Aortic Regurgitation - Cormedicalgroup.com
... symptoms begin to appear. The most common symptoms are: fatigue, shortness of breath, especially when doing exercise or vigorous activities, and swelling of the feet and ankles (edema). Some patients develop angina pectoris, which is chest pain that occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enou ...
... symptoms begin to appear. The most common symptoms are: fatigue, shortness of breath, especially when doing exercise or vigorous activities, and swelling of the feet and ankles (edema). Some patients develop angina pectoris, which is chest pain that occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enou ...
CVS EXAM
... S1: Mitral & tricuspid closure, beginning of ventricular systole S2: Aortic & Pulmonary closure: end of systole/beginning of diastole Normal Splitting: A2 then P2 (lower pressure in pulm system) Increased by inspiration ( VR to right side) Increased normal splitting: (wider on inspiration) Delayed ...
... S1: Mitral & tricuspid closure, beginning of ventricular systole S2: Aortic & Pulmonary closure: end of systole/beginning of diastole Normal Splitting: A2 then P2 (lower pressure in pulm system) Increased by inspiration ( VR to right side) Increased normal splitting: (wider on inspiration) Delayed ...
File - Prepared Rescuer, LLC
... Parasternal Long Axis Generally the first view obtained in a routine transthoracic echocardiogram. It is the standard view for making M-mode and 2D measurements of the left ventricle, estimate size & contractility of the right and left ventricle (septum and posterior wall), and to assess morphology ...
... Parasternal Long Axis Generally the first view obtained in a routine transthoracic echocardiogram. It is the standard view for making M-mode and 2D measurements of the left ventricle, estimate size & contractility of the right and left ventricle (septum and posterior wall), and to assess morphology ...
142e926d30b7e6bb1fc54138a557531e
... diuretics), is usually low in the elderly C ✘ Secondary hypertension is most commonly detected in young subjects with resistant hypertension D ✔The risk of heart failure can be reduced by 30–40% E ✘ The risk of stroke is reduced by ~33% and MI by 25% 1.10 A ✘ Persistent, symptomatic second or third ...
... diuretics), is usually low in the elderly C ✘ Secondary hypertension is most commonly detected in young subjects with resistant hypertension D ✔The risk of heart failure can be reduced by 30–40% E ✘ The risk of stroke is reduced by ~33% and MI by 25% 1.10 A ✘ Persistent, symptomatic second or third ...
aorticStenosisPregnancy
... Murmur appreciated and echo performed: on 9/15 showing AS <.6cm2, probable bicuspid valve and EF 65%. Pt followed for change in symptoms…. Mid Oct. at about 35 wks. Gestation she complains of increased CP and SOB especially with exertion but also at rest. .1%-1.4% pregnancies with clinically signifi ...
... Murmur appreciated and echo performed: on 9/15 showing AS <.6cm2, probable bicuspid valve and EF 65%. Pt followed for change in symptoms…. Mid Oct. at about 35 wks. Gestation she complains of increased CP and SOB especially with exertion but also at rest. .1%-1.4% pregnancies with clinically signifi ...
Transcatheter Heart Valves
... Iliofemoral vessel would preclude safe placement of 22F or 24F introduction sheath such as severe obstruction calcification, severe tortuosity or vessel size less than 7mm in diameter (applicable for transfemoral introduction) ...
... Iliofemoral vessel would preclude safe placement of 22F or 24F introduction sheath such as severe obstruction calcification, severe tortuosity or vessel size less than 7mm in diameter (applicable for transfemoral introduction) ...
Bolest na hrudi nebo v zádech
... right basal anterior segment close to the heart. Heart of aortic shape, dilated to the left. Aorta is sclerotic, aortic arch is markedly enlarged, Transthoracic echocardiography: Left ventricular diameter 50 mm (norma 21-43), right ventricular diameter 33 mm (norma 9 -31), left atrium 34 mm (norma 2 ...
... right basal anterior segment close to the heart. Heart of aortic shape, dilated to the left. Aorta is sclerotic, aortic arch is markedly enlarged, Transthoracic echocardiography: Left ventricular diameter 50 mm (norma 21-43), right ventricular diameter 33 mm (norma 9 -31), left atrium 34 mm (norma 2 ...
Valvular heart disease and cardiac murmurx
... TTE- LV systolic function, LV dimension, leaflet number and morphology, etiology of AR TEE- more accurate for aortic dissection then TTE ...
... TTE- LV systolic function, LV dimension, leaflet number and morphology, etiology of AR TEE- more accurate for aortic dissection then TTE ...
Heart and Vessels - Montgomery County Schools
... ●Your heart is a double pump. Circulation is a double circuit: Pulmonary (lungs only) and systemic (rest of the body) ●Heart has 4 chambers: o 2 Atria – thin upper chambers that receive blood returning to the heart through veins.. Right and Left Atrium o 2 Ventricles – thick, muscular lower chambers ...
... ●Your heart is a double pump. Circulation is a double circuit: Pulmonary (lungs only) and systemic (rest of the body) ●Heart has 4 chambers: o 2 Atria – thin upper chambers that receive blood returning to the heart through veins.. Right and Left Atrium o 2 Ventricles – thick, muscular lower chambers ...
Cardiovascular 22 – Heart Valve Disease
... Exercise induced angina (heart pain) dyspnoea (breathlessness) and syncope (fainting) Carotid pulse is slow rising. Obvious apex heart beat due to LV hypertrophy. Systolic murmur <> Ejection click of bicuspid valve. INVESTIGATIONS Chest X-Ray – shows small heart with prominent dilated de ...
... Exercise induced angina (heart pain) dyspnoea (breathlessness) and syncope (fainting) Carotid pulse is slow rising. Obvious apex heart beat due to LV hypertrophy. Systolic murmur <> Ejection click of bicuspid valve. INVESTIGATIONS Chest X-Ray – shows small heart with prominent dilated de ...
high yield - Wayne State University
... Height of LI R wave + depth of LIII S wave >25mm, + for LVH Mitral valve prolapse Mitral stenosis Tender nodules in palms/soles, suggestive of infectious endocarditis Microvascular polyangitis Exaggerated decrease of SBP during inspiration (>10mm), seen in pericarditis/tamponade Pulse is weak and la ...
... Height of LI R wave + depth of LIII S wave >25mm, + for LVH Mitral valve prolapse Mitral stenosis Tender nodules in palms/soles, suggestive of infectious endocarditis Microvascular polyangitis Exaggerated decrease of SBP during inspiration (>10mm), seen in pericarditis/tamponade Pulse is weak and la ...
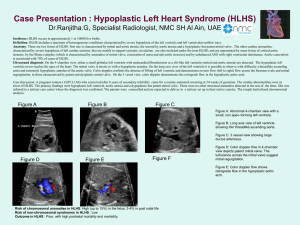
A case of hypoplastic left heart syndrome
... Case discussion: A pregnant women ( G2P1L1A0) who conceived after 8 years of secondary infertility came for a routine antenatal screening at 24 weeks of gestation. The cardiac abnormalities were in favor of HLHS. The primary findings were hypoplastic left ventricle, aortic atresia and a hypoplastic ...
... Case discussion: A pregnant women ( G2P1L1A0) who conceived after 8 years of secondary infertility came for a routine antenatal screening at 24 weeks of gestation. The cardiac abnormalities were in favor of HLHS. The primary findings were hypoplastic left ventricle, aortic atresia and a hypoplastic ...
study guide 13
... 12. Which way do veins carry blood? 13. Which way do arteries carry blood? 14. Name the 2 large veins associated which the atrium. 15. What is the purpose of the tricuspid valve? 16. What is the purpose of the pulmonary valve? 17. What is the purpose of the bicuspid valve? 18. What is the purpose of ...
... 12. Which way do veins carry blood? 13. Which way do arteries carry blood? 14. Name the 2 large veins associated which the atrium. 15. What is the purpose of the tricuspid valve? 16. What is the purpose of the pulmonary valve? 17. What is the purpose of the bicuspid valve? 18. What is the purpose of ...
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEART
... • Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What is his right atrial pressure? Why might he be short of breath? ...
... • Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What is his right atrial pressure? Why might he be short of breath? ...
Impact of Aortic Valve Design, component materials and
... 4. Charlson E et Decision-making and outcomes in severe symptomatic aortic stenosis al.. J Heart Valve Dis2006;15:312-321 ...
... 4. Charlson E et Decision-making and outcomes in severe symptomatic aortic stenosis al.. J Heart Valve Dis2006;15:312-321 ...
Abstract_Azamat_Dec_2015_Serbia_PL
... in-hospital mortality, bypass time and morbidity in all patients undergoing open heart surgery at our Center using a combination of port access and direct vision. Methods: Between January 2013 and September 2015 164 patients (69% female) underwent open heart surgery using above-mentioned technique. ...
... in-hospital mortality, bypass time and morbidity in all patients undergoing open heart surgery at our Center using a combination of port access and direct vision. Methods: Between January 2013 and September 2015 164 patients (69% female) underwent open heart surgery using above-mentioned technique. ...
Pulmonary valve stenosis
... Valve transplant at 53 and then a heart transplant, he later died of heart infection at age ...
... Valve transplant at 53 and then a heart transplant, he later died of heart infection at age ...
Week 10 Activity INUR3306
... overload of the left atrium and the left ventricle. The increased pressures in the left side of the heart may inhibit drainage of blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins and lead to pulmonary ...
... overload of the left atrium and the left ventricle. The increased pressures in the left side of the heart may inhibit drainage of blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins and lead to pulmonary ...
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your
... Aortic or RSB: right 2nd intercostal space (just under and right of angle of Louis) Pulmonic or LUSB: left second intercostal space, just left of sternum Tricuspid or LLSB: left fourth intercostal space Mitral or Apex: 5th intercostal space in midclavicular line Optional: left 3rd intercostal space ...
... Aortic or RSB: right 2nd intercostal space (just under and right of angle of Louis) Pulmonic or LUSB: left second intercostal space, just left of sternum Tricuspid or LLSB: left fourth intercostal space Mitral or Apex: 5th intercostal space in midclavicular line Optional: left 3rd intercostal space ...
S 2
... young adults. A loud S3 is abnormal and is audible in large shunt VSD, congestive heart failure. Fourth heart sound (S4): The S4 is a lowfrequency of late diastole and is rare in infants and children. It is always pathologic. It is seen in conditions with decreased ...
... young adults. A loud S3 is abnormal and is audible in large shunt VSD, congestive heart failure. Fourth heart sound (S4): The S4 is a lowfrequency of late diastole and is rare in infants and children. It is always pathologic. It is seen in conditions with decreased ...
Mitral Systolic Anterior Motion (SAM) with Dynamic Left Ventricular
... but leaflets did not “touch” the interventricular septum nor cause a subaortic gradient (Fig. 2). However, because of the sigmoid septum and “redundant” chords, a myectomy was performed at the time of AVR. Histological evaluation of the myectomy specimen revealed myocardial hypertrophy, but myocyte ...
... but leaflets did not “touch” the interventricular septum nor cause a subaortic gradient (Fig. 2). However, because of the sigmoid septum and “redundant” chords, a myectomy was performed at the time of AVR. Histological evaluation of the myectomy specimen revealed myocardial hypertrophy, but myocyte ...
David Duncan, M.D. Chief of Cardiothoracic surgery :36 Walking
... candidates for doing surgery 3:02 – and if you look at the STS data based for 20112012, there was a little less than 100,000 aortic valves done in the United States 3:09 and it turns out that there’s about another 30,000-40,000 folks who’ve not had their aortic valve treated appropriately or by reco ...
... candidates for doing surgery 3:02 – and if you look at the STS data based for 20112012, there was a little less than 100,000 aortic valves done in the United States 3:09 and it turns out that there’s about another 30,000-40,000 folks who’ve not had their aortic valve treated appropriately or by reco ...
Aortic stenosis

Aortic stenosis (AS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occurs due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercise. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially with lying down, at night, and with exercise as well as swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis.Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve and rheumatic fever. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population while rheumatic heart disease mostly occurring in the developing world. A normal valve, however, may also harden over the decades. Risk factors are similar to those of coronary artery disease and include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and being male. The aortic valve usually has three leaflets and is located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta. AS typically results in a heart murmur. Its severity can be divided into mild, moderate, severe, and very severe based on ultrasound of the heart findings.Aortic stenosis is typically followed using repeated ultrasounds. Once it has become severe treatment primarily involves valve replacement surgery with transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) being an option in some who are at high risk from surgery. Valves may either be mechanical or bioprosthetic with each having risks and benefits. Another less invasive procedure, balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) may result in benefit but this is for only for a few months. Complications like heart failure may be treated as per normal in those with mild to moderate AS. In those with severe disease a number of medications should be avoided including ACE inhibitors, nitroglycerin, and some beta blockers. Nitroprusside or phenylephrine may be used in those with decompensated heart failure depending on the blood pressure.Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease in the developed world. It affects about 2% of people who are over 65 years of age. Estimated rates are not known in most of the developing world as of 2014. In those who have symptoms, without repair, the chance of death at five years is about 50% and at 10 years is about 90%. Aortic stenosis was first described by French physician Lazare Rivière in 1663.