Simultaneous detection of rotational and translational motion in
... and rotational Brownian motion - however, the latter does not have any measurable signature for symmetric, non-birefringent particles. The rotational Brownian motion is more pronounced for particles having birefringence [1], or in asymmetric particles due to unbalanced scattering forces, which also ...
... and rotational Brownian motion - however, the latter does not have any measurable signature for symmetric, non-birefringent particles. The rotational Brownian motion is more pronounced for particles having birefringence [1], or in asymmetric particles due to unbalanced scattering forces, which also ...
Lecture 10 - KFUPM Faculty List
... depending on their intensity, i.e. all-optical switching. The classic cases are optical bistability in which the output transmission of light from a cavity can be either high or low for the same input intensity and integrated optics devices such as nonlinear directional couplers which can be used fo ...
... depending on their intensity, i.e. all-optical switching. The classic cases are optical bistability in which the output transmission of light from a cavity can be either high or low for the same input intensity and integrated optics devices such as nonlinear directional couplers which can be used fo ...
Investigation of ultrafast demagnetization and cubic optical
... the film contained 724⫾3 Å of Ni and a 15.5⫾3 Å overlayer of Ni oxide that formed upon exposure to atmosphere. The Ni had a fcc structure with a lattice constant of 3.52 Å corresponding to that of the bulk phase.6 The average grain size was determined to be about 80 Å, and the film was found to have ...
... the film contained 724⫾3 Å of Ni and a 15.5⫾3 Å overlayer of Ni oxide that formed upon exposure to atmosphere. The Ni had a fcc structure with a lattice constant of 3.52 Å corresponding to that of the bulk phase.6 The average grain size was determined to be about 80 Å, and the film was found to have ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... To determine the physical thickness d and refractive index n of the medium, we measure ∆fPAR and ∆fMR. We used a microscope objective with high numerical aperture in combination with a set of apertures allowing for a controllable selection of optical rays. An iris diaphragm that only transmits the p ...
... To determine the physical thickness d and refractive index n of the medium, we measure ∆fPAR and ∆fMR. We used a microscope objective with high numerical aperture in combination with a set of apertures allowing for a controllable selection of optical rays. An iris diaphragm that only transmits the p ...
0625/2 - alwakrassoteam
... “When potatoes are bought in a market, the weight of a bag full of potatoes is affected by the density of the potatoes. A lady fills her bag when she buys 5 kg of large potatoes. A man buys 5 kg of small potatoes. He puts them in a bag of the same size as the lady’s, but his bag is not filled.” (a) ...
... “When potatoes are bought in a market, the weight of a bag full of potatoes is affected by the density of the potatoes. A lady fills her bag when she buys 5 kg of large potatoes. A man buys 5 kg of small potatoes. He puts them in a bag of the same size as the lady’s, but his bag is not filled.” (a) ...
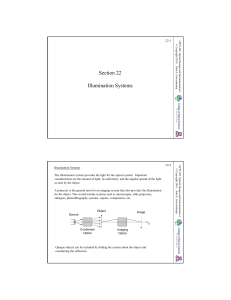
502-22 Illumination Systems
... throughput of specular illumination is needed. A larger light bulb is not always an option (A major rule of optical engineering is that there is never enough light!!). The system should be designed as specular illumination with a little diffusion added. For example, one side of the condenser lens mi ...
... throughput of specular illumination is needed. A larger light bulb is not always an option (A major rule of optical engineering is that there is never enough light!!). The system should be designed as specular illumination with a little diffusion added. For example, one side of the condenser lens mi ...
Improvement to Load-pull Technique for Design of Large
... The uncertainty of |ΓL | is due to the non-zero reflection coefficient of the launcher itself which is increasing with frequency. Reflected wave from the launcher interferes with the reflected wave from the tuner and this creates the ripple visible in the resulting values of |ΓL |. It can be conclud ...
... The uncertainty of |ΓL | is due to the non-zero reflection coefficient of the launcher itself which is increasing with frequency. Reflected wave from the launcher interferes with the reflected wave from the tuner and this creates the ripple visible in the resulting values of |ΓL |. It can be conclud ...
rtf
... zero. In this case we have no interference between the two waves. Thus coherent waves interfere whilst coherent aberrations effect the interference between waves, and incoherent waves do not interfere so that incoherent aberrations can be considered by summing intensities. (A middle ground with par ...
... zero. In this case we have no interference between the two waves. Thus coherent waves interfere whilst coherent aberrations effect the interference between waves, and incoherent waves do not interfere so that incoherent aberrations can be considered by summing intensities. (A middle ground with par ...
The AntIer-Townes effect revisited
... one to study the behavior of atoms put in resonant cavities having a very high finesse. ln such (real) cavities, the number N of photons has a definite meaning. For example, the cavity can be empty (N = 0) and one can then study how the spontaneous emission rates and the Lamb shift are modified by t ...
... one to study the behavior of atoms put in resonant cavities having a very high finesse. ln such (real) cavities, the number N of photons has a definite meaning. For example, the cavity can be empty (N = 0) and one can then study how the spontaneous emission rates and the Lamb shift are modified by t ...
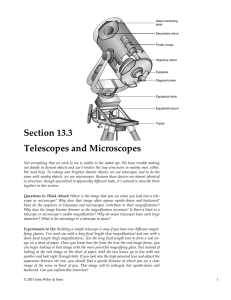
Section 13.3 Telescopes and Microscopes
... visual telescope doesn’t create a real image behind its final lens. Instead, it creates a virtual image in front of its final lens. To understand a visual telescope, imagine removing the film or light sensor from a photographic telescope. With nothing to stop it, light continues past the real image ...
... visual telescope doesn’t create a real image behind its final lens. Instead, it creates a virtual image in front of its final lens. To understand a visual telescope, imagine removing the film or light sensor from a photographic telescope. With nothing to stop it, light continues past the real image ...
The Response of Polarization Maintaining Fibers upon Temperature
... radiation with no disturbance of external thermal field, the phase shift φ will be equal to zero and the corresponding Stokes component S2 = 0. For optical fiber length different from a multiple of its beat length and without effect of the external thermal field disturbance the phase shift will be n ...
... radiation with no disturbance of external thermal field, the phase shift φ will be equal to zero and the corresponding Stokes component S2 = 0. For optical fiber length different from a multiple of its beat length and without effect of the external thermal field disturbance the phase shift will be n ...
Interferometry
Interferometry is a family of techniques in which waves, usually electromagnetic, are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, and velocimetry.Interferometers are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of small displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In analytical science, interferometers are used in continuous wave Fourier transform spectroscopy to analyze light containing features of absorption or emission associated with a substance or mixture. An astronomical interferometer consists of two or more separate telescopes that combine their signals, offering a resolution equivalent to that of a telescope of diameter equal to the largest separation between its individual elements.