Chapter 7 Photosynthesis
... (oxidation-reduction) process. – CO2 becomes reduced to sugar as electrons along with hydrogen ions from water are added to it. – Water molecules are oxidized when they lose electrons along with hydrogen ions. ...
... (oxidation-reduction) process. – CO2 becomes reduced to sugar as electrons along with hydrogen ions from water are added to it. – Water molecules are oxidized when they lose electrons along with hydrogen ions. ...
File
... Valence electrons (found in the valence shell) usually determine how an atom will react Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is full Atoms can gain or lose electrons to become stable ...
... Valence electrons (found in the valence shell) usually determine how an atom will react Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is full Atoms can gain or lose electrons to become stable ...
Chemical Reactions
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Principles of Ecology
... Analyze current farming practices that are designed to make the best use of energy flow in ecosystems and cycles of matter. Accept all reasonable responses. Fertilizers replace nitrogen, phosphorus, and other minerals that are lost from the soil when vegetable matter is harvested and removed. Pestic ...
... Analyze current farming practices that are designed to make the best use of energy flow in ecosystems and cycles of matter. Accept all reasonable responses. Fertilizers replace nitrogen, phosphorus, and other minerals that are lost from the soil when vegetable matter is harvested and removed. Pestic ...
Atoms and Molecules - Gulfport School District
... •Chemical Reactions- water is required for chemical reactions to take place. •Transport- soluble substances can be transported through the body when dissolved. Chapter 2 – The Body’s Chemical Makeup ...
... •Chemical Reactions- water is required for chemical reactions to take place. •Transport- soluble substances can be transported through the body when dissolved. Chapter 2 – The Body’s Chemical Makeup ...
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
... Step 3: Multiply the half-reactions by integers that will allow for cancellation of electrons. Step 4: Combine half-reactions, and simplify by combining and canceling duplicated species. Step 5 (Only if the solution is under basic conditions): Add enough OH- (to both sides) to neutralize any H+ ions ...
... Step 3: Multiply the half-reactions by integers that will allow for cancellation of electrons. Step 4: Combine half-reactions, and simplify by combining and canceling duplicated species. Step 5 (Only if the solution is under basic conditions): Add enough OH- (to both sides) to neutralize any H+ ions ...
Re-typed from The Ultimate Chemical Equations Handbook by
... of water molecules needs to be adjusted. 5. If there is an odd number of an element on one side and an even number on the other, the odd number will need to be evened out – so use a coefficient of 2 for that substance. 6. If there are polyatomic ions that remain together as a unit during the reactio ...
... of water molecules needs to be adjusted. 5. If there is an odd number of an element on one side and an even number on the other, the odd number will need to be evened out – so use a coefficient of 2 for that substance. 6. If there are polyatomic ions that remain together as a unit during the reactio ...
Extra Unit 3 Problems for the Web Site (Honors
... How many grams of ammonia will be required to react with 80. g of O2? 4. In the commercial preparation of hydrogen chloride gas, what mass of HCl in grams may be obtained by heating 234 g of NaCl with excess H2SO4? The balanced equation for the reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + 2HCl 5. A chemi ...
... How many grams of ammonia will be required to react with 80. g of O2? 4. In the commercial preparation of hydrogen chloride gas, what mass of HCl in grams may be obtained by heating 234 g of NaCl with excess H2SO4? The balanced equation for the reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + 2HCl 5. A chemi ...
Chapter 8
... oxygen, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of light and heat. Reactive elements combine with oxygen ...
... oxygen, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of light and heat. Reactive elements combine with oxygen ...
Take notes on this document while you are watching the recorded
... 1. The lipids are a large and diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are related by their solubility (will dissolve) in nonpolar5 organic solvents (e.g. ether, chloroform, acetone & benzene) and general insolubility in water (do not dissolve in water - repel water; hydrophobic). ...
... 1. The lipids are a large and diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are related by their solubility (will dissolve) in nonpolar5 organic solvents (e.g. ether, chloroform, acetone & benzene) and general insolubility in water (do not dissolve in water - repel water; hydrophobic). ...
Year 11 Chemistry Balancing Equations
... Looking over your electron configurations, are there any elements above that have similar valence electron configurations to those of other elements? If so, list below the elements that are similar (in terms of valence electrons) and state the similarity for each of the groups. ...
... Looking over your electron configurations, are there any elements above that have similar valence electron configurations to those of other elements? If so, list below the elements that are similar (in terms of valence electrons) and state the similarity for each of the groups. ...
1.2 PowerPoint
... You must wear safety glasses for this lab. Please, be very careful with the chemicals. You may work in groups of three. ...
... You must wear safety glasses for this lab. Please, be very careful with the chemicals. You may work in groups of three. ...
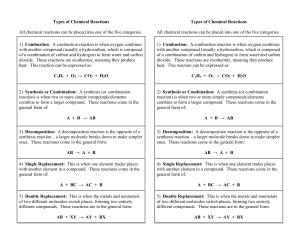
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
Chem MCQ for Class-9th
... c. Do not change from left to right in a period d. Decrease from top to bottom in a group 2. The amount of energy given out when an electron is added to an atom is called: a. Lattice entery b. ionization entergy c. electronegativity d. electron affinity 3. Mendeleev Periodic Table was based upon the ...
... c. Do not change from left to right in a period d. Decrease from top to bottom in a group 2. The amount of energy given out when an electron is added to an atom is called: a. Lattice entery b. ionization entergy c. electronegativity d. electron affinity 3. Mendeleev Periodic Table was based upon the ...
ChemFinalgeocities
... If 9.0 g of water contain 1.0 g of hydrogen, what mass of oxygen is contained in 36 g of water? a. 4.0 g c. 10.0 g b. 8.0 g d. 32 g Which of the following statements is not a main point of Dalton's atomic theory? a. All matter is made up of atoms. b. Atoms are made up of smaller particles. c. Atoms ...
... If 9.0 g of water contain 1.0 g of hydrogen, what mass of oxygen is contained in 36 g of water? a. 4.0 g c. 10.0 g b. 8.0 g d. 32 g Which of the following statements is not a main point of Dalton's atomic theory? a. All matter is made up of atoms. b. Atoms are made up of smaller particles. c. Atoms ...
Part II Biochemistry
... these compounds can be expressed as hydrates of carbon. • Glucose, for example, has the molecular formula C6H12O6, which might be written as C6(H2O)6. • Carbohydrates are now defined as: ...
... these compounds can be expressed as hydrates of carbon. • Glucose, for example, has the molecular formula C6H12O6, which might be written as C6(H2O)6. • Carbohydrates are now defined as: ...
I PUC Chemistry Mock Paper
... 24. a) Give the laboratory method of preparation of dihydrogen. Write the equation.[2+1] b) Give one difference between hard water and soft water. 25. Give any three anomalous properties of Boron. 26. Write the chemical reaction that takes place during the manufacture of sodium hydroxide by Castner- ...
... 24. a) Give the laboratory method of preparation of dihydrogen. Write the equation.[2+1] b) Give one difference between hard water and soft water. 25. Give any three anomalous properties of Boron. 26. Write the chemical reaction that takes place during the manufacture of sodium hydroxide by Castner- ...
2.3 Photosynthesis
... if candidate answers in terms of comparing rate of change then the rate of change of photosynthesis must be in the correct direction for 1 mark any two from: ...
... if candidate answers in terms of comparing rate of change then the rate of change of photosynthesis must be in the correct direction for 1 mark any two from: ...
1.2 Properties and Changes of Matter
... You must wear safety glasses for this lab. Please, be very careful with the chemicals. You may work in groups of three. ...
... You must wear safety glasses for this lab. Please, be very careful with the chemicals. You may work in groups of three. ...
C4C5C6
... • don’t conduct electricity when solid • When melted or dissolved - conduct electricity – ions free to move. ...
... • don’t conduct electricity when solid • When melted or dissolved - conduct electricity – ions free to move. ...
C2 Knowledge PowerPoint
... • Delocalised electrons in metals enable electricity and heat to pass through the metal easily • Alloys are made from two or more different metals. The different sized atoms of the metals distort the layers in the structure, making it more difficult for them to slide over each other, and so make the ...
... • Delocalised electrons in metals enable electricity and heat to pass through the metal easily • Alloys are made from two or more different metals. The different sized atoms of the metals distort the layers in the structure, making it more difficult for them to slide over each other, and so make the ...
Document
... • Delocalised electrons in metals enable electricity and heat to pass through the metal easily • Alloys are made from two or more different metals. The different sized atoms of the metals distort the layers in the structure, making it more difficult for them to slide over each other, and so make the ...
... • Delocalised electrons in metals enable electricity and heat to pass through the metal easily • Alloys are made from two or more different metals. The different sized atoms of the metals distort the layers in the structure, making it more difficult for them to slide over each other, and so make the ...
Artificial photosynthesis

Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into Hydrogen Ions and oxygen, and is a main research area in artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another studied process, replicating natural carbon fixation.Research developed in this field encompasses design and assembly of devices (and their components) for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Many, if not most, of the artificial approaches are bio-inspired, i.e., they rely on biomimetics.