Comment_on
... where the powers α, β, γ,…yield the correct dimensions for Q1 and the dimensionless factor g can be either a pure number or a function of dimensionless power-law combinations of Q2, Q3,…,(if such combinations exist, see, e.g., Jensen (2013) and its references). It may be possible to choose the power ...
... where the powers α, β, γ,…yield the correct dimensions for Q1 and the dimensionless factor g can be either a pure number or a function of dimensionless power-law combinations of Q2, Q3,…,(if such combinations exist, see, e.g., Jensen (2013) and its references). It may be possible to choose the power ...
Lecture 10 - Second order linear differential equations
... We will encounter most second order linear differential equations in the form: p(t)y 00 + q(t)y 0 + r(t)y = g(t) If g(t) = 0, then we call such an equation homogeneous. If g(t) 6= 0, we call it nonhomogeneous. (People who are familiar with Linear Algebra, take notice!) We will first study homogeneou ...
... We will encounter most second order linear differential equations in the form: p(t)y 00 + q(t)y 0 + r(t)y = g(t) If g(t) = 0, then we call such an equation homogeneous. If g(t) 6= 0, we call it nonhomogeneous. (People who are familiar with Linear Algebra, take notice!) We will first study homogeneou ...
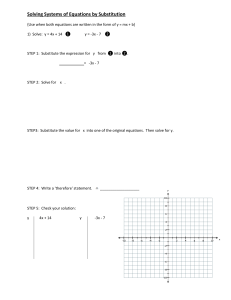
File - Kihei Charter STEM Academy Middle School
... Step 2: Subtract the equations. Since the coefficients of l are the same, subtract to eliminate l. 2l + 6s = 190 - (2l + 3s = 130) 0 + 3s = 60 Subtract s = 20 Solve for e (Divide both sides by 3) ...
... Step 2: Subtract the equations. Since the coefficients of l are the same, subtract to eliminate l. 2l + 6s = 190 - (2l + 3s = 130) 0 + 3s = 60 Subtract s = 20 Solve for e (Divide both sides by 3) ...
2(3x+7y=188)
... The first step is to combine the two equations. To do this you multiply the whole problems, so that when they’re 4x+2y=109.5 added together at least one variable will be 3x+7y=188 canceled. From there, you simplify the resulting equation until you find a solution 7(4x+2y=109.5) -2(3x+7y=188) for the ...
... The first step is to combine the two equations. To do this you multiply the whole problems, so that when they’re 4x+2y=109.5 added together at least one variable will be 3x+7y=188 canceled. From there, you simplify the resulting equation until you find a solution 7(4x+2y=109.5) -2(3x+7y=188) for the ...
2 Matrices and systems of linear equations
... a line in the plane and so has infinitely many solutions. To solve both equations simultaneously, we need to find the points, if any, which lie on both lines. There are 3 possibilities: (a) there’s just one (the usual case), (b) there is no solution (if the two lines are parallel and distinct), or ( ...
... a line in the plane and so has infinitely many solutions. To solve both equations simultaneously, we need to find the points, if any, which lie on both lines. There are 3 possibilities: (a) there’s just one (the usual case), (b) there is no solution (if the two lines are parallel and distinct), or ( ...
A Point of Intersection
... 3. Any ordered pair that does not satisfy the equation would represent a point, which is not on the plotted straight line. 4. Any point that is not on the plotted straight line will have coordinates whose ordered pair will not satisfy the linear equation. Putting “Linear Functions” in Mathematical t ...
... 3. Any ordered pair that does not satisfy the equation would represent a point, which is not on the plotted straight line. 4. Any point that is not on the plotted straight line will have coordinates whose ordered pair will not satisfy the linear equation. Putting “Linear Functions” in Mathematical t ...
Lecture24
... • Mass flow rate (kg/s) on the left must be equal to the mass flow rate on the right. • Imaginary tubes bound the flow of the fluid. ...
... • Mass flow rate (kg/s) on the left must be equal to the mass flow rate on the right. • Imaginary tubes bound the flow of the fluid. ...