be absorbed by the reactants. The amount that must be absorbed to start the reaction is called the ...
Chapter 2 BIO 100 Chemistry
... unshared orbitals overlap, each atom can count both electrons toward its goal of filling the valence shell. ...
... unshared orbitals overlap, each atom can count both electrons toward its goal of filling the valence shell. ...
2 Types of Chemical Bonds
... • A chemical bond is formed when atoms of elements change the number of valence electrons they have to get 8 or 2 • A chemical bond combines elements together to form a compound! ...
... • A chemical bond is formed when atoms of elements change the number of valence electrons they have to get 8 or 2 • A chemical bond combines elements together to form a compound! ...
Fundamentals Fall Final Review
... (C) NaOH (D) FeS 14. What type of bond forms between a metal and a nonmetal? 15. What type of bond forms between two metals? 16. What type of bond forms between two nonmetals? 17. Give an example of a polar molecule and explain why it is polar. 18. Write covalent formulas for: (A) carbon tetrachlori ...
... (C) NaOH (D) FeS 14. What type of bond forms between a metal and a nonmetal? 15. What type of bond forms between two metals? 16. What type of bond forms between two nonmetals? 17. Give an example of a polar molecule and explain why it is polar. 18. Write covalent formulas for: (A) carbon tetrachlori ...
Chemistry Unit Test Review
... before. What might have accounted for the mass being different after? ...
... before. What might have accounted for the mass being different after? ...
CHAPTER 9 HYDROGEN Position of Hydrogen in Periodic Table
... These are the compounds of H2 formed with most of the s-block elements which are highly electro positive. (ii) Covalent or molecular hydrides:-These are the compounds of hydrogen formed with most of the p-block elements [a]Electron deficient:- The hydrides which do not have sufficient number of el ...
... These are the compounds of H2 formed with most of the s-block elements which are highly electro positive. (ii) Covalent or molecular hydrides:-These are the compounds of hydrogen formed with most of the p-block elements [a]Electron deficient:- The hydrides which do not have sufficient number of el ...
Covalent Bonds - WordPress.com
... • A molecule’s shape is usually very important to its function • A molecule’s shape is determined by the positions of its atoms’ valence orbitals • Biological molecules recognize and interact with each other with a specificity based on ...
... • A molecule’s shape is usually very important to its function • A molecule’s shape is determined by the positions of its atoms’ valence orbitals • Biological molecules recognize and interact with each other with a specificity based on ...
Forces I
... Hydrogen Bonds: water Hydrogen bonding is a critical feature of the structure of liquid water. Water molecules are extensively hydrogen bonded to one another, and these strong interactions account for the unusually high boiling point of water compared to other simple liquids and many of the other a ...
... Hydrogen Bonds: water Hydrogen bonding is a critical feature of the structure of liquid water. Water molecules are extensively hydrogen bonded to one another, and these strong interactions account for the unusually high boiling point of water compared to other simple liquids and many of the other a ...
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE 20%-50%
... Special fire fighting procedures: Evacuate all non-essential personnel. Intervention only by capable personnel who are trained and aware of hazards of the product. Wear self-contained breathing apparatus when in close proximity or in confined spaces. When intervention in close proximity, wear acid ...
... Special fire fighting procedures: Evacuate all non-essential personnel. Intervention only by capable personnel who are trained and aware of hazards of the product. Wear self-contained breathing apparatus when in close proximity or in confined spaces. When intervention in close proximity, wear acid ...
Ch. 2-1 Nature of Matter
... Covalent Bonding • Valence electrons are shared by atoms • Sharing electrons means that the moving electrons actually travel in the orbitals of both atoms. ...
... Covalent Bonding • Valence electrons are shared by atoms • Sharing electrons means that the moving electrons actually travel in the orbitals of both atoms. ...
Elementary my dear Watson review
... For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) is made up of 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen. ...
... For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) is made up of 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen. ...
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... charge), protons (positive charge), and electrons (negative charge). Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Ele ...
... charge), protons (positive charge), and electrons (negative charge). Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Ele ...
Chapter 6 Quiz
... the octet rule? a. 1 b. 5 c. 3 d. 8 ______ 6. What group of elements satisfies the octet rule without forming compounds? a. halogen b. alkali metal c. noble gas d. alkaline-earth metal ______ 7. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the hydrogen chloride molecule, HCl. a. tetrahedral b. bent c. l ...
... the octet rule? a. 1 b. 5 c. 3 d. 8 ______ 6. What group of elements satisfies the octet rule without forming compounds? a. halogen b. alkali metal c. noble gas d. alkaline-earth metal ______ 7. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the hydrogen chloride molecule, HCl. a. tetrahedral b. bent c. l ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.