ch15-Atmospheric Chemistry
... Free radicals are highly chemically reactive because of the strong pairing tendency of their unpaired electrons – Undergo series of chain reactions generating more free radicals – Chain termination such as H3C• + H3C• C2H6 ...
... Free radicals are highly chemically reactive because of the strong pairing tendency of their unpaired electrons – Undergo series of chain reactions generating more free radicals – Chain termination such as H3C• + H3C• C2H6 ...
Surface chemistry and Catalysis
... Incoming species lands on an active site and forms bonds with the catalyst. It may use some of the bonding electrons in the molecules thus weakening them and making a subsequent reaction easier. Reaction (STEPS 2 and 3) Adsorbed gases may be held on the surface in just the right orientation for a re ...
... Incoming species lands on an active site and forms bonds with the catalyst. It may use some of the bonding electrons in the molecules thus weakening them and making a subsequent reaction easier. Reaction (STEPS 2 and 3) Adsorbed gases may be held on the surface in just the right orientation for a re ...
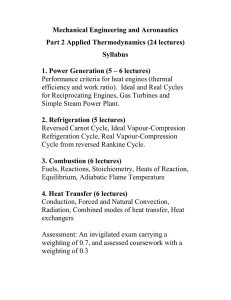
Mechanical Engineering and Aeronautics
... Any material that can be burned to release heat and energy is called a fuel. Fuels can exist in gaseous form, liquid form, or solid form. Most familiar fuels consist primarily of hydrogen and carbon. They are called hydrocarbon fuels, and are denoted by the formula CnHm. Hydrocarbon fuels are classi ...
... Any material that can be burned to release heat and energy is called a fuel. Fuels can exist in gaseous form, liquid form, or solid form. Most familiar fuels consist primarily of hydrogen and carbon. They are called hydrocarbon fuels, and are denoted by the formula CnHm. Hydrocarbon fuels are classi ...
Unique Solutions
... a ripening of fruit b ice changes to water c milk is set into curd d rusting of iron Hydrogen combines with chlorine to form hydrogen chloride. Which of the following is a correct balanced equation for the above reaction ? ...
... a ripening of fruit b ice changes to water c milk is set into curd d rusting of iron Hydrogen combines with chlorine to form hydrogen chloride. Which of the following is a correct balanced equation for the above reaction ? ...
1. dia
... Main source: combustion of fossile fuels Sulfur content of coal and crude oil differs. ...
... Main source: combustion of fossile fuels Sulfur content of coal and crude oil differs. ...
File
... Which of the following best describes the variation of the electronegativity of the elements with respect to their position on the periodic table? a. Increases across a period; increases down a group. b. Increases across a period; decreases down a group. c. Decreases across a period; increases down ...
... Which of the following best describes the variation of the electronegativity of the elements with respect to their position on the periodic table? a. Increases across a period; increases down a group. b. Increases across a period; decreases down a group. c. Decreases across a period; increases down ...
Unit 1: Sig. Figs, Compounds, Elements, Homo/Hetero mixtures
... d. solutions. e. compounds. 2. Which group of substances contains only elements? a. hydrogen, plastics, carbon b. salt, copper, aluminum c. gold, silver, limestone d. steel, carbon, oxygen e. calcium, carbon, helium 3. Carbon dioxide, water (H2O), and nitrous oxide are best characterized as a. atoms ...
... d. solutions. e. compounds. 2. Which group of substances contains only elements? a. hydrogen, plastics, carbon b. salt, copper, aluminum c. gold, silver, limestone d. steel, carbon, oxygen e. calcium, carbon, helium 3. Carbon dioxide, water (H2O), and nitrous oxide are best characterized as a. atoms ...
2 C2H6 (g)
... A. 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) + heat B. NH3 (g) + HCl (g) NH4Cl (s) + heat C. AgCl (s) + heat Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) D. 2 Fe2O3 (s) + 3 C (s) + heat 4 Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g) E. C (graphite) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + heat F. CH4 (g) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O (l) + heat Question 27 of 28 Based on their de ...
... A. 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) + heat B. NH3 (g) + HCl (g) NH4Cl (s) + heat C. AgCl (s) + heat Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) D. 2 Fe2O3 (s) + 3 C (s) + heat 4 Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g) E. C (graphite) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + heat F. CH4 (g) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O (l) + heat Question 27 of 28 Based on their de ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... 8 Which type of bonding is present in a sample of an element that is malleable? (1) ionic (3) nonpolar covalent (2) metallic (4) polar covalent 9 Which atom has the greatest attraction for the electrons in a chemical bond? (1) hydrogen (3) silicon (2) oxygen (4) sulfur ...
... 8 Which type of bonding is present in a sample of an element that is malleable? (1) ionic (3) nonpolar covalent (2) metallic (4) polar covalent 9 Which atom has the greatest attraction for the electrons in a chemical bond? (1) hydrogen (3) silicon (2) oxygen (4) sulfur ...
(cobalamin)-dependent enzymes
... coenzyme and carbon. One form, methylcobalamin (MeCbl), is involved in methylation reactions in which the methyl group is transferred to and from cobalt. The other form, adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), serves as a source of carbon-based free radicals that are ‘unmasked’ by homolysis of the bond between ...
... coenzyme and carbon. One form, methylcobalamin (MeCbl), is involved in methylation reactions in which the methyl group is transferred to and from cobalt. The other form, adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), serves as a source of carbon-based free radicals that are ‘unmasked’ by homolysis of the bond between ...
RxnTypesPrednotesIIAP
... written as H-OH. In an acid-base neutralization reaction, the acid is the source of the hydrogen ion while the base is the source of the hydroxide ion in the formation of the water molecule. In the synthesis reaction of an acid anhydride with a basic anhydride, only a salt is formed because the two ...
... written as H-OH. In an acid-base neutralization reaction, the acid is the source of the hydrogen ion while the base is the source of the hydroxide ion in the formation of the water molecule. In the synthesis reaction of an acid anhydride with a basic anhydride, only a salt is formed because the two ...
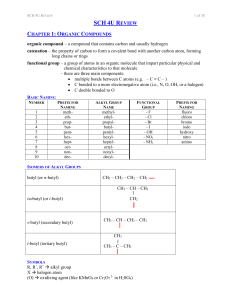
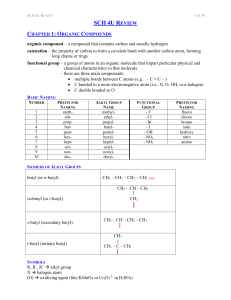
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
H - Deans Community High School
... The method mentioning all the equipment used and measurements made, readings and variable kept constant/changed etc 7. A table (with headings) of your measurements, and a sample average and rate = 1/t calculation) and your line graph. 8. Your conclusion (what you found out – must mention results and ...
... The method mentioning all the equipment used and measurements made, readings and variable kept constant/changed etc 7. A table (with headings) of your measurements, and a sample average and rate = 1/t calculation) and your line graph. 8. Your conclusion (what you found out – must mention results and ...
Dr David`s Chemistry Revision Themes
... 6. How does the 1st ionisation energy of elements in a group vary as the group is descended? Explain. The 1st ionisation energy of elements in a group decreases as the group is descended. This is because the atoms are increasing in size (increasing atomic radius) as the shielding effect balances the ...
... 6. How does the 1st ionisation energy of elements in a group vary as the group is descended? Explain. The 1st ionisation energy of elements in a group decreases as the group is descended. This is because the atoms are increasing in size (increasing atomic radius) as the shielding effect balances the ...
Water - UFMG
... The molecules of the biologically important gases CO2, O2, and N2 are nonpolar. In O2 and N2, electrons are shared equally by both atoms. In CO2, each CUO bond is polar, but the two dipoles are oppositely directed and cancel each other (Table 4–3). The movement of molecules from the disordered gas p ...
... The molecules of the biologically important gases CO2, O2, and N2 are nonpolar. In O2 and N2, electrons are shared equally by both atoms. In CO2, each CUO bond is polar, but the two dipoles are oppositely directed and cancel each other (Table 4–3). The movement of molecules from the disordered gas p ...
Aqueous Reactions
... Aqueous reactions are reactions that take place in water. To understand them, it is important to understand how compounds behave in water. Some compounds are electrolytes- they dissociate into separate ions in water. However, not all electrolytes behave the same way. Some are strong electrolytes, an ...
... Aqueous reactions are reactions that take place in water. To understand them, it is important to understand how compounds behave in water. Some compounds are electrolytes- they dissociate into separate ions in water. However, not all electrolytes behave the same way. Some are strong electrolytes, an ...
Spring 2013 Semester Exam Study Guide (Bonding, Nomenclature
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
File
... All metals (on the left side of the periodic table) form cations and nonmetals (on the left side of the periodic table) form anions primarily. In order to determine the formula of the compound they create you must make sure their ions sum to zero. For example, table salt is sodium chloride. Using th ...
... All metals (on the left side of the periodic table) form cations and nonmetals (on the left side of the periodic table) form anions primarily. In order to determine the formula of the compound they create you must make sure their ions sum to zero. For example, table salt is sodium chloride. Using th ...
2012 C13 Exam answers
... 32 Which statement about catalysts is incorrect? 28 A cylinder of unknown volume contains helium gas, He(g), at 3.50 atm and 315 K. The helium gas is then transferred to a 7.0 L gas cylinder containing Ne(g), at 2.50 atm and 315 K. If the final total pressure at 315 K is 5.75 atm, then what is the v ...
... 32 Which statement about catalysts is incorrect? 28 A cylinder of unknown volume contains helium gas, He(g), at 3.50 atm and 315 K. The helium gas is then transferred to a 7.0 L gas cylinder containing Ne(g), at 2.50 atm and 315 K. If the final total pressure at 315 K is 5.75 atm, then what is the v ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 Elements of Chemical Change
... substance is its molecular weight expressed in grams. Thus, a GMW of NaOH would be 40 grams, where the atomic weights are as follows: Na = 23, O = 16, and H = 1. Thus, .5 GMW of NaOH would be 20 grams, and so forth. A mole is one-gram molecular weight of a substance. Thus, a mole of NaOH is 40 grams ...
... substance is its molecular weight expressed in grams. Thus, a GMW of NaOH would be 40 grams, where the atomic weights are as follows: Na = 23, O = 16, and H = 1. Thus, .5 GMW of NaOH would be 20 grams, and so forth. A mole is one-gram molecular weight of a substance. Thus, a mole of NaOH is 40 grams ...
+ H 2 O
... Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes Electrolytes- compounds that conduct an electric current in aqueous solution, or in the molten state – all ionic compounds are electrolytes because they dissociate into ions (they are also called “salts”) barium sulfate- will conduct when molten, but is insoluble ...
... Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes Electrolytes- compounds that conduct an electric current in aqueous solution, or in the molten state – all ionic compounds are electrolytes because they dissociate into ions (they are also called “salts”) barium sulfate- will conduct when molten, but is insoluble ...
Instructor`s Guide - Ventura Educational Systems
... Lesson 4: Making Molecules 1… Getting Started Teacher Sheet Background Atoms are nature’s building blocks, but we very seldom see atoms by themselves in nature. More often than not, atoms bond with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. Covalent Molecules, like ...
... Lesson 4: Making Molecules 1… Getting Started Teacher Sheet Background Atoms are nature’s building blocks, but we very seldom see atoms by themselves in nature. More often than not, atoms bond with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. Covalent Molecules, like ...
12 U Chem Review
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
5H2O → CuSO4 + 5H2O(g)
... Most reactions in general chemistry take place in an aqueous environment. What does that mean? Terms: ◦ Solution: homogeneous mixture of two or more substances ◦ Solute: substance present in smaller amount ◦ Solvent: substance present in greater amount ◦ Aqueous solution: solvent is water ...
... Most reactions in general chemistry take place in an aqueous environment. What does that mean? Terms: ◦ Solution: homogeneous mixture of two or more substances ◦ Solute: substance present in smaller amount ◦ Solvent: substance present in greater amount ◦ Aqueous solution: solvent is water ...
Artificial photosynthesis

Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into Hydrogen Ions and oxygen, and is a main research area in artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another studied process, replicating natural carbon fixation.Research developed in this field encompasses design and assembly of devices (and their components) for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Many, if not most, of the artificial approaches are bio-inspired, i.e., they rely on biomimetics.