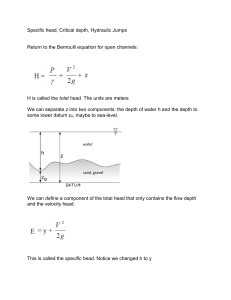
Math 240: Transition to Advanced Math
... statements or relations involving rate of change. In mathematical terms, statements are equations and rates are derivatives. Definition: An equation containing derivatives is called a differential equation. Differential equation (DE) play a prominent role in physics, engineering, chemistry, biology ...
... statements or relations involving rate of change. In mathematical terms, statements are equations and rates are derivatives. Definition: An equation containing derivatives is called a differential equation. Differential equation (DE) play a prominent role in physics, engineering, chemistry, biology ...
chapter 5 test - aubreyisd.net
... CHAPTER 4 & 5 REVIEW 1. Determine if each of the following equations represents a direct variation. If the equation is direct then find the constant of variation. (A) 2 y 5 x 1 (B) 5 x 6 y 0 (C) y 13 x Yes, 1/3 Not a representation Yes, 5/6 2. Find the rate of change for each situation: (A ...
... CHAPTER 4 & 5 REVIEW 1. Determine if each of the following equations represents a direct variation. If the equation is direct then find the constant of variation. (A) 2 y 5 x 1 (B) 5 x 6 y 0 (C) y 13 x Yes, 1/3 Not a representation Yes, 5/6 2. Find the rate of change for each situation: (A ...
Dynamics and stability of a fluid filled cylinder rolling on an inclined
... These studies were all performed on a system where the cylindrical wall rotates at a constant angular velocity. In the current study, we analyze the dynamics of a system where the cylindrical wall accelerates. We consider the case of a hollow cylindrical shell fully filled with a viscous fluid and r ...
... These studies were all performed on a system where the cylindrical wall rotates at a constant angular velocity. In the current study, we analyze the dynamics of a system where the cylindrical wall accelerates. We consider the case of a hollow cylindrical shell fully filled with a viscous fluid and r ...
Algebra Review
... Step 2: Multiply in constants to make the coefficients of x become opposites (6x and –6x) 2x – 6y = 19 multiply by 3 6x – 18y = 57 –3x + 2y = 10 multiply by 2 –6x + 4y = 20 Step 3: Add the two revised equations ( 6x – 18y = 57) + (–6x + 4y = 20) –14y = 77 divide by –14 y = –77/14 = –11/2 ...
... Step 2: Multiply in constants to make the coefficients of x become opposites (6x and –6x) 2x – 6y = 19 multiply by 3 6x – 18y = 57 –3x + 2y = 10 multiply by 2 –6x + 4y = 20 Step 3: Add the two revised equations ( 6x – 18y = 57) + (–6x + 4y = 20) –14y = 77 divide by –14 y = –77/14 = –11/2 ...
AP Calculus Section 6.2
... 9. Suppose that a point moves along some unknown curve y f ( x) in the xy plane in such a way that at each point x, y on the curve, the tangent line has slope x 2 . Find an equation for the curve given that it passes through the point 2,1 . ...
... 9. Suppose that a point moves along some unknown curve y f ( x) in the xy plane in such a way that at each point x, y on the curve, the tangent line has slope x 2 . Find an equation for the curve given that it passes through the point 2,1 . ...
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Equations
... Sandy is thinking of a number. When 33 is added to the number, the sum is equal to 55. What number is Sandy thinking of? ...
... Sandy is thinking of a number. When 33 is added to the number, the sum is equal to 55. What number is Sandy thinking of? ...
Acoustic wave equation
... Acoustic wave equation In physics, the acoustic wave equation governs the propagation of acoustic waves through a material medium. The form of the equation is a second order partial differential equation. The equation describes the evolution of acoustic pressure p or particle velocity u as a functio ...
... Acoustic wave equation In physics, the acoustic wave equation governs the propagation of acoustic waves through a material medium. The form of the equation is a second order partial differential equation. The equation describes the evolution of acoustic pressure p or particle velocity u as a functio ...