Light Tasks
... New experiences that don’t fit the patterns they are familiar with o Refraction: Spear fishing demonstration, coin in cup o Force and motion: Falling objects, weight in a vacuum, cart with constant force o Buoyancy: Alka-Seltzer demonstration o Color, reflection, or intensity: ???? New patterns ...
... New experiences that don’t fit the patterns they are familiar with o Refraction: Spear fishing demonstration, coin in cup o Force and motion: Falling objects, weight in a vacuum, cart with constant force o Buoyancy: Alka-Seltzer demonstration o Color, reflection, or intensity: ???? New patterns ...
Imaging of Intrinsic Signals in the Retina
... Research Site: University of California, Berkeley Research Advisor: Austin Roorda Research Supervisor: Kate Grieve Home Institution: DePaul University Adaptive optics (AO) is used to correct ocular aberrations of the human eye and so improves lateral and axial resolution and brightness of images of ...
... Research Site: University of California, Berkeley Research Advisor: Austin Roorda Research Supervisor: Kate Grieve Home Institution: DePaul University Adaptive optics (AO) is used to correct ocular aberrations of the human eye and so improves lateral and axial resolution and brightness of images of ...
BE112A Topic 1: Introduction to Biomechanics
... material. Therefore, a major objective of biomechanics is identifying the constitutive law for biological cells and tissues. • Biomechanics involves the interplay of experimental measurement in living tissues and theoretical analysis based on physical foundations • Biomechanics has numerous applicat ...
... material. Therefore, a major objective of biomechanics is identifying the constitutive law for biological cells and tissues. • Biomechanics involves the interplay of experimental measurement in living tissues and theoretical analysis based on physical foundations • Biomechanics has numerous applicat ...
The principles of statistical optics and image formation A Statistical
... approach in order to solve many important statistical problems in optics. ...
... approach in order to solve many important statistical problems in optics. ...
33-6 Radiation Pressure
... Unpolarized electromagnetic waves couldn’t represent easily have a mess of double arrows Fig. 33-10a simplify the mess by resolving each electric field into y z components As the wave travels past us the net y component oscillates parallel to the y axis z component oscillates para ...
... Unpolarized electromagnetic waves couldn’t represent easily have a mess of double arrows Fig. 33-10a simplify the mess by resolving each electric field into y z components As the wave travels past us the net y component oscillates parallel to the y axis z component oscillates para ...
Chapter 8 Wave Optics
... This phenomenon is quite important. The resolution of many instrument like telescope and microscope depends on this. 8.2.3 The diffraction grating (衍射光栅) Suppose that, instead of a single slit, or two slits side by side in Yong’s experiments, we have a very large number of parallel slits, all of the ...
... This phenomenon is quite important. The resolution of many instrument like telescope and microscope depends on this. 8.2.3 The diffraction grating (衍射光栅) Suppose that, instead of a single slit, or two slits side by side in Yong’s experiments, we have a very large number of parallel slits, all of the ...
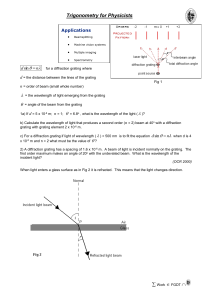
trigonometry
... b) If light arrives at an angle of 15o to the normal at an air-to-glass boundary for which the refractive index is 1.5, what is the expected angle of refraction? 4) The Refractive Index for an air-to-diamond boundary is about 2.42. If light arrives at an angle of 60o to the normal at an air-to-diamo ...
... b) If light arrives at an angle of 15o to the normal at an air-to-glass boundary for which the refractive index is 1.5, what is the expected angle of refraction? 4) The Refractive Index for an air-to-diamond boundary is about 2.42. If light arrives at an angle of 60o to the normal at an air-to-diamo ...
Physics
... UNIT-3: Thermodynamics-I Thermodynamic system and Zeroth law of thermodynamics. First law of thermodynamics and its limitations, reversible and irreversible process. Second law of thermodynamics and its significance, Carnot theorem, Absolute scale of temperature, Absolute Zero and magnitude of each ...
... UNIT-3: Thermodynamics-I Thermodynamic system and Zeroth law of thermodynamics. First law of thermodynamics and its limitations, reversible and irreversible process. Second law of thermodynamics and its significance, Carnot theorem, Absolute scale of temperature, Absolute Zero and magnitude of each ...
The Making of Quantum Theory
... … in addition to this, studies reveal that: Electrons behave as particles in some experiments while in other experiments they behave as WAVES In order to describe the motion of an electron in an atom, both the electron's wave and particle nature must be taken into account. HEISENBERG UNCERTAINTY PRI ...
... … in addition to this, studies reveal that: Electrons behave as particles in some experiments while in other experiments they behave as WAVES In order to describe the motion of an electron in an atom, both the electron's wave and particle nature must be taken into account. HEISENBERG UNCERTAINTY PRI ...
PHYSICS 202 – FINAL EXAM
... calculations or explain your reasoning unless requested. Also, no partial credit will be awarded for incorrect answers. Problems B1-B9 are worth 8 points each. For these nine problems, you must show your work and/or explain your reasoning to receive any credit for a problem. Merely stating the answe ...
... calculations or explain your reasoning unless requested. Also, no partial credit will be awarded for incorrect answers. Problems B1-B9 are worth 8 points each. For these nine problems, you must show your work and/or explain your reasoning to receive any credit for a problem. Merely stating the answe ...
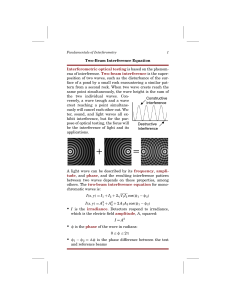
Two-Beam Interference Equation Interferometric optical testing is
... in the beam because they are so thin, but they are fragile and very sensitive to vibrations, making them difficult to use in an interferometer. Diffraction Grating as a Beamsplitter A diffraction grating can be used as a beamsplitter for a source that is nearly monochromatic. When placed in a beam, ...
... in the beam because they are so thin, but they are fragile and very sensitive to vibrations, making them difficult to use in an interferometer. Diffraction Grating as a Beamsplitter A diffraction grating can be used as a beamsplitter for a source that is nearly monochromatic. When placed in a beam, ...
Physics: Light 1.a Introduction, Ancient History of theories of light
... • Light is comprised of particles. This was the notion put forth by Isaac Newton in his treatise ‘Opticks’. He thought that light was made of a large number of small particles. On the whole it behaved like a wave. • Light is a wave phenomenon. This view was first put forward by Christian Huygens at ...
... • Light is comprised of particles. This was the notion put forth by Isaac Newton in his treatise ‘Opticks’. He thought that light was made of a large number of small particles. On the whole it behaved like a wave. • Light is a wave phenomenon. This view was first put forward by Christian Huygens at ...
Chapter 24 Lecture Notes
... change direction at the slit. However, particles entering perpendicular will either go straight through or they bounce back. We find that light will diffract and behave like a wave. What about geometric optics? It only works when the wavelength of light is small compared to the geometry involved. Wh ...
... change direction at the slit. However, particles entering perpendicular will either go straight through or they bounce back. We find that light will diffract and behave like a wave. What about geometric optics? It only works when the wavelength of light is small compared to the geometry involved. Wh ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".