ANTEROLATERAL THIGH FLAP
... reach the skin whereas in other cases they travel in the septum between the VL and RF. The more proximal portion of the anterolateral thigh skin is often supplied by a vessel from the transverse branch of the LCFA. Figure 1 This flap would necessarily have a shorter pedicle. ...
... reach the skin whereas in other cases they travel in the septum between the VL and RF. The more proximal portion of the anterolateral thigh skin is often supplied by a vessel from the transverse branch of the LCFA. Figure 1 This flap would necessarily have a shorter pedicle. ...
19 O A and V Patterns C H A P T E R
... muscles and in A esotropia by underacting lateral rectus muscles. If this were true, one would invariably find an A-pattern esotropia in patients with bilateral abducens paresis. This is clearly not the case. Indeed, we have occasionally observed a Vpattern esotropia in this condition, which contrad ...
... muscles and in A esotropia by underacting lateral rectus muscles. If this were true, one would invariably find an A-pattern esotropia in patients with bilateral abducens paresis. This is clearly not the case. Indeed, we have occasionally observed a Vpattern esotropia in this condition, which contrad ...
Four cases of variations in the forearm extensor musculature in a
... a tendon transfer and the extra muscles found in this region can be useful in the surgical rehabilitation of patients with paralytic disorders. Case 2 As mentioned earlier most of the reported variations of APL are about the variations in its tendons and their insertion.[6-9] A case of additional be ...
... a tendon transfer and the extra muscles found in this region can be useful in the surgical rehabilitation of patients with paralytic disorders. Case 2 As mentioned earlier most of the reported variations of APL are about the variations in its tendons and their insertion.[6-9] A case of additional be ...
34 Scapulectomy
... both. Chondrosarcomas are the most common primary malignancy of the scapula in adults; in children the most common primary malignancy of the scapula is Ewing’s sarcoma (Figures 34.2 and 34.3). Soft-tissue tumors may involve the periscapular musculature and secondarily invade the scapula. The first l ...
... both. Chondrosarcomas are the most common primary malignancy of the scapula in adults; in children the most common primary malignancy of the scapula is Ewing’s sarcoma (Figures 34.2 and 34.3). Soft-tissue tumors may involve the periscapular musculature and secondarily invade the scapula. The first l ...
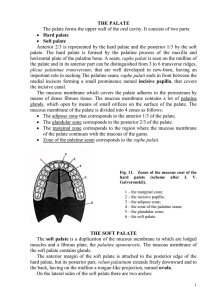
the palate
... palatinum in the transverse direction. e) Musculus uvulae arises from the spina nasalis posterior and from the aponeurosis of the soft palate and inserts within the uvula. This muscle shortens the uvula. THE PALATINE TONSIL The palatine tonsil, tonsilla palatina is a lymphoid organ that accomplishes ...
... palatinum in the transverse direction. e) Musculus uvulae arises from the spina nasalis posterior and from the aponeurosis of the soft palate and inserts within the uvula. This muscle shortens the uvula. THE PALATINE TONSIL The palatine tonsil, tonsilla palatina is a lymphoid organ that accomplishes ...
lower leg anatomy
... Deep peroneal n arises in PL and then passes to lie on interosseous membrane (Lat to vessels) Artery---initially lies on I/M between tib ant and EDL, then crossed by EHL so at ankle 2 muscles on each side Peroneus Longus Type IV muscle from peroneal—perforators through FHL (drains into short sapheno ...
... Deep peroneal n arises in PL and then passes to lie on interosseous membrane (Lat to vessels) Artery---initially lies on I/M between tib ant and EDL, then crossed by EHL so at ankle 2 muscles on each side Peroneus Longus Type IV muscle from peroneal—perforators through FHL (drains into short sapheno ...
lower extremity structure list
... deep to the adductor longus muscle. It gives off three major branches to supply the different regions of the thigh: the medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries and the perforating arteries. The lateral circumflex artery branches most often from the upper lateral portion of the profunda femori ...
... deep to the adductor longus muscle. It gives off three major branches to supply the different regions of the thigh: the medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries and the perforating arteries. The lateral circumflex artery branches most often from the upper lateral portion of the profunda femori ...
6. The Fascię and Muscles of the Trunk. a. The Deep Muscles of the
... The Iliocostalis lumborum (Iliocostalis muscle; Sacrolumbalis muscle) is inserted, by six or seven flattened tendons, into the inferior borders of the angles of the lower six or seven ribs. The Iliocostalis dorsi (Musculus accessorius) arises by flattened tendons from the upper borders of the angles ...
... The Iliocostalis lumborum (Iliocostalis muscle; Sacrolumbalis muscle) is inserted, by six or seven flattened tendons, into the inferior borders of the angles of the lower six or seven ribs. The Iliocostalis dorsi (Musculus accessorius) arises by flattened tendons from the upper borders of the angles ...
Scapular Flap
... disability of the shoulder is reported to be low [50, 190, 273]. Postoperative care includes immobilization of the arm for 3–4 days and physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles of the shoulder girdle, starting about 2–3 weeks after surgery. The main disadvantage of the scapular donor site is the fact ...
... disability of the shoulder is reported to be low [50, 190, 273]. Postoperative care includes immobilization of the arm for 3–4 days and physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles of the shoulder girdle, starting about 2–3 weeks after surgery. The main disadvantage of the scapular donor site is the fact ...
19 Topography of lower limb.
... The iliopectineal arch divides the space below the inguinal ligament into two parts: +the muscular part (lacuna musculorum) and vascular part (lacuna vasorum) -the foramen suprapiriforme and foramen infrapiriforme -the obturator canal and femoral canal -the obturator canal and femoral groove ...
... The iliopectineal arch divides the space below the inguinal ligament into two parts: +the muscular part (lacuna musculorum) and vascular part (lacuna vasorum) -the foramen suprapiriforme and foramen infrapiriforme -the obturator canal and femoral canal -the obturator canal and femoral groove ...
Muscles and Fascia of Pelvic Wall
... The lateral pelvic walls: Have a bony framework formed by the hip bones, including the obturator foramen ; the obturator foramen is closed by the obturator membrane . Are covered and padded by the obturator internus muscles .Each obturator internus passes posteriorly from its origin within the ...
... The lateral pelvic walls: Have a bony framework formed by the hip bones, including the obturator foramen ; the obturator foramen is closed by the obturator membrane . Are covered and padded by the obturator internus muscles .Each obturator internus passes posteriorly from its origin within the ...
Inglês
... the axillary nerve presented that the posterior part of deltoid muscle was innervated in 90 percent of the cases by the posterior branch of the axillary nerve. In 10 percent, innervation was entirely by the anterior branch (Hong et al.). Wang et al., declerated that range of the size of the posterio ...
... the axillary nerve presented that the posterior part of deltoid muscle was innervated in 90 percent of the cases by the posterior branch of the axillary nerve. In 10 percent, innervation was entirely by the anterior branch (Hong et al.). Wang et al., declerated that range of the size of the posterio ...
VBA201 Lecture Note
... 5. Coccygeal (caudal) region consists of caudal coccygeal vertebrae which are progressively reduced. They serve as site for the insertion for the muscle which makes the tail. A typical vertebra consists surrounded by an arch that completes the closure of the vertebral foramen; it is a summation of t ...
... 5. Coccygeal (caudal) region consists of caudal coccygeal vertebrae which are progressively reduced. They serve as site for the insertion for the muscle which makes the tail. A typical vertebra consists surrounded by an arch that completes the closure of the vertebral foramen; it is a summation of t ...
Occipital Neurostimulation-Induced Muscle Spasms
... Conclusion: Lead placement at the level of C1 or C1-2 may cause some patients to have intolerable neck/occipital spasm during neurostimulation. This is the first known published report of technical variation in the location of lead placement, at the nuchal line in a transverse fashion, for ONS. Plac ...
... Conclusion: Lead placement at the level of C1 or C1-2 may cause some patients to have intolerable neck/occipital spasm during neurostimulation. This is the first known published report of technical variation in the location of lead placement, at the nuchal line in a transverse fashion, for ONS. Plac ...
10b
... The primary function of deep thoracic muscles is to promote movement for breathing External intercostals – more superficial layer that lifts the rib cage and increases thoracic volume to allow inspiration Figure 10.10a ...
... The primary function of deep thoracic muscles is to promote movement for breathing External intercostals – more superficial layer that lifts the rib cage and increases thoracic volume to allow inspiration Figure 10.10a ...
Brachial muscles in the chick embryo: the fate of
... This muscle originates on the coracoid and passes over the shoulder to insert on the dorsal surface of the humerus. About 75 % of this muscle is derived from somites 17 and 18, with the remainder derived from somite 19. However, quail cells were seen in this muscle in one out of five chimaeras that ...
... This muscle originates on the coracoid and passes over the shoulder to insert on the dorsal surface of the humerus. About 75 % of this muscle is derived from somites 17 and 18, with the remainder derived from somite 19. However, quail cells were seen in this muscle in one out of five chimaeras that ...
Head_and_Neck_annotation
... Branch of the first part of the subclavian artery Gives off the inferior thyroid artery, transverse cervical artery, and suprascapular artery Arterial supply to: lower neck, posterior shoulder, and thyroid gland Arises between the origin and inner border of scalenus anterior muscle thyrohyoi ...
... Branch of the first part of the subclavian artery Gives off the inferior thyroid artery, transverse cervical artery, and suprascapular artery Arterial supply to: lower neck, posterior shoulder, and thyroid gland Arises between the origin and inner border of scalenus anterior muscle thyrohyoi ...
The Modified External Oblique Musculocutaneous Flap
... oblique muscle gets one or two branches of the deep circumflex iliac artery which contribute significantly to the main blood supply of the muscle. In fact, these branches could be considered the dominant vascular pedicle of the muscle because they are larger than the segmental pedicles. The success ...
... oblique muscle gets one or two branches of the deep circumflex iliac artery which contribute significantly to the main blood supply of the muscle. In fact, these branches could be considered the dominant vascular pedicle of the muscle because they are larger than the segmental pedicles. The success ...
Multi-axis passive and active stiffnesses of the glenohumeral joint
... Objective. To investigate passive and active glenohumeral stiffness in the anterior, posterior, superior, and inferior directions at different lateral positions of the humerus. Design. Glenohumeral stiffness along multiple axes was determined in fresh-frozen shoulder specimens under both passive (no si ...
... Objective. To investigate passive and active glenohumeral stiffness in the anterior, posterior, superior, and inferior directions at different lateral positions of the humerus. Design. Glenohumeral stiffness along multiple axes was determined in fresh-frozen shoulder specimens under both passive (no si ...
Skeletal muscle

Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue which is under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibers known as tendons.Skeletal muscle is made up of individual muscle cells or myocytes, known as muscle fibers. They are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts (a type of embryonic progenitor cell that gives rise to a muscle cell) in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibres are cylindrical, and multinucleated.Muscle fibers are in turn composed of myofibrils. The myofibrils are composed of actin and myosin filaments, repeated in units called sarcomeres, the basic functional units of the muscle fiber. The sarcomere is responsible for the striated appearance of skeletal muscle, and forms the basic machinery necessary for muscle contraction. The term muscle refers to multiple bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. All muscles also contain connective tissue arranged in layers of fasciae. Each muscle is enclosed in a layer of fascia; each fascicle is enclosed by a layer of fascia and each individual muscle fiber is also enclosed in a layer of fascia.