Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Outline I. Molar Mass and
... 20. Sodium metal and water react to form hydrogen and sodium hydroxide. If 5.98 g of sodium react with water to form 0.26 g of hydrogen and 10.40 g of sodium hydroxide, what mass of water was consumed in the reaction? a. 10.66 g b. 4.68 g c. 10.14 g d. 5.98 g 21. What is the chemical formula for str ...
... 20. Sodium metal and water react to form hydrogen and sodium hydroxide. If 5.98 g of sodium react with water to form 0.26 g of hydrogen and 10.40 g of sodium hydroxide, what mass of water was consumed in the reaction? a. 10.66 g b. 4.68 g c. 10.14 g d. 5.98 g 21. What is the chemical formula for str ...
2. Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but must be present fo ...
... catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but must be present fo ...
Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... reaction they catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but ...
... reaction they catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but ...
Preview Sample 1
... D) are always some form of carbohydrate. E) are naturally similar to sugars. 102) Alaska Natives have a lower incidence of heart disease even though their diets are high in fat and cholesterol. This may be due to the large amount of ________ in their diets. A) steroids B) omega-3 fatty acids C) trig ...
... D) are always some form of carbohydrate. E) are naturally similar to sugars. 102) Alaska Natives have a lower incidence of heart disease even though their diets are high in fat and cholesterol. This may be due to the large amount of ________ in their diets. A) steroids B) omega-3 fatty acids C) trig ...
CHAPTER 10 - NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... The ratio of oxygen in these two compounds is 3 to 4. Ionic bonding When chemical bonds are formed, electrons are shared between atoms or they are transferred from one atom to another to create a positive and negative ion. When chemical bonds are formed due to electron transfer, this process is call ...
... The ratio of oxygen in these two compounds is 3 to 4. Ionic bonding When chemical bonds are formed, electrons are shared between atoms or they are transferred from one atom to another to create a positive and negative ion. When chemical bonds are formed due to electron transfer, this process is call ...
Chemistry for Changing Times
... • Arranged in order of increasing atomic mass and by chemical property – Some elements don’t fit where their atomic mass ...
... • Arranged in order of increasing atomic mass and by chemical property – Some elements don’t fit where their atomic mass ...
Dalton`s Laws worksheet
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory of Matter 1. Which of the following statements is part of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter? a. All atoms are identical b. All atoms of a given element are identical c. All atoms differ from one another d. Atoms of the same element can have a different shape 2. Dalton suggested ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory of Matter 1. Which of the following statements is part of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter? a. All atoms are identical b. All atoms of a given element are identical c. All atoms differ from one another d. Atoms of the same element can have a different shape 2. Dalton suggested ...
2nd nine weeks benchmark review homework
... would most improve the validity of an experiment? a- increasing the number of variables b- decreasing the range of the independent variable c- repeating the ...
... would most improve the validity of an experiment? a- increasing the number of variables b- decreasing the range of the independent variable c- repeating the ...
Exam practice answers 5
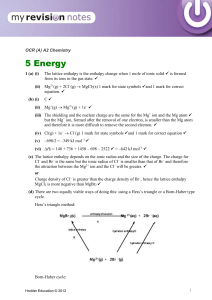
... There are other ways of doing this such as: Both solutions would conduct electricity. If electricity is passed through the MgCl2 a green gas will be evolved at the anode, but with MgBr2 an orange/brown liquid will be produced. If F2(g) is bubbled into either MgCl2 or MgBr2 it will oxidise the halide ...
... There are other ways of doing this such as: Both solutions would conduct electricity. If electricity is passed through the MgCl2 a green gas will be evolved at the anode, but with MgBr2 an orange/brown liquid will be produced. If F2(g) is bubbled into either MgCl2 or MgBr2 it will oxidise the halide ...
Nature of Atoms Atomic Structure
... • During some chemical reactions, electrons can be transferred from one atom to another – Still retain the energy of their position in the atom – Oxidation = loss of an electron – Reduction = gain of an electron (reduced charge) ...
... • During some chemical reactions, electrons can be transferred from one atom to another – Still retain the energy of their position in the atom – Oxidation = loss of an electron – Reduction = gain of an electron (reduced charge) ...
Chemistry: The Basics
... – Discovered by James Chadwick in 1932. – Actual mass = 1.67 x 10-24 grams – No charge ...
... – Discovered by James Chadwick in 1932. – Actual mass = 1.67 x 10-24 grams – No charge ...
FREE Sample Here
... 29) During ionization, water molecules disrupt the ionic bonds of a solute and a mixture of ions is produced. These ions are called A) anions. B) dissociates. C) anti-ions. D) electrolytes. E) cations. ...
... 29) During ionization, water molecules disrupt the ionic bonds of a solute and a mixture of ions is produced. These ions are called A) anions. B) dissociates. C) anti-ions. D) electrolytes. E) cations. ...
Bonding practice lessons 1-3
... The results of these tests suggest that A) both solids contain only ionic bonds B) both solids contain only covalent bonds C) solid A contains only covalent bonds and solid B contains only ionic bonds D) solid A contains only ionic bonds and solid B contains only covalent bonds 22. The bonds between ...
... The results of these tests suggest that A) both solids contain only ionic bonds B) both solids contain only covalent bonds C) solid A contains only covalent bonds and solid B contains only ionic bonds D) solid A contains only ionic bonds and solid B contains only covalent bonds 22. The bonds between ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... The atomic number for O is 8. How many protons in O? How many electrons in O? The atomic mass of O is 16. How many neutrons in O? Draw an Oxygen atom. Show the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and the electrons in the energy ...
... The atomic number for O is 8. How many protons in O? How many electrons in O? The atomic mass of O is 16. How many neutrons in O? Draw an Oxygen atom. Show the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and the electrons in the energy ...
Water, H2O
... If you look at the ice model you might become worried about the stability of the structure, assuming that it is the hydrogen bonds that hold the whole thing together. Only 2 of the 4 possible links can be filled at any one time. You might try to construct a toy of an object with 4 holes and only 2 l ...
... If you look at the ice model you might become worried about the stability of the structure, assuming that it is the hydrogen bonds that hold the whole thing together. Only 2 of the 4 possible links can be filled at any one time. You might try to construct a toy of an object with 4 holes and only 2 l ...
Chemistry-Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Page
... - Transfer of electrons between atoms - Atoms that GAIN electrons have a net negative charge (anion) - Atoms that LOSE electrons have a net positive charge (cation) - Oppositely charged ions are mutually attractive - Common in inorganic molecules ...
... - Transfer of electrons between atoms - Atoms that GAIN electrons have a net negative charge (anion) - Atoms that LOSE electrons have a net positive charge (cation) - Oppositely charged ions are mutually attractive - Common in inorganic molecules ...
unit 2 - chemistry
... corn oil, safflower oil, sunflower oil, cottonseed oil, sesame oil, soybean oil help reduce cholesterol 3.Proteins - C, H, O, N body structure, physiological activities ( catalysts) amino acids – 20 different and are the building blocks - amino group NH2 - carboxyl group COOH - side chain – ...
... corn oil, safflower oil, sunflower oil, cottonseed oil, sesame oil, soybean oil help reduce cholesterol 3.Proteins - C, H, O, N body structure, physiological activities ( catalysts) amino acids – 20 different and are the building blocks - amino group NH2 - carboxyl group COOH - side chain – ...
Nature of Atoms Atomic Structure Atomic number Atomic mass
... Molecules are groups of atoms held together in a stable association Compounds are molecules containing yp of element more than one type Atoms are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds ...
... Molecules are groups of atoms held together in a stable association Compounds are molecules containing yp of element more than one type Atoms are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds ...
Unit 2 - Biochemistry Notes
... Molecule – when two or more atoms bond. CO2 , O2 , H2 and H2O are all molecules. Compound – when different elements combine. CO2 and H2O are molecules, but they are also compounds because they are molecules containing more than one element. ...
... Molecule – when two or more atoms bond. CO2 , O2 , H2 and H2O are all molecules. Compound – when different elements combine. CO2 and H2O are molecules, but they are also compounds because they are molecules containing more than one element. ...
CHAPTER 2 THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2.1 Chemical Elements
... charge. A hydrogen bond is a weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative oxygen or nitrogen atom within the same or a different molecule. Many hydrogen bonds taken together are relatively strong and help maintain the structure and function of cellular molecules ...
... charge. A hydrogen bond is a weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative oxygen or nitrogen atom within the same or a different molecule. Many hydrogen bonds taken together are relatively strong and help maintain the structure and function of cellular molecules ...
chapter 6 sec 2 resonance structure
... Bond energy is the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral isolated atoms. ...
... Bond energy is the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral isolated atoms. ...
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... a. What are the formal charges of Cl, N, and O in each structure? b. Are any of the oxygen atoms equivalent? c. What nitrogen- and oxygen-containing ion is isoelectronic with ClNO2? 22. Which contains a multiple bond in its Lewis structure? a. ICl b. SO2 c. Cl2 d. NH4+ ...
... a. What are the formal charges of Cl, N, and O in each structure? b. Are any of the oxygen atoms equivalent? c. What nitrogen- and oxygen-containing ion is isoelectronic with ClNO2? 22. Which contains a multiple bond in its Lewis structure? a. ICl b. SO2 c. Cl2 d. NH4+ ...
Chem Bonding Notes
... 9. Metallic bonding occurs between atoms of (1) sulfur (3) fluorine (2) copper (4) carbon 10. Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are (1) transferred from one atom to another (2) captured by the nucleus (3) mobile within a metal (4) shared between two atoms ...
... 9. Metallic bonding occurs between atoms of (1) sulfur (3) fluorine (2) copper (4) carbon 10. Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are (1) transferred from one atom to another (2) captured by the nucleus (3) mobile within a metal (4) shared between two atoms ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.