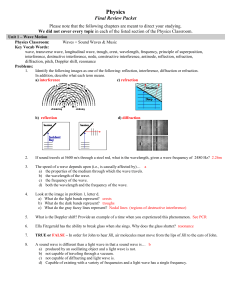
Diffraction-of-light
... Optical effects resulting from diffraction are produced through the interference of light waves. To visualize this, imagine light waves as water waves. If water waves contact a float on the water surface, the float would bounce up and down in response to the oncoming waves, thenproducing more waves ...
... Optical effects resulting from diffraction are produced through the interference of light waves. To visualize this, imagine light waves as water waves. If water waves contact a float on the water surface, the float would bounce up and down in response to the oncoming waves, thenproducing more waves ...
12 Using LEDs to Measure Planck`s Constant
... where e is 1.6 x 10-19 Coulombs, Vthreshold is in Volts, and f is in 1/seconds. When these units are used, Planck’s constant will be in units of Joules x seconds (Js). Using the data that we collected in the first two activities and the equations found above, record and determine the values for each ...
... where e is 1.6 x 10-19 Coulombs, Vthreshold is in Volts, and f is in 1/seconds. When these units are used, Planck’s constant will be in units of Joules x seconds (Js). Using the data that we collected in the first two activities and the equations found above, record and determine the values for each ...
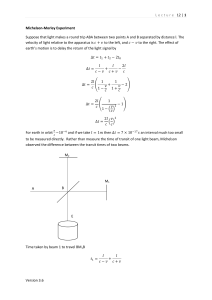
Lecture 12 | 1 Version 3.6 Michelson
... expected to show periodic changes in direction and magnitude during the course of a sidereal day. Because of the motion of the Earth around the Sun, it was expected that yearly cycles would also be detectable in the measured data. ...
... expected to show periodic changes in direction and magnitude during the course of a sidereal day. Because of the motion of the Earth around the Sun, it was expected that yearly cycles would also be detectable in the measured data. ...
Spectroscopy - Universität Wien
... With strong external field: splitting (S = +1/2 and S = -1/2) (here: EPR spectra are obtained by keeping the microwave frequency constant and varying the magnetic field until resonance is reached) → Effect of the (spinning) nucleus on unpaired electrons: hyperfine coupling tensor, leads to hyperfine ...
... With strong external field: splitting (S = +1/2 and S = -1/2) (here: EPR spectra are obtained by keeping the microwave frequency constant and varying the magnetic field until resonance is reached) → Effect of the (spinning) nucleus on unpaired electrons: hyperfine coupling tensor, leads to hyperfine ...
1s + 2p
... of different energy, one considers a wavefunction of the form eit + eit . If 1 and 2 are different, this means that the two spatial functions cycle in- and out-of-phase with one another. If at a certain time they add, at a time 0.5/(1-2) later they will subtract. e.g. (1s+2pz) will becom ...
... of different energy, one considers a wavefunction of the form eit + eit . If 1 and 2 are different, this means that the two spatial functions cycle in- and out-of-phase with one another. If at a certain time they add, at a time 0.5/(1-2) later they will subtract. e.g. (1s+2pz) will becom ...
Introduction to Fiber Optics
... travels in straight lines, so it is no problem. What if the hallway has a bend in it? You could place a mirror at the bend to reflect the light beam around the corner. What if the hallway is very winding with multiple bends? You might line the walls with mirrors and angle the beam so that it bounces ...
... travels in straight lines, so it is no problem. What if the hallway has a bend in it? You could place a mirror at the bend to reflect the light beam around the corner. What if the hallway is very winding with multiple bends? You might line the walls with mirrors and angle the beam so that it bounces ...
Light - UDChemistry
... Wave Nature of Light • Rutherford’s model of the atom could not explain chemical behavior • Bohr and others described the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus • These arrangements could account for differences between the elements • Bohr’s model was based on spectroscopic ...
... Wave Nature of Light • Rutherford’s model of the atom could not explain chemical behavior • Bohr and others described the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus • These arrangements could account for differences between the elements • Bohr’s model was based on spectroscopic ...
The structure of the energy bands and optical absorption in osmium
... low-energy peak A is also raised on the theoretical curve. In addition, the calculation gives a whole array of peaks in the spectral range 5.5-9 eV, which are not found experimentally. These peaks are formed by electronic transitions from the filled part of the d band to empty states of the d or mix ...
... low-energy peak A is also raised on the theoretical curve. In addition, the calculation gives a whole array of peaks in the spectral range 5.5-9 eV, which are not found experimentally. These peaks are formed by electronic transitions from the filled part of the d band to empty states of the d or mix ...
Document
... Planck developed a formula for the spectrum that explains the observed spectrum behavior. • Planck’s hypothesis: - Blackbody radiation is produced by submicroscopic charged oscillation (resonators). - The resonators are allowed to have only certain discrete energies given by: n = quantum number (po ...
... Planck developed a formula for the spectrum that explains the observed spectrum behavior. • Planck’s hypothesis: - Blackbody radiation is produced by submicroscopic charged oscillation (resonators). - The resonators are allowed to have only certain discrete energies given by: n = quantum number (po ...
doc - The Crowned Anarchist Literature
... Interferometer, instrument that utilizes the phenomenon of interference of light waves for the ultraprecise measurement of wavelengths of light itself, of small distances, and of certain optical phenomena. Because the instrument measures distances in terms of light waves, it permits the definition o ...
... Interferometer, instrument that utilizes the phenomenon of interference of light waves for the ultraprecise measurement of wavelengths of light itself, of small distances, and of certain optical phenomena. Because the instrument measures distances in terms of light waves, it permits the definition o ...
Optical Activity - Chemistry With BT
... A substance is optically active if it rotates the plane of polarized light. In order for a substance to exhibit optical activity, it must be chiral and one enantiomer must be present in excess of the other. ...
... A substance is optically active if it rotates the plane of polarized light. In order for a substance to exhibit optical activity, it must be chiral and one enantiomer must be present in excess of the other. ...
Optical Activity
... Optically active organic molecules have a spiral structure like a right-handed or lefthanded screw. It is this spiral nature of the molecule, which rotates the plane of polarization of light passing through it. Right-handed molecules will rotate the plane of polarization clockwise as viewed in the d ...
... Optically active organic molecules have a spiral structure like a right-handed or lefthanded screw. It is this spiral nature of the molecule, which rotates the plane of polarization of light passing through it. Right-handed molecules will rotate the plane of polarization clockwise as viewed in the d ...
Fiber Optic
... The receiver includes a light detector or photocell and a decoder. The light detector is very often either a PIN (p-typeintrinsic-n-type) diode or an APD (avalanche photodiode). The light detector, acting as the receiving element, converts the received light pulses back to pulses of electrical curre ...
... The receiver includes a light detector or photocell and a decoder. The light detector is very often either a PIN (p-typeintrinsic-n-type) diode or an APD (avalanche photodiode). The light detector, acting as the receiving element, converts the received light pulses back to pulses of electrical curre ...
Instruction Manual PH511: Physics Laboratory-III DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
... Now consider applying a weak magnetic field H1 oriented in the XY plane and rotating about Zaxis (Fig. 1.1b) in the same direction as the Larmor precession. If the angular frequency w1 of the magnetic field is not equal to wo , then the angle q between m and H1will continuously change and hence the ...
... Now consider applying a weak magnetic field H1 oriented in the XY plane and rotating about Zaxis (Fig. 1.1b) in the same direction as the Larmor precession. If the angular frequency w1 of the magnetic field is not equal to wo , then the angle q between m and H1will continuously change and hence the ...
Cristaux Photoniques, PO-014 Ecole doctorale photonique Romuald
... Reflectivity & transmission measurements Quantitative measurement Note: it is not easy to measure directly reflectivity coefficients close to unity This would imply being able to discriminate between e.g. R=0.999 and R=0.997 Usually much more convenient to use the mirror to make a high Q optical cav ...
... Reflectivity & transmission measurements Quantitative measurement Note: it is not easy to measure directly reflectivity coefficients close to unity This would imply being able to discriminate between e.g. R=0.999 and R=0.997 Usually much more convenient to use the mirror to make a high Q optical cav ...