Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in H SO ? A)
... In any oxidation-reduction reaction, the total number of electrons gained is A) greater than the total number of electrons lost B) equal to the total number of electrons lost ...
... In any oxidation-reduction reaction, the total number of electrons gained is A) greater than the total number of electrons lost B) equal to the total number of electrons lost ...
Name - Deans Community High School
... b) Is the forward reaction is exothermic or endothermic. ............................................ 1 c) Gold and platinum both catalyse the reaction. For the forward reaction EA using gold is 30 kJ, while EA using platinum is 40 kJ. i) using different dotted lines add this information to the grap ...
... b) Is the forward reaction is exothermic or endothermic. ............................................ 1 c) Gold and platinum both catalyse the reaction. For the forward reaction EA using gold is 30 kJ, while EA using platinum is 40 kJ. i) using different dotted lines add this information to the grap ...
ch8 - Otterville R-VI School District
... organize reactants and products Be sure to include symbols showing states of each reactant and product Be sure to write the correct formula ...
... organize reactants and products Be sure to include symbols showing states of each reactant and product Be sure to write the correct formula ...
SNC2D EXAM REVIEW Lab Safety Unit 1 - Chemistry
... Physical Property: a description of a substance that does not involve forming a new substance (color, density, smell) Chemical property: a description of what a substance does as it changes into one or more new substances (ex: burning) Physical Change: a change in a substances state without creati ...
... Physical Property: a description of a substance that does not involve forming a new substance (color, density, smell) Chemical property: a description of what a substance does as it changes into one or more new substances (ex: burning) Physical Change: a change in a substances state without creati ...
Lecture Notes
... The melting point of a substance is that temperature at a given pressure at which a substance changes from the solid state to the liquid state. For pure water themelting point is 32oF or 0oC. The Freezing point of a substance is the same as the melting point, since the process of freezing is the opp ...
... The melting point of a substance is that temperature at a given pressure at which a substance changes from the solid state to the liquid state. For pure water themelting point is 32oF or 0oC. The Freezing point of a substance is the same as the melting point, since the process of freezing is the opp ...
9.1 Electron Transfer Reactions
... 5. O is usually – 2 (except for peroxides where it is – 1) 6. H is usually +1 (except for hydrides where it is – 1) 7. The periodic table can used as a guide for an atom’s oxidation number in a compound (ex: F is usually – 1, alkali metals are usually +1) ...
... 5. O is usually – 2 (except for peroxides where it is – 1) 6. H is usually +1 (except for hydrides where it is – 1) 7. The periodic table can used as a guide for an atom’s oxidation number in a compound (ex: F is usually – 1, alkali metals are usually +1) ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... • We would choose the production of O2(g) and Cu(s). • But the voltage for producing O2(g) from solution is considerably higher than the standard potential, because of the high activation energy needed to form O2(g). • The voltage for this half cell seems to be closer to –1.5 V in reality. • The ...
... • We would choose the production of O2(g) and Cu(s). • But the voltage for producing O2(g) from solution is considerably higher than the standard potential, because of the high activation energy needed to form O2(g). • The voltage for this half cell seems to be closer to –1.5 V in reality. • The ...
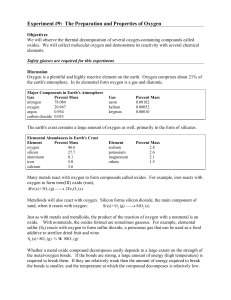
Experiment # 9 Properties of Oxygen
... with a thistle tube. The reaction will take place in the generator bottle and then the oxygen gas will move through the tubing into the collecting trough where the collection bottles will be. 1. Partly fill the collecting trough with water, making sure that the shelf is covered with water. 2. Fill t ...
... with a thistle tube. The reaction will take place in the generator bottle and then the oxygen gas will move through the tubing into the collecting trough where the collection bottles will be. 1. Partly fill the collecting trough with water, making sure that the shelf is covered with water. 2. Fill t ...
Chapter 3
... one of them first. This reactant limits how much can be made. Analogy: Putting together a bicycle – parts on hand are 200 frames and 350 wheels. How many bicycles can you make? Ex) 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O Suppose a vessel contained 10 molecules of H2 and 7 ...
... one of them first. This reactant limits how much can be made. Analogy: Putting together a bicycle – parts on hand are 200 frames and 350 wheels. How many bicycles can you make? Ex) 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O Suppose a vessel contained 10 molecules of H2 and 7 ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Proton
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
File
... Prefixes are used to tell how many atoms are of each type are in the molecule (prefixes can be found on the back of the periodic table) * mono is used only for the 2nd element * Eg. CO2 = carbon dioxide, CCl4 = carbon tetrachloride Some molecular compounds do not follow simple naming rules – M ...
... Prefixes are used to tell how many atoms are of each type are in the molecule (prefixes can be found on the back of the periodic table) * mono is used only for the 2nd element * Eg. CO2 = carbon dioxide, CCl4 = carbon tetrachloride Some molecular compounds do not follow simple naming rules – M ...
Balancing RedOx reactions handout
... 3. Write a half reaction for the reduction process (addition of electrons…electrons added to the left side). 4. Write a half reaction for the oxidation process (loss of electrons…electrons added to the right side). 5. If the atoms being oxidized and reduced are not already balanced, balance them and ...
... 3. Write a half reaction for the reduction process (addition of electrons…electrons added to the left side). 4. Write a half reaction for the oxidation process (loss of electrons…electrons added to the right side). 5. If the atoms being oxidized and reduced are not already balanced, balance them and ...
Chemistry Notes
... You can see that on the left is the Sodium part and the right has the Oxygen/Hydrogen part. The bond which binds the Hydrogen to the Oxygen is covalent. The Sodium is bonded to the HYDROXIDE part of the compound with an ionic bond. This is a very good example of how there can be different types of b ...
... You can see that on the left is the Sodium part and the right has the Oxygen/Hydrogen part. The bond which binds the Hydrogen to the Oxygen is covalent. The Sodium is bonded to the HYDROXIDE part of the compound with an ionic bond. This is a very good example of how there can be different types of b ...
Test Booklet
... 22 Using the solubility graph provided, a student performs an experiment to find the solubility of a substance. The student finds the amount of substance needed to make a saturated solution in 100 g of water at different temperatures. The student’s data are shown in the table below the graph. ...
... 22 Using the solubility graph provided, a student performs an experiment to find the solubility of a substance. The student finds the amount of substance needed to make a saturated solution in 100 g of water at different temperatures. The student’s data are shown in the table below the graph. ...
Step 2
... structures built from a few hundred atoms and are 1100nm big. They show different properties to the same materials in bulk. They also have a large surface area to volume ratio and their properties could lead to new developments in computers, building materials etc. ...
... structures built from a few hundred atoms and are 1100nm big. They show different properties to the same materials in bulk. They also have a large surface area to volume ratio and their properties could lead to new developments in computers, building materials etc. ...
Step 2 - The Grange School Blogs
... structures built from a few hundred atoms and are 1100nm big. They show different properties to the same materials in bulk. They also have a large surface area to volume ratio and their properties could lead to new developments in computers, building materials etc. ...
... structures built from a few hundred atoms and are 1100nm big. They show different properties to the same materials in bulk. They also have a large surface area to volume ratio and their properties could lead to new developments in computers, building materials etc. ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl It loses its 1 valence electron leaving 2 below it 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 3 (a triple) 99. Ionic ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl It loses its 1 valence electron leaving 2 below it 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 3 (a triple) 99. Ionic ...
How to Make a Collage
... competent with using scientific notation in the above mathematical applications. Utilize the internet to help you find ways to improve your skills. If you do not practice these skills you lose the ability to perform them quickly, confidently and competently. Flash cards will help you throughout this ...
... competent with using scientific notation in the above mathematical applications. Utilize the internet to help you find ways to improve your skills. If you do not practice these skills you lose the ability to perform them quickly, confidently and competently. Flash cards will help you throughout this ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons,
... now has a charge. For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a ...
... now has a charge. For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a ...
Unit 7 Packet
... 5. Combustion (combines with oxygen; most or all products contain oxygen; releases energy to environment) CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O + energy (burning natural gas) C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + energy ...
... 5. Combustion (combines with oxygen; most or all products contain oxygen; releases energy to environment) CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O + energy (burning natural gas) C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + energy ...
Document
... 0.786 mol carbon dioxide to grams 2.67 g lithium carbonate to mol 1.000 atom of C12 to grams ...
... 0.786 mol carbon dioxide to grams 2.67 g lithium carbonate to mol 1.000 atom of C12 to grams ...
200 Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... foods such as bread, beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, cookies, spaghetti, corn, and cherry pie. In this activity, you will: - learn to interpret the molecular and structural formulas of some carbohydrates. - construct molecular models of some carbohydrates. - learn about the various functions carbohy ...
... foods such as bread, beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, cookies, spaghetti, corn, and cherry pie. In this activity, you will: - learn to interpret the molecular and structural formulas of some carbohydrates. - construct molecular models of some carbohydrates. - learn about the various functions carbohy ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
200things2know
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
Artificial photosynthesis

Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into Hydrogen Ions and oxygen, and is a main research area in artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another studied process, replicating natural carbon fixation.Research developed in this field encompasses design and assembly of devices (and their components) for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Many, if not most, of the artificial approaches are bio-inspired, i.e., they rely on biomimetics.