Aortic Stenosis Fact Sheet
... from experiencing the expected benefit from fixing their aortic stenosis. This procedure enables the placement of a balloon-expandable heart valve into the body with a tubebased delivery system (catheter). The valve is designed to replace a patient’s diseased native aortic valve without traditional ...
... from experiencing the expected benefit from fixing their aortic stenosis. This procedure enables the placement of a balloon-expandable heart valve into the body with a tubebased delivery system (catheter). The valve is designed to replace a patient’s diseased native aortic valve without traditional ...
Anaesthetic management of a patient with severe aortic stenosis for
... Asymptomatic women with mild obstruction and normal LV systolic function before conception will tolerate pregnancy well and can be managed conservatively, while those with symptoms and severe AS (Aortic valve area <1 cm2, mean gradient t>40 mmHg)4 are at higher risk. The major maternal concern in th ...
... Asymptomatic women with mild obstruction and normal LV systolic function before conception will tolerate pregnancy well and can be managed conservatively, while those with symptoms and severe AS (Aortic valve area <1 cm2, mean gradient t>40 mmHg)4 are at higher risk. The major maternal concern in th ...
cardiovascular history hpi
... - Radio-Radial delay ( = vascular disease en route to brachial arteries ) - Radiofemoral Delay (Co-arctation or stenosis of Aorta) The heart rate increases with inspiration and decreases with expiration ...
... - Radio-Radial delay ( = vascular disease en route to brachial arteries ) - Radiofemoral Delay (Co-arctation or stenosis of Aorta) The heart rate increases with inspiration and decreases with expiration ...
Persistent Native Aortic Valve Function
... diograms showed that the native leaflets were displaced against the aortic wall; however, there was persistent opening and closing of the native left and posterior coronary cusps (Fig. 3). In systole, the native aortic valve commissure had an opening of 0.63 cm 2 as measured by planimetry. There was ...
... diograms showed that the native leaflets were displaced against the aortic wall; however, there was persistent opening and closing of the native left and posterior coronary cusps (Fig. 3). In systole, the native aortic valve commissure had an opening of 0.63 cm 2 as measured by planimetry. There was ...
Current Surgical Cardiac Procedures
... • AVR is the most common valve operation • Most performed to treat aortic stenosis – Affects from 2% - 7% of people > 65 yrs. Of age in the US – On-pump AVR has low risk with marked benefits with mortality <1% at larger, experienced centers – Less invasive techniques needed for higher risk pts. Such ...
... • AVR is the most common valve operation • Most performed to treat aortic stenosis – Affects from 2% - 7% of people > 65 yrs. Of age in the US – On-pump AVR has low risk with marked benefits with mortality <1% at larger, experienced centers – Less invasive techniques needed for higher risk pts. Such ...
Print This Information
... enough to let blood flow through (stenosis) or cannot close well enough to prevent backflow of the blood (regurgitation). Heart valve disease can affect any of the four valves in different ways, including a combination of stenosis and regurgitation. These diseases include: ...
... enough to let blood flow through (stenosis) or cannot close well enough to prevent backflow of the blood (regurgitation). Heart valve disease can affect any of the four valves in different ways, including a combination of stenosis and regurgitation. These diseases include: ...
Aortic Stenosis Client Handout PESC
... WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? Blood is pumped from the left ventricle to a particularly large blood vessel called the ‘aorta’. (The aorta is the body’s largest artery.) The valve that separates the left ventricle from the aorta is called the ‘aortic valve’. The left ventricle narrows as it leads to the a ...
... WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? Blood is pumped from the left ventricle to a particularly large blood vessel called the ‘aorta’. (The aorta is the body’s largest artery.) The valve that separates the left ventricle from the aorta is called the ‘aortic valve’. The left ventricle narrows as it leads to the a ...
Aortic Stenosis Explained - New - CardioRespiratory Pet Referrals
... WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? Blood is pumped from the left ventricle to a particularly large blood vessel called the ‘aorta’. (The aorta is the body’s largest artery.) The valve that separates the left ventricle from the aorta is called the ‘aortic valve’. The left ventricle narrows as it leads to the a ...
... WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? Blood is pumped from the left ventricle to a particularly large blood vessel called the ‘aorta’. (The aorta is the body’s largest artery.) The valve that separates the left ventricle from the aorta is called the ‘aortic valve’. The left ventricle narrows as it leads to the a ...
Diagnosis of valvular diseases
... Global burden of valvular heart disease • Primary valvular heart disease ranks below coronary heart disease, stroke, hypertension, obesity, and diabetes as major threats to the public health. • Rheumatic fever is the dominant cause of valvular heart disease in developing countries. Prevalence and m ...
... Global burden of valvular heart disease • Primary valvular heart disease ranks below coronary heart disease, stroke, hypertension, obesity, and diabetes as major threats to the public health. • Rheumatic fever is the dominant cause of valvular heart disease in developing countries. Prevalence and m ...
valvular heart disease - New Cardiovascular Horizons
... A pressure gradient develops between the left ventricle and the aorta. (increased afterload) ...
... A pressure gradient develops between the left ventricle and the aorta. (increased afterload) ...
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
... Physical Findings in Aortic Stenosis • Slow rising carotid pulse (pulsus tardus) & decreased pulse amplitude (pulsus parvus) • Heart sounds- soft and split second heart sound, S4 gallop due to LVH. • Systolic ejection murmur- cresendodecrescendo character. This peaks later as the severity of the st ...
... Physical Findings in Aortic Stenosis • Slow rising carotid pulse (pulsus tardus) & decreased pulse amplitude (pulsus parvus) • Heart sounds- soft and split second heart sound, S4 gallop due to LVH. • Systolic ejection murmur- cresendodecrescendo character. This peaks later as the severity of the st ...
Familial Subvalvular Aortic Stenosis in Rottweilers
... • Commonly reported congenital heart disease • Characterized by aortic subvalvular ridge • Most common in large breed dogs • Familial link demonstrated in Newfoundlands & golden retrievers ...
... • Commonly reported congenital heart disease • Characterized by aortic subvalvular ridge • Most common in large breed dogs • Familial link demonstrated in Newfoundlands & golden retrievers ...
Cardiovascular System 1 - University of Manitoba
... Heart chamber with thicker wall Provides information about electrical activity of heart (abbr) Nervous system controller of heart rate (abbr) Too rapid ventricular contraction Heart sound marking closure of aortic and pulmonary valves Pouch-like atrial appendage Drugs that breakup blood clots ...
... Heart chamber with thicker wall Provides information about electrical activity of heart (abbr) Nervous system controller of heart rate (abbr) Too rapid ventricular contraction Heart sound marking closure of aortic and pulmonary valves Pouch-like atrial appendage Drugs that breakup blood clots ...
The time between S1 and S2
... aortic valves don't both occur at the same millisecond. Both valves closing make up the S2. When you breathe in, the pressure in your thorax decreases - the diaphragm creates a little vacuum. This decreased pressure means less force is placed on the pulmonic valve to close (remember that the pulmoni ...
... aortic valves don't both occur at the same millisecond. Both valves closing make up the S2. When you breathe in, the pressure in your thorax decreases - the diaphragm creates a little vacuum. This decreased pressure means less force is placed on the pulmonic valve to close (remember that the pulmoni ...
Slide ()
... Schematic of cardiac morphogenesis. Oblique views of whole embryo and frontal views of cardiac precursors during human cardiac development are shown. Day 15: First heart field cells form a crescent shape in the anterior embryo with second heart field cells medial to the first heart field. Day 21: Se ...
... Schematic of cardiac morphogenesis. Oblique views of whole embryo and frontal views of cardiac precursors during human cardiac development are shown. Day 15: First heart field cells form a crescent shape in the anterior embryo with second heart field cells medial to the first heart field. Day 21: Se ...
Aortic Stenosis and Hypertension
... subjected to two additive loads: a valvular load and an arterial load. On the other hand, it is well known that the assessment of patients with AS includes the measurement of transvalvular pressure gradient and aortic valve area, as well as assessment of left ventricular geometry and function. Accor ...
... subjected to two additive loads: a valvular load and an arterial load. On the other hand, it is well known that the assessment of patients with AS includes the measurement of transvalvular pressure gradient and aortic valve area, as well as assessment of left ventricular geometry and function. Accor ...
echocardiography in chd
... suspected heart failure to be offered the appropriate investigations (e.G. Electrocardiography, echocardiography) that will confirm or refute the diagnosis. For those in whom heart failure is confirmed, its cause should be identified. The treatments most likely to both relieve symptoms and reduc ...
... suspected heart failure to be offered the appropriate investigations (e.G. Electrocardiography, echocardiography) that will confirm or refute the diagnosis. For those in whom heart failure is confirmed, its cause should be identified. The treatments most likely to both relieve symptoms and reduc ...
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEART
... S2: Aortic and pulmonic valves (semilunar) closing Loudest at base (top of heart is base) Usually splits with inspiration this is audible only in pulmonic area Combines sounds of closing Aortic (A2) and Pulmonic (P2) valves Aortic is louder; can distinguish Pulmonic (P2) at LUSB - its area Pulmonic ...
... S2: Aortic and pulmonic valves (semilunar) closing Loudest at base (top of heart is base) Usually splits with inspiration this is audible only in pulmonic area Combines sounds of closing Aortic (A2) and Pulmonic (P2) valves Aortic is louder; can distinguish Pulmonic (P2) at LUSB - its area Pulmonic ...
Management
... “ A 72 year old lady presents with a history of increasing SOB, orthoponea and palpitations over a few months. She has a history of Angina, Hypertension. She is found to be in Atrial fibrillation” ...
... “ A 72 year old lady presents with a history of increasing SOB, orthoponea and palpitations over a few months. She has a history of Angina, Hypertension. She is found to be in Atrial fibrillation” ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
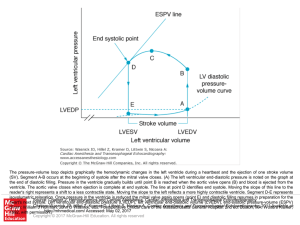
... The pressure-volume loop depicts graphically the hemodynamic changes in the left ventricle during a heartbeat and the ejection of one stroke volume (SV). Segment A-B occurs at the beginning of systole after the mitral valve closes. (A) The left ventricular end-diastolic pressure is noted on the grap ...
... The pressure-volume loop depicts graphically the hemodynamic changes in the left ventricle during a heartbeat and the ejection of one stroke volume (SV). Segment A-B occurs at the beginning of systole after the mitral valve closes. (A) The left ventricular end-diastolic pressure is noted on the grap ...
Grade 0/6 denotes no murmur. Grade 1/6 and 2/6 murmurs are
... This hereditary heart defect may be mild and not affect the quality or longevity of the dog's life, or it may be severe and result in symptoms, such as exercise intolerance and syncope (fainting). It is also one of the causes of sudden death. Symptoms can occur [a] as a direct result of the defect o ...
... This hereditary heart defect may be mild and not affect the quality or longevity of the dog's life, or it may be severe and result in symptoms, such as exercise intolerance and syncope (fainting). It is also one of the causes of sudden death. Symptoms can occur [a] as a direct result of the defect o ...
How I manage a patient with aortic valve stenosis scheduled
... • AS is the most frequent and the most serious valvular disease in Europe countries • AS is an independent risk factor for MACE and mortality in noncardiac surgery • Both preoperative strategy and anaesthetic management are challenging • The decision making process should be ...
... • AS is the most frequent and the most serious valvular disease in Europe countries • AS is an independent risk factor for MACE and mortality in noncardiac surgery • Both preoperative strategy and anaesthetic management are challenging • The decision making process should be ...
Causes of Left-Sided Heart Enlargement
... enlarged. The disease usually progresses to include eccentric hypertrophy of both the atrium and ventricle, resulting in obvious enlargement of both chambers. ...
... enlarged. The disease usually progresses to include eccentric hypertrophy of both the atrium and ventricle, resulting in obvious enlargement of both chambers. ...
Abstract - Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions
... and had congestive heart failure with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III or IV symptoms. They were deemed inoperable by cardiac surgeons because surgical aortic valve replacement would be associated with a predicted probability of ≥50% of death within 30 days after surgery or development of ...
... and had congestive heart failure with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III or IV symptoms. They were deemed inoperable by cardiac surgeons because surgical aortic valve replacement would be associated with a predicted probability of ≥50% of death within 30 days after surgery or development of ...
Icd 10 severe aortic stenosis
... stenosis? Aortic valve stenosis is a narrowing of the aortic valve. The aortic valve allows blood to flow from the heart's lower left chamber. Complete review of aortic stenosis symptoms, causes, dangers and surgical treatment options for patients and caregivers. Short description: Mitral/aortic val ...
... stenosis? Aortic valve stenosis is a narrowing of the aortic valve. The aortic valve allows blood to flow from the heart's lower left chamber. Complete review of aortic stenosis symptoms, causes, dangers and surgical treatment options for patients and caregivers. Short description: Mitral/aortic val ...
Aortic stenosis

Aortic stenosis (AS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occurs due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercise. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially with lying down, at night, and with exercise as well as swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis.Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve and rheumatic fever. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population while rheumatic heart disease mostly occurring in the developing world. A normal valve, however, may also harden over the decades. Risk factors are similar to those of coronary artery disease and include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and being male. The aortic valve usually has three leaflets and is located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta. AS typically results in a heart murmur. Its severity can be divided into mild, moderate, severe, and very severe based on ultrasound of the heart findings.Aortic stenosis is typically followed using repeated ultrasounds. Once it has become severe treatment primarily involves valve replacement surgery with transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) being an option in some who are at high risk from surgery. Valves may either be mechanical or bioprosthetic with each having risks and benefits. Another less invasive procedure, balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) may result in benefit but this is for only for a few months. Complications like heart failure may be treated as per normal in those with mild to moderate AS. In those with severe disease a number of medications should be avoided including ACE inhibitors, nitroglycerin, and some beta blockers. Nitroprusside or phenylephrine may be used in those with decompensated heart failure depending on the blood pressure.Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease in the developed world. It affects about 2% of people who are over 65 years of age. Estimated rates are not known in most of the developing world as of 2014. In those who have symptoms, without repair, the chance of death at five years is about 50% and at 10 years is about 90%. Aortic stenosis was first described by French physician Lazare Rivière in 1663.