Atoms, Energy, Electrons, Oh My!! - Rimac-Science-Web
... • What are the 3 parts that make up the atom? • Protons (+), neutrons, electrons(-) • Which particles make up the mass of the atom? • What does the atomic number on the periodic table tell us? • What is the electron’s job? • What can we say about a “group” of elements on the periodic table? ...
... • What are the 3 parts that make up the atom? • Protons (+), neutrons, electrons(-) • Which particles make up the mass of the atom? • What does the atomic number on the periodic table tell us? • What is the electron’s job? • What can we say about a “group” of elements on the periodic table? ...
On the use of ERL for gamma production
... optical resonator of FEL. These FEL features make possible the use of intracavity high power light pulses and therefore eliminate special optical resonator, which is used to increase the energy of light pulses for other types of lasers. This mode of operation is successfully used for many years at t ...
... optical resonator of FEL. These FEL features make possible the use of intracavity high power light pulses and therefore eliminate special optical resonator, which is used to increase the energy of light pulses for other types of lasers. This mode of operation is successfully used for many years at t ...
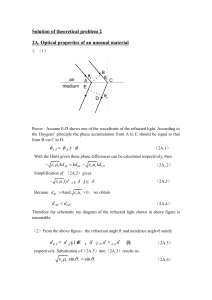
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 SECTION - A ALL
... 1. Mention the important properties of de Broglie waves. 2. What are the important applications of an electron microscope? 3. Give the physical significance of the wave function. 4. What do you mean by tunneling through a potential barrier? 5. What is Hermitian operator? 6. Show that [Lx, Ly] = i ħ ...
... 1. Mention the important properties of de Broglie waves. 2. What are the important applications of an electron microscope? 3. Give the physical significance of the wave function. 4. What do you mean by tunneling through a potential barrier? 5. What is Hermitian operator? 6. Show that [Lx, Ly] = i ħ ...
UNIVERSITAT POLITÈCNICA DE CATALUNYA
... In that small frequency band the electric susceptibility frequency dependence is assumed to be well described by a Taylor expansion around the carrier frequency roo in which terms up to second order are considered, namely ...
... In that small frequency band the electric susceptibility frequency dependence is assumed to be well described by a Taylor expansion around the carrier frequency roo in which terms up to second order are considered, namely ...
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (KCSE) - KCPE-KCSE
... (b) A mine worker stands between two vertical cliffs 400m from the nearer cliff. The cliffs are x distance apart. Every time he strikes the rock once, he hears two echoes, the first one after 2.5 seconds and the second follows 2 seconds later. From this information calculate ; (i) the speed of the s ...
... (b) A mine worker stands between two vertical cliffs 400m from the nearer cliff. The cliffs are x distance apart. Every time he strikes the rock once, he hears two echoes, the first one after 2.5 seconds and the second follows 2 seconds later. From this information calculate ; (i) the speed of the s ...
class1_BK - Center for Detectors
... http://www.fda.gov/fdac/features/2000/400_sun.html Sunburn is caused by a type of UV light known as UVB. The thinking was if you prevent sunburn, you'd prevent skin cancer. In recent years, scientists have come to appreciate that UVA, may be just as, or even more, important in causing some skin diso ...
... http://www.fda.gov/fdac/features/2000/400_sun.html Sunburn is caused by a type of UV light known as UVB. The thinking was if you prevent sunburn, you'd prevent skin cancer. In recent years, scientists have come to appreciate that UVA, may be just as, or even more, important in causing some skin diso ...
Young`s Double Slits
... seperation respectively. Part 4: Using a diffraction grating (Optional) Replace the double slit grating with a diffarction grating. ...
... seperation respectively. Part 4: Using a diffraction grating (Optional) Replace the double slit grating with a diffarction grating. ...
Y8-Physics-Keyword-L..
... A smooth, flat mirror A diagram showing the passage of light rays Angle between an incoming light ray and the normal The angle between the normal and the ray of light leaving a mirror A ray of light going towards the mirror or other object An imaginary line at right angles to the surface of a mirror ...
... A smooth, flat mirror A diagram showing the passage of light rays Angle between an incoming light ray and the normal The angle between the normal and the ray of light leaving a mirror A ray of light going towards the mirror or other object An imaginary line at right angles to the surface of a mirror ...
Topics: Measurement, Vectors, Graphic Analysis, One
... Speed of Light Special Relativity and its Consequences Equivalence of Mass and Energy Blackbody Radiation Wave-Particle Duality Uncertainty Principle Atomic Spectra ...
... Speed of Light Special Relativity and its Consequences Equivalence of Mass and Energy Blackbody Radiation Wave-Particle Duality Uncertainty Principle Atomic Spectra ...
File
... The amount of energy gained by an electron being accelerated a potential difference of 1 Volt. ( 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 Joules) Photoelectric emission: The emission of an electron from the surface of a metal when light of a suitable frequency falls on it. Photon: a packet of electromagnetic energy. (its ...
... The amount of energy gained by an electron being accelerated a potential difference of 1 Volt. ( 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 Joules) Photoelectric emission: The emission of an electron from the surface of a metal when light of a suitable frequency falls on it. Photon: a packet of electromagnetic energy. (its ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".