General Chemistry
... represents a large charge density. A hydrogen bond results when this strong positive charge density attracts a lone pair of electrons on another heteroatom, which becomes the hydrogen-bond acceptor. The most ubiquitous, and perhaps simplest, example of a hydrogen bond is found between water molecule ...
... represents a large charge density. A hydrogen bond results when this strong positive charge density attracts a lone pair of electrons on another heteroatom, which becomes the hydrogen-bond acceptor. The most ubiquitous, and perhaps simplest, example of a hydrogen bond is found between water molecule ...
Week 8 - Day 3 (End of Chapter 6)
... Audio 0:38:09.158442 1. Mix at least 2 nonequivalent atomic orbitals (e.g. s and p). Hybrid orbitals have very different shape from original atomic orbitals. 2. Number of hybrid orbitals is equal to number of pure atomic orbitals used in the hybridization process. 3. Covalent bonds are formed by: ...
... Audio 0:38:09.158442 1. Mix at least 2 nonequivalent atomic orbitals (e.g. s and p). Hybrid orbitals have very different shape from original atomic orbitals. 2. Number of hybrid orbitals is equal to number of pure atomic orbitals used in the hybridization process. 3. Covalent bonds are formed by: ...
Damage in hydrogen plasma implanted silicon
... investigated experimentally and theoretically. Our RBS/C results indicate that the damaged layer is quite broad, and different from that observed in single-energy beamline ion implantation in which the damage only occurs near the projected range of the implanted ions. The broadness of the damage zon ...
... investigated experimentally and theoretically. Our RBS/C results indicate that the damaged layer is quite broad, and different from that observed in single-energy beamline ion implantation in which the damage only occurs near the projected range of the implanted ions. The broadness of the damage zon ...
chemistry -- questions -
... __ 23. An atom's atomic number is best described as the number of a) protons it contains. b) neutrons it contains. c) electrons in the outermost shell. d) protons and neutrons it contains. e) protons and electrons it contains. __ 24. An atom's atomic mass is best described as the mass of a) the pro ...
... __ 23. An atom's atomic number is best described as the number of a) protons it contains. b) neutrons it contains. c) electrons in the outermost shell. d) protons and neutrons it contains. e) protons and electrons it contains. __ 24. An atom's atomic mass is best described as the mass of a) the pro ...
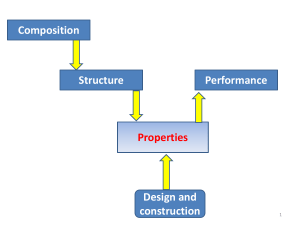
follow up solids
... • Displacement of neighboring planes does not lead to charge effects and therefore malleability and ductility •High conductivity because the valence electrons never remain near any particular atom very long ...
... • Displacement of neighboring planes does not lead to charge effects and therefore malleability and ductility •High conductivity because the valence electrons never remain near any particular atom very long ...
(H) +
... • Contain C and H • Usually larger than inorganic molecules • Dissolve in water and organic liquids • Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Inorganic molecules • Generally do not contain C • Usually smaller than organic molecules • Usually dissociate in water, forming ions • Water, oxyg ...
... • Contain C and H • Usually larger than inorganic molecules • Dissolve in water and organic liquids • Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Inorganic molecules • Generally do not contain C • Usually smaller than organic molecules • Usually dissociate in water, forming ions • Water, oxyg ...
Unit 1 Review, pages 138–145
... 63. (a) Ionic compounds have high melting points because their ions are held tightly together in a repeating pattern by strong electrostatic forces. (b) Ionic compounds are hard because their strong bonds resist being stretched. (c) An ionic compound breaks when struck with a hammer because its latt ...
... 63. (a) Ionic compounds have high melting points because their ions are held tightly together in a repeating pattern by strong electrostatic forces. (b) Ionic compounds are hard because their strong bonds resist being stretched. (c) An ionic compound breaks when struck with a hammer because its latt ...
Isomeric forms of Cu(quinoline-2-carboxylate) O Spectroscopic and magnetic properties H
... The distortion of the CuN2O3 chromophore causes the appearance of an asymmetric band in d-d reflectance spectra, with a maximum at 13 890 cm–1. There is also evidence of a weak, poorly resolved shoulder on the low-frequency side with almost comparable intensity at about 10 200 cm–1, separated by ca. ...
... The distortion of the CuN2O3 chromophore causes the appearance of an asymmetric band in d-d reflectance spectra, with a maximum at 13 890 cm–1. There is also evidence of a weak, poorly resolved shoulder on the low-frequency side with almost comparable intensity at about 10 200 cm–1, separated by ca. ...
Chapters 9 and 10
... c. In the SO2 molecule, both of the bonds between sulfur and oxygen have the same length. Explain this observation, supporting your explanation by drawing a Lewis electron-dot diagram (or diagrams) for the SO2 molecule. d. On the basis of your Lewis electron-dot diagram(s) in part (c), identify the ...
... c. In the SO2 molecule, both of the bonds between sulfur and oxygen have the same length. Explain this observation, supporting your explanation by drawing a Lewis electron-dot diagram (or diagrams) for the SO2 molecule. d. On the basis of your Lewis electron-dot diagram(s) in part (c), identify the ...
CHEMISTRY 103 – Practice Problems #3 Chapters 8 – 10 http
... e. The two atoms found above the plane in a trigonal bipyramidal electron domain geometry are axial atoms. 36. State whether each of the following are True or False. a. The central atom in a trigonal pyramidal molecule has a sp2 hybridization. b. sp2 hybridized atoms will always have a double bond. ...
... e. The two atoms found above the plane in a trigonal bipyramidal electron domain geometry are axial atoms. 36. State whether each of the following are True or False. a. The central atom in a trigonal pyramidal molecule has a sp2 hybridization. b. sp2 hybridized atoms will always have a double bond. ...
Revised crystal structure model of Li2NH by neutron powder diffraction
... facts: (i) the structure has a f cc symmetry with a ∼ 5.07 Å, (ii) one unit cell includes four molecules of Li2 NH. In reality, it is easy to determine that there exist only five space groups that satisfy the two conditions: F 23, F m3̄, F 432, F 4̄3m, and F m3̄m. However, we confirmed that no stru ...
... facts: (i) the structure has a f cc symmetry with a ∼ 5.07 Å, (ii) one unit cell includes four molecules of Li2 NH. In reality, it is easy to determine that there exist only five space groups that satisfy the two conditions: F 23, F m3̄, F 432, F 4̄3m, and F m3̄m. However, we confirmed that no stru ...
Ch9_10notes maroon edition
... atom. We write the symbol of the atom in question, then draw the appropriate number of dots (= # of valence e-). Top, bottom, left right; these are not important, but it is standard to place a single dot on each side before doubling up. Sketch dot symbols for Li, N, Cl, O, B, and He in the space bel ...
... atom. We write the symbol of the atom in question, then draw the appropriate number of dots (= # of valence e-). Top, bottom, left right; these are not important, but it is standard to place a single dot on each side before doubling up. Sketch dot symbols for Li, N, Cl, O, B, and He in the space bel ...
balancing chemical equations worksheet
... 4. finally balance. The following questions relate to these four steps. a. What symbols should we use to describe the physical states? b. Chemists and other scientists always balance chemical equations. Please explain why this is so important. (Hint, refer to the law of conservation of mass) PART B, ...
... 4. finally balance. The following questions relate to these four steps. a. What symbols should we use to describe the physical states? b. Chemists and other scientists always balance chemical equations. Please explain why this is so important. (Hint, refer to the law of conservation of mass) PART B, ...
Dalton Model Reading
... his equipment, resulted in his table being highly flawed. For instance, he believed oxygen atoms were 5.5 times heavier than hydrogen atoms, because in water he measured 5.5 grams of oxygen for every 1 gram of hydrogen and believed the formula for water was HO (an oxygen atom is actually 16 times he ...
... his equipment, resulted in his table being highly flawed. For instance, he believed oxygen atoms were 5.5 times heavier than hydrogen atoms, because in water he measured 5.5 grams of oxygen for every 1 gram of hydrogen and believed the formula for water was HO (an oxygen atom is actually 16 times he ...
Chapter 2 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... are covalent bonds that form a cell’s molecules. • Weak chemical bonds, such as ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds, are also important. • Weak chemical bonds reinforce shapes of large molecules and help molecules adhere to each other. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cumm ...
... are covalent bonds that form a cell’s molecules. • Weak chemical bonds, such as ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds, are also important. • Weak chemical bonds reinforce shapes of large molecules and help molecules adhere to each other. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cumm ...
formation of chemical bonds. -
... Chlorine can gain one electron and c) What is the valency of element X? forms chloride ion (anion) to get octet d) How many covalent bonds are there configuration like Argon. in the molecule? Cl + e- Cle) Suggest a name for the elements These oppositely charged ions get X and Y. together due to el ...
... Chlorine can gain one electron and c) What is the valency of element X? forms chloride ion (anion) to get octet d) How many covalent bonds are there configuration like Argon. in the molecule? Cl + e- Cle) Suggest a name for the elements These oppositely charged ions get X and Y. together due to el ...
2011
... lone pair – lone pair > bond pair – bond pair > lone pair – bond pair B) lone pair – lone pair > lone pair – bond pair > bond pair – bond pair C) bond pair – bond pair > lone pair – bond pair > lone pair – lone pair D) bond pair – bond pair > lone pair – lone pair > lone pair – bond pair ...
... lone pair – lone pair > bond pair – bond pair > lone pair – bond pair B) lone pair – lone pair > lone pair – bond pair > bond pair – bond pair C) bond pair – bond pair > lone pair – bond pair > lone pair – lone pair D) bond pair – bond pair > lone pair – lone pair > lone pair – bond pair ...
Bonding
... The species represented above all have the same number of chlorine atoms attached to the central atom. b.On the basis of the Lewis structures drawn in part (a), answer the following questions about the particular species indicated. i. What is the Cl-Ge-Cl bond angle in GeCl4? ii.Is SeCl4 polar? Expl ...
... The species represented above all have the same number of chlorine atoms attached to the central atom. b.On the basis of the Lewis structures drawn in part (a), answer the following questions about the particular species indicated. i. What is the Cl-Ge-Cl bond angle in GeCl4? ii.Is SeCl4 polar? Expl ...
Chemical Bonding
... Draw valence molecular orbital diagrams (i.e. omitting inner shell orbitals) for the following homonuclear diatomic species, H2!, He2+, O2, N2!, C22!, Ne2+, (Na2, Mg2, P2, you can assume that third period diatomics form valence molecular orbitals similar to second period diatomics but with n=3) and ...
... Draw valence molecular orbital diagrams (i.e. omitting inner shell orbitals) for the following homonuclear diatomic species, H2!, He2+, O2, N2!, C22!, Ne2+, (Na2, Mg2, P2, you can assume that third period diatomics form valence molecular orbitals similar to second period diatomics but with n=3) and ...
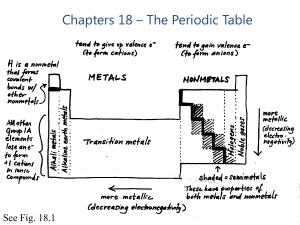
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... 3. Sulfur trioxide (SO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). SO3, formed from SO2 over V2O5 catalysts, is then converted to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is the cheapest strong acid and is so widely used in industry that its production level is an indicator of a nation’s economic strength. Strong dehydrating ...
... 3. Sulfur trioxide (SO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). SO3, formed from SO2 over V2O5 catalysts, is then converted to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is the cheapest strong acid and is so widely used in industry that its production level is an indicator of a nation’s economic strength. Strong dehydrating ...
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... traditional unit, the debye (D, 1 D = 3.34 x 10–30 C·m), is often used. Depending on the spatial arrangement of the bonds, a molecule containing highly polar bonds can be nonpolar … the vector addition of the dipole moments yields a net dipole moment of zero for the overall molecule. Bond order is t ...
... traditional unit, the debye (D, 1 D = 3.34 x 10–30 C·m), is often used. Depending on the spatial arrangement of the bonds, a molecule containing highly polar bonds can be nonpolar … the vector addition of the dipole moments yields a net dipole moment of zero for the overall molecule. Bond order is t ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... substances can combine during a chemical reaction to produce new substances. The substances that undergo change are called reactants. The new substances are products. Sometimes during a chemical reaction, one type of reactant will be used up before the other reactants. This reactant is the limiting ...
... substances can combine during a chemical reaction to produce new substances. The substances that undergo change are called reactants. The new substances are products. Sometimes during a chemical reaction, one type of reactant will be used up before the other reactants. This reactant is the limiting ...
EXAMPLE
... Ionic Bond bond formed between oppositely charged ions. This happens when the stronger atom steals 1+ electrons from the weaker atom. They both have their outer shells filled, so all is good. ...
... Ionic Bond bond formed between oppositely charged ions. This happens when the stronger atom steals 1+ electrons from the weaker atom. They both have their outer shells filled, so all is good. ...
bond
... like the one shown in the preceding illustration (corresponding to resonance of the two Kekulé structures), the -electrons form double donut-shaped clouds, one above and one below the plane of the ring. ...
... like the one shown in the preceding illustration (corresponding to resonance of the two Kekulé structures), the -electrons form double donut-shaped clouds, one above and one below the plane of the ring. ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.