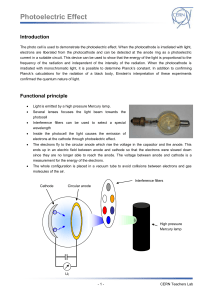
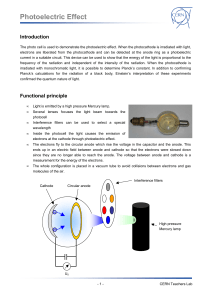
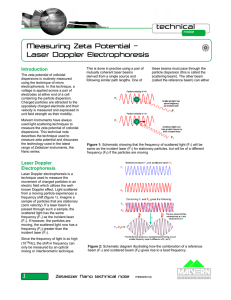
Measurement of Surface Quality 1. Lyot Test 2. FECO 3. Nomarski
... The path difference between the two beams can be adjusted by laterally translating the Wollaston prism. When the axes of the polarizer and analyzer are parallel and the prism is centered, the path lengths are equal and white light is seen for a perfect test surface with no tilt. When the polarizer a ...
... The path difference between the two beams can be adjusted by laterally translating the Wollaston prism. When the axes of the polarizer and analyzer are parallel and the prism is centered, the path lengths are equal and white light is seen for a perfect test surface with no tilt. When the polarizer a ...
Course Syllabus - Pellissippi State Community College
... The examples and problems selected for the course give the students the necessary knowledge and skills to read and analyze scientific data with proper understanding of the units involved and the type of physical quantity measured. The first few chapters lay down the foundation that is absolutely nec ...
... The examples and problems selected for the course give the students the necessary knowledge and skills to read and analyze scientific data with proper understanding of the units involved and the type of physical quantity measured. The first few chapters lay down the foundation that is absolutely nec ...
Part 1
... The sign between kx and t determines the direction the wave travels along the x-axis. + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match ...
... The sign between kx and t determines the direction the wave travels along the x-axis. + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match ...
Electromagnetic Mediums PowerPoint
... Distributed Summarizing: Look at the picture to the right. Discuss the following questions with a partner. How is the girl able to see the trees outside the ...
... Distributed Summarizing: Look at the picture to the right. Discuss the following questions with a partner. How is the girl able to see the trees outside the ...
Chapter 3
... Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Theory, Photons and Light September 5,8 Electromagnetic waves 3.1 Basic laws of electromagnetic theory Lights are electromagnetic waves. Electric fields are generated by electric charges or time-varying magnetic fields. Magnetic fields are generated by electric currents or ...
... Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Theory, Photons and Light September 5,8 Electromagnetic waves 3.1 Basic laws of electromagnetic theory Lights are electromagnetic waves. Electric fields are generated by electric charges or time-varying magnetic fields. Magnetic fields are generated by electric currents or ...
Effects of strain on electron spin transport in semiconductor epilayers
... Sorting category: Dd Conducting electrons in condensed matter Keywords: semiconductors, spin, optics, strain ...
... Sorting category: Dd Conducting electrons in condensed matter Keywords: semiconductors, spin, optics, strain ...
Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03
... a) The wavelength is independent of the speed of the wave for a fixed frequency. b) The wavelength is inversely proportional to the speed of the wave. c) The wavelength is the same for all types electromagnetic waves. d) The wavelength is directly proportional to the frequency of the wave. e) The wa ...
... a) The wavelength is independent of the speed of the wave for a fixed frequency. b) The wavelength is inversely proportional to the speed of the wave. c) The wavelength is the same for all types electromagnetic waves. d) The wavelength is directly proportional to the frequency of the wave. e) The wa ...
Link to PowerPoint Presentation
... ٭There is a special case of Snell’s Law ٭When going from high density to low density, there is a point after which all of the light is reflected ٭This point is the Critical Angle ...
... ٭There is a special case of Snell’s Law ٭When going from high density to low density, there is a point after which all of the light is reflected ٭This point is the Critical Angle ...
concave lens
... The refraction of light in nature that forms rainbows and red lunar eclipses is beautiful, but refraction also is useful. In 1303, French physician Bernard of Gordon wrote of the use of lenses to correct eyesight. Around 1610, Galileo used two lenses to make a telescope, with which he discovered th ...
... The refraction of light in nature that forms rainbows and red lunar eclipses is beautiful, but refraction also is useful. In 1303, French physician Bernard of Gordon wrote of the use of lenses to correct eyesight. Around 1610, Galileo used two lenses to make a telescope, with which he discovered th ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".