2017 AHA/ACC Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline
... nonrandomized comparative and descriptive studies, case series, cohort studies, systematic reviews, and expert opinion. Only key references are cited. An independent evidence review committee (ERC) is commissioned when there are 1 or more questions deemed of utmost clinical importance that merit for ...
... nonrandomized comparative and descriptive studies, case series, cohort studies, systematic reviews, and expert opinion. Only key references are cited. An independent evidence review committee (ERC) is commissioned when there are 1 or more questions deemed of utmost clinical importance that merit for ...
Articles in PresS. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol (February 3, 2012
... throughout both the ventricle (13) and the His-Purkinje system (16, 18, 48, 55). Age-related ...
... throughout both the ventricle (13) and the His-Purkinje system (16, 18, 48, 55). Age-related ...
ESC Guidelines for the management of grown
... The content of these European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines has been published for personal and educational use only. No commercial use is authorized. No part of the ESC Guidelines may be translated or reproduced in any form without written permission from the ESC. Permission can be obtaine ...
... The content of these European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines has been published for personal and educational use only. No commercial use is authorized. No part of the ESC Guidelines may be translated or reproduced in any form without written permission from the ESC. Permission can be obtaine ...
8951203.pps - MyPACS.net
... from ventriculostomy or other maneuvers performed during heart surgery ...
... from ventriculostomy or other maneuvers performed during heart surgery ...
Progression of Central Pulse Pressure Over 1 Decade of
... the method of maximum likelihood. The overall goodnessof-fit of the ACE model was compared against the saturated model (which perfectly describes the data without any assumptions) using likelihood ratio tests. The significance of each of the ACE parameters was tested by setting it to zero and testin ...
... the method of maximum likelihood. The overall goodnessof-fit of the ACE model was compared against the saturated model (which perfectly describes the data without any assumptions) using likelihood ratio tests. The significance of each of the ACE parameters was tested by setting it to zero and testin ...
Assessment of Coronary Microcirculation in a Swine Animal Model
... of the curve in diastole, and the X-intercept of the line was used to calculate the Pzf ...
... of the curve in diastole, and the X-intercept of the line was used to calculate the Pzf ...
Circulation Research AUGUST
... utilization has been recognized by many investigators, and studies over the past few years have supported this view (5-9). It has also been appreciated that the increase in MVoo associated with muscular exercise or administration of catecholamines is often disproportionate to the changes in myocardi ...
... utilization has been recognized by many investigators, and studies over the past few years have supported this view (5-9). It has also been appreciated that the increase in MVoo associated with muscular exercise or administration of catecholamines is often disproportionate to the changes in myocardi ...
Tetralogy of Fallot: from fetus to adult
... result of the outflow tract obstruction. Thus, the characteristic four features of TOF are an overriding aorta, RV outflow tract obstruction, malalignment VSD, and RV hypertrophy (Figure 1). [1, 4-5, 8] The anatomy of TOF explains much of the pathophysiology seen. The RV outflow tract obstruction to ...
... result of the outflow tract obstruction. Thus, the characteristic four features of TOF are an overriding aorta, RV outflow tract obstruction, malalignment VSD, and RV hypertrophy (Figure 1). [1, 4-5, 8] The anatomy of TOF explains much of the pathophysiology seen. The RV outflow tract obstruction to ...
Syncope - UC Irvine`s Department of Medicine
... NEURO: CN II-XII grossly intact ;BUE and BLE : 5/5 strength, normal sensory, reflexes and gait SKIN: no rashes or bruises ...
... NEURO: CN II-XII grossly intact ;BUE and BLE : 5/5 strength, normal sensory, reflexes and gait SKIN: no rashes or bruises ...
Goldman MJ (1986): Principles of Clinical Electrocardiography, 12th
... Bundle-branch block denotes a conduction defect in either of the bundle-branches or in either fascicle of the left bundle-branch. If the two bundle-branches exhibit a block simultaneously, the progress of activation from the atria to the ventricles is completely inhibited; this is regarded as third- ...
... Bundle-branch block denotes a conduction defect in either of the bundle-branches or in either fascicle of the left bundle-branch. If the two bundle-branches exhibit a block simultaneously, the progress of activation from the atria to the ventricles is completely inhibited; this is regarded as third- ...
Diastolic closure rate of normal mitral valve - Heart
... phonocardiogram was obtained using a piezoelectric The mitral valve echogram was recorded using a Smith- crystal microphone placed in the second intercostal Kline Instruments Ekoline 20 ultrasound recorder pro- space at the left sternal edge. A small cannula was introviding a repetition rate of iooo ...
... phonocardiogram was obtained using a piezoelectric The mitral valve echogram was recorded using a Smith- crystal microphone placed in the second intercostal Kline Instruments Ekoline 20 ultrasound recorder pro- space at the left sternal edge. A small cannula was introviding a repetition rate of iooo ...
Aging and Arterial Stiffness
... in the central artery causes elastin fiber fatigue and fracture. Increased vascular calcification and endothelial dysfunction are also characteristic of arterial aging. These changes lead to increased pulse wave velocity, especially along central elastic arteries, and increases in systolic blood pre ...
... in the central artery causes elastin fiber fatigue and fracture. Increased vascular calcification and endothelial dysfunction are also characteristic of arterial aging. These changes lead to increased pulse wave velocity, especially along central elastic arteries, and increases in systolic blood pre ...
Development of the Heart
... • Describe the embryological components that contribute to the left and right atria and ventricles. • Be able to describe the role of the foramen ovale in blood flow changes at birth. • Explain the partitioning into right and left ventricles and the separation of both the conus cordis and truncus ar ...
... • Describe the embryological components that contribute to the left and right atria and ventricles. • Be able to describe the role of the foramen ovale in blood flow changes at birth. • Explain the partitioning into right and left ventricles and the separation of both the conus cordis and truncus ar ...
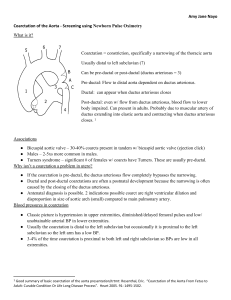
Amy Jane Nayo Coarctation of the Aorta
... ● Preductal/patent ductus arteriosus: While the ductus arteriosus is open there is right to left shunting through the ductus arteriosus since there is minimal flow from the aorta above the ductus where the coarctation is. The right to left shunting dilutes the oxygen concentration of blood to the lo ...
... ● Preductal/patent ductus arteriosus: While the ductus arteriosus is open there is right to left shunting through the ductus arteriosus since there is minimal flow from the aorta above the ductus where the coarctation is. The right to left shunting dilutes the oxygen concentration of blood to the lo ...
of End-Diastolic Volume
... Background. Maximal ventricular power (PWRIUOX) reflects contractile state and has the potential to be noninvasively determined. However, its sensitivities to preload, afterload resistance, and inotropic state are incompletely defined. The present study determines these dependencies and proposes a n ...
... Background. Maximal ventricular power (PWRIUOX) reflects contractile state and has the potential to be noninvasively determined. However, its sensitivities to preload, afterload resistance, and inotropic state are incompletely defined. The present study determines these dependencies and proposes a n ...
Iatrogenic Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade in the Percutaneous
... LV (ⱖ10 mm) may act to seal small perforations, balancing the higher intrachamber pressures. However, even a small guidewire perforation may not be tolerated if it occurs in patients with resistance to LV outflow, such as in severe aortic stenosis. In this case, very high LV pressure and high afterl ...
... LV (ⱖ10 mm) may act to seal small perforations, balancing the higher intrachamber pressures. However, even a small guidewire perforation may not be tolerated if it occurs in patients with resistance to LV outflow, such as in severe aortic stenosis. In this case, very high LV pressure and high afterl ...
How to use echo-Doppler in clinical trials: different modalities for
... population (on the basis of echo-Doppler parameters). The other type of trial involves echo-Doppler measurements [e.g. chamber volumes, Left ventricular (LV) mass] as primary or secondary endpoints for efficacy and safety purposes. While echoDoppler parameters are considered acceptable as a proof of ...
... population (on the basis of echo-Doppler parameters). The other type of trial involves echo-Doppler measurements [e.g. chamber volumes, Left ventricular (LV) mass] as primary or secondary endpoints for efficacy and safety purposes. While echoDoppler parameters are considered acceptable as a proof of ...
Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Idiopathic
... measured echocardiographically between the enidocardial echo of the posterior left ventricular wall and the endocardial border of the left septal surface. The minor diameter at end~diastole (Sd) was measured at the time of the R wave of the simultaneously recorded electrocardiogram, and that at end- ...
... measured echocardiographically between the enidocardial echo of the posterior left ventricular wall and the endocardial border of the left septal surface. The minor diameter at end~diastole (Sd) was measured at the time of the R wave of the simultaneously recorded electrocardiogram, and that at end- ...
Rheumatic mitral stenosis in associationwith partial
... connected normally to the left atrium, and the atrial septum was intact. There was extreme stenosis of the mitral valve, the orifice measuring no more than 1 cm. Initial occlusion of the venous channel linking the left pulmonary veins to the superior vena cava produced an abrupt elevation in pressur ...
... connected normally to the left atrium, and the atrial septum was intact. There was extreme stenosis of the mitral valve, the orifice measuring no more than 1 cm. Initial occlusion of the venous channel linking the left pulmonary veins to the superior vena cava produced an abrupt elevation in pressur ...
ESC Guidelines for the management of grown
... Guidelines summarize and evaluate all currently available evidence on a particular issue with the aim of assisting physicians in selecting the best management strategies for an individual patient, suffering from a given condition, taking into account the impact on outcome, as well as the risk–benefi ...
... Guidelines summarize and evaluate all currently available evidence on a particular issue with the aim of assisting physicians in selecting the best management strategies for an individual patient, suffering from a given condition, taking into account the impact on outcome, as well as the risk–benefi ...
Double outlet right ventricle with intact ventricular
... limits the interatrial communication. Thus, intact ventricular septum as well as intact atrial septum or restrictive ASD are usually observed in these patients. Patients are usually presented urgently in the neonatal term due to restrictive ASD. Unless balloon atrial septostomy or stent intervention ...
... limits the interatrial communication. Thus, intact ventricular septum as well as intact atrial septum or restrictive ASD are usually observed in these patients. Patients are usually presented urgently in the neonatal term due to restrictive ASD. Unless balloon atrial septostomy or stent intervention ...
Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by
... severely abnormal, which reflect the degree to which measurements deviate from normal. In addition to providing normative data, it would be beneficial to standardize cutoffs for severity of abnormality for all parameters across echocardiography laboratories, such that the term moderately abnormal, f ...
... severely abnormal, which reflect the degree to which measurements deviate from normal. In addition to providing normative data, it would be beneficial to standardize cutoffs for severity of abnormality for all parameters across echocardiography laboratories, such that the term moderately abnormal, f ...
Aneurysms of the Sinuses of Valsalva
... of a large SVA and the gradual progression of a small perforation. Acute, large rupture may present with dramatic onset of marked substernal chest pain, upper abdominal pain or severe dyspnea with sudden hemodynamic collapse. Symptoms often follow physical stress, with acute dyspnea and chest pain d ...
... of a large SVA and the gradual progression of a small perforation. Acute, large rupture may present with dramatic onset of marked substernal chest pain, upper abdominal pain or severe dyspnea with sudden hemodynamic collapse. Symptoms often follow physical stress, with acute dyspnea and chest pain d ...
Idiopathic Ventricular Tachycardia: Transcatheter Ablation
... Less frequently, idiopathic VTs/PVCs arise from the mitral annulus (about 5% of all idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias). In these circumstances, the most frequently involved area is the anteroseptal region of the annulus. Similar to aortic cusp VTs, a delayed potential is recorded during sinus rhyth ...
... Less frequently, idiopathic VTs/PVCs arise from the mitral annulus (about 5% of all idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias). In these circumstances, the most frequently involved area is the anteroseptal region of the annulus. Similar to aortic cusp VTs, a delayed potential is recorded during sinus rhyth ...
Tetralogy of Fallot | SpringerLink
... with very mild right ventricular outflow tract obstruction at birth may be diagnosed at a couple months of age as the obstruction worsens resulting in newly noticed cyanosis and a louder murmur. Because patients with tetralogy of Fallot have obstruction to pulmonary blood flow, they will not present ...
... with very mild right ventricular outflow tract obstruction at birth may be diagnosed at a couple months of age as the obstruction worsens resulting in newly noticed cyanosis and a louder murmur. Because patients with tetralogy of Fallot have obstruction to pulmonary blood flow, they will not present ...
Aortic stenosis

Aortic stenosis (AS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occurs due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercise. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially with lying down, at night, and with exercise as well as swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis.Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve and rheumatic fever. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population while rheumatic heart disease mostly occurring in the developing world. A normal valve, however, may also harden over the decades. Risk factors are similar to those of coronary artery disease and include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and being male. The aortic valve usually has three leaflets and is located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta. AS typically results in a heart murmur. Its severity can be divided into mild, moderate, severe, and very severe based on ultrasound of the heart findings.Aortic stenosis is typically followed using repeated ultrasounds. Once it has become severe treatment primarily involves valve replacement surgery with transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) being an option in some who are at high risk from surgery. Valves may either be mechanical or bioprosthetic with each having risks and benefits. Another less invasive procedure, balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) may result in benefit but this is for only for a few months. Complications like heart failure may be treated as per normal in those with mild to moderate AS. In those with severe disease a number of medications should be avoided including ACE inhibitors, nitroglycerin, and some beta blockers. Nitroprusside or phenylephrine may be used in those with decompensated heart failure depending on the blood pressure.Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease in the developed world. It affects about 2% of people who are over 65 years of age. Estimated rates are not known in most of the developing world as of 2014. In those who have symptoms, without repair, the chance of death at five years is about 50% and at 10 years is about 90%. Aortic stenosis was first described by French physician Lazare Rivière in 1663.