Group 2 - UC Davis Canvas
... 11. The bond energy of the noble gas fluorine is too small to offset the energy required to break the F—F bond. 13. Iodide ion is slowly oxidized to iodine, which is yellow-brown in aqueous solution, by oxygen in the air: 4 I − ( aq ) + O 2 ( g ) + 4 H + ( aq ) → 2 I 2 ( aq ) + 2 H 2 O(l) . 15. D ...
... 11. The bond energy of the noble gas fluorine is too small to offset the energy required to break the F—F bond. 13. Iodide ion is slowly oxidized to iodine, which is yellow-brown in aqueous solution, by oxygen in the air: 4 I − ( aq ) + O 2 ( g ) + 4 H + ( aq ) → 2 I 2 ( aq ) + 2 H 2 O(l) . 15. D ...
Complete the following equations
... (Nitrogen, oxygen and argon. Gases are extracted by fractional distillation of liquefied air. Extracting oxygen from seawater involves distillation of the water (to remove salts) and electrolysis. These processes are energy intensive) ...
... (Nitrogen, oxygen and argon. Gases are extracted by fractional distillation of liquefied air. Extracting oxygen from seawater involves distillation of the water (to remove salts) and electrolysis. These processes are energy intensive) ...
IGCSE Revision Guide (Double Award) | PDF
... Define an atom as the particle of which all matter is composed and which cannot be broken down chemically. Define a molecule as a particle that consists of two or more atoms joined together. ...
... Define an atom as the particle of which all matter is composed and which cannot be broken down chemically. Define a molecule as a particle that consists of two or more atoms joined together. ...
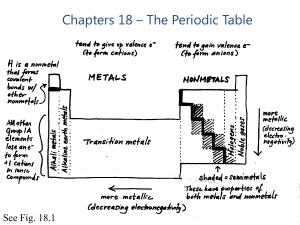
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... 3. Sulfur trioxide (SO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). SO3, formed from SO2 over V2O5 catalysts, is then converted to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is the cheapest strong acid and is so widely used in industry that its production level is an indicator of a nation’s economic strength. Strong dehydrating ...
... 3. Sulfur trioxide (SO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). SO3, formed from SO2 over V2O5 catalysts, is then converted to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is the cheapest strong acid and is so widely used in industry that its production level is an indicator of a nation’s economic strength. Strong dehydrating ...
2018 Specimen Paper 2 - Cambridge International Examinations
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Chemical Equations
... The reactants that enter into a reaction The products that are formed by the reaction The relative amounts of each substance used and ...
... The reactants that enter into a reaction The products that are formed by the reaction The relative amounts of each substance used and ...
1 Lecture 11. Redox Chemistry Many elements in the periodic table
... sequence, organic matter is combusted in order by O2, NO3, MnO2, Fe2O3 then SO42- to provide this energy. Most of these reactions have slow kinetics if left to occur on their own. Bacteria mediate most of these reactions and get the energy for their life processes. Because the energy of the sun is t ...
... sequence, organic matter is combusted in order by O2, NO3, MnO2, Fe2O3 then SO42- to provide this energy. Most of these reactions have slow kinetics if left to occur on their own. Bacteria mediate most of these reactions and get the energy for their life processes. Because the energy of the sun is t ...
An element`s properties depend on the structure of its atoms
... • There is a rift between biology and chemistry text books. • The biology book often speaks of “weak bonds” when they really mean intermolecular forces (forces of electrostatic attraction “between molecules”) which are not at all the same as sharing a pair of electrons within a molecule • IMFs are i ...
... • There is a rift between biology and chemistry text books. • The biology book often speaks of “weak bonds” when they really mean intermolecular forces (forces of electrostatic attraction “between molecules”) which are not at all the same as sharing a pair of electrons within a molecule • IMFs are i ...
CHEM102 Chemistry II Spring 10-11 Mid
... C) One mole of methane reacts with two moles of oxygen to produce one mole of carbon dioxide and 2 moles of water. D) A, B and C are correct. E) A and C are correct. 45) A reaction that is spontaneous can be described as 45) E A) having the same rate in both the forward and reverse directions. B) re ...
... C) One mole of methane reacts with two moles of oxygen to produce one mole of carbon dioxide and 2 moles of water. D) A, B and C are correct. E) A and C are correct. 45) A reaction that is spontaneous can be described as 45) E A) having the same rate in both the forward and reverse directions. B) re ...
Practice Exam-Final Fall 2016 W-Ans
... 16. How many hydrogen atoms are there in 48.0 g of CH4? (a) 1.81x1023 (b) 7.22x1024 (c) 6.02x1023 (d) 1.20x1025 (e) 4.70x1025 Hint: According to the chemical formula, one mole of CH4 contains 1 mole of C atoms and 4 moles of hydrogen atoms. Thus, the mole of H = 4 x {mass of CH4/molar mass of CH4}. ...
... 16. How many hydrogen atoms are there in 48.0 g of CH4? (a) 1.81x1023 (b) 7.22x1024 (c) 6.02x1023 (d) 1.20x1025 (e) 4.70x1025 Hint: According to the chemical formula, one mole of CH4 contains 1 mole of C atoms and 4 moles of hydrogen atoms. Thus, the mole of H = 4 x {mass of CH4/molar mass of CH4}. ...
Net Ionic Equations
... Determining Oxidation Number of Elements & Molecules 1. In uncombined or free elements (not ionized), each atom has an oxidation number of 0. E.g., all of the atoms in these molecules: H2, Na, S8, O2, P4. 2. In simple ions (i.e., charged species which contain only one atom), the oxidation number is ...
... Determining Oxidation Number of Elements & Molecules 1. In uncombined or free elements (not ionized), each atom has an oxidation number of 0. E.g., all of the atoms in these molecules: H2, Na, S8, O2, P4. 2. In simple ions (i.e., charged species which contain only one atom), the oxidation number is ...
Balancing reaction equations, oxidation state, and reduction
... Determining Oxidation Number of Elements & Molecules 1. In uncombined or free elements (not ionized), each atom has an oxidation number of 0. E.g., all of the atoms in these molecules: H2, Na, S8, O2, P4. 2. In simple ions (i.e., charged species which contain only one atom), the oxidation number is ...
... Determining Oxidation Number of Elements & Molecules 1. In uncombined or free elements (not ionized), each atom has an oxidation number of 0. E.g., all of the atoms in these molecules: H2, Na, S8, O2, P4. 2. In simple ions (i.e., charged species which contain only one atom), the oxidation number is ...
Name: 1) At 1 atmosphere and 298 K, 1 mole of H O(l) molecules
... Using your knowledge of chemistry and the information in the Vapor Pressure of Four Liquids chemistry reference table, which statement concerning propanone and water at 50DC is true? A) Propanone has a lower vapor pressure and weaker intermolecular forces than water. B) Propanone has a lower vapor p ...
... Using your knowledge of chemistry and the information in the Vapor Pressure of Four Liquids chemistry reference table, which statement concerning propanone and water at 50DC is true? A) Propanone has a lower vapor pressure and weaker intermolecular forces than water. B) Propanone has a lower vapor p ...
2007 - SolPass
... Property of the Virginia Department of Education ©2007 by the Commonwealth of Virginia, Department of Education, P.O. Box 2120, Richmond, Virginia 23218-2120. All rights reserved. Except as permitted by law, this material may not be reproduced or used in any form or by any means, electronic or mecha ...
... Property of the Virginia Department of Education ©2007 by the Commonwealth of Virginia, Department of Education, P.O. Box 2120, Richmond, Virginia 23218-2120. All rights reserved. Except as permitted by law, this material may not be reproduced or used in any form or by any means, electronic or mecha ...
Review 1
... a liquid. Have the alcohol molecules been changed by the process? Explain your answer. Solution The alcohol is reversibly changed from a liquid to a solid and back again. It is the same material regardless of state. Changes in phase are physical changes. ...
... a liquid. Have the alcohol molecules been changed by the process? Explain your answer. Solution The alcohol is reversibly changed from a liquid to a solid and back again. It is the same material regardless of state. Changes in phase are physical changes. ...
What are the general types of reactions?
... – Mass is not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction – For practical purposes • Same types of atoms before and after a reaction • Same number of each type of atom before and after ...
... – Mass is not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction – For practical purposes • Same types of atoms before and after a reaction • Same number of each type of atom before and after ...
Direct production of hydrogen peroxide from CO, O2, and H2O over
... Table 1 shows the catalytic results for H2O2 production from CO/O2/H2O over several types of metal nanoparticles dispersed on alumina prepared by the wet reduction (WR) method, which has recently been shown to be an effective method for the preparation of various amorphous alloy catalysts for versati ...
... Table 1 shows the catalytic results for H2O2 production from CO/O2/H2O over several types of metal nanoparticles dispersed on alumina prepared by the wet reduction (WR) method, which has recently been shown to be an effective method for the preparation of various amorphous alloy catalysts for versati ...
4.1Atoms and Isotopes
... Positive charge (+1) Mass 1 atomic mass unit (a.m.u.) If an atom gains or loses one or more protons, it becomes an atom of a different element E.g. If N lost a proton, it would become C (losing or gaining a proton takes a massive amount of energy – can really only occur in the laboratory if the prop ...
... Positive charge (+1) Mass 1 atomic mass unit (a.m.u.) If an atom gains or loses one or more protons, it becomes an atom of a different element E.g. If N lost a proton, it would become C (losing or gaining a proton takes a massive amount of energy – can really only occur in the laboratory if the prop ...
Chap 9 Redox Review Q`s
... Which processes occur during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? I. Sodium and chloride ions move through the electrolyte. II. Electrons move through the external circuit. III. Oxidation takes place at the positive electrode (anode). ...
... Which processes occur during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? I. Sodium and chloride ions move through the electrolyte. II. Electrons move through the external circuit. III. Oxidation takes place at the positive electrode (anode). ...
AP Chemistry Name: Ch.2 – The Nuclear Atom Date: Period:
... It is useful to determine how much of a compound’s mass is made up of each element. Water, H2O, for example has a molar mass of 18.02 g. The H’s mass is 2(1.0079) = 2.02 g. The O’s mass is 16.00 g. We can set up fractions for each element: ...
... It is useful to determine how much of a compound’s mass is made up of each element. Water, H2O, for example has a molar mass of 18.02 g. The H’s mass is 2(1.0079) = 2.02 g. The O’s mass is 16.00 g. We can set up fractions for each element: ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules d. 4 3. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of all 12. In nonpolar covalent bonds, valence electrons are atoms are shared in ...
... d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules d. 4 3. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of all 12. In nonpolar covalent bonds, valence electrons are atoms are shared in ...
Key concepts of chemistry from high school chemistry
... termed isotopes. Isotopes of an element have very similar properties since they differ only in the number of neutral-‐charged particles. A carbon with 6 neutrons behaves very much the same as a ...
... termed isotopes. Isotopes of an element have very similar properties since they differ only in the number of neutral-‐charged particles. A carbon with 6 neutrons behaves very much the same as a ...
Structure of Molecules and Compounds | Principles of Biology from
... chemical reaction. The reactants in a cake may include flour, sugar, butter, and eggs. In a chemical reaction, the ingredients are elements or compounds. The reactants combine during the chemical reaction to form the product. In the cake analogy, the product is the cake. In a chemical reaction, the ...
... chemical reaction. The reactants in a cake may include flour, sugar, butter, and eggs. In a chemical reaction, the ingredients are elements or compounds. The reactants combine during the chemical reaction to form the product. In the cake analogy, the product is the cake. In a chemical reaction, the ...
Document
... – No chemical bonding between components – Can be separated by physical means, such as straining or filtering – Heterogeneous or homogeneous ...
... – No chemical bonding between components – Can be separated by physical means, such as straining or filtering – Heterogeneous or homogeneous ...
Artificial photosynthesis

Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into Hydrogen Ions and oxygen, and is a main research area in artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another studied process, replicating natural carbon fixation.Research developed in this field encompasses design and assembly of devices (and their components) for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Many, if not most, of the artificial approaches are bio-inspired, i.e., they rely on biomimetics.