Title of the communication (Times new Roman 16 bold
... Femtosecond absorption spectroscopy (left) reveals three kinetic processes. The excited state of NBA decays within 0.5 ps, an intermediate I has a lifetime of 70 ps and an intermediate II vanishes in ~ 2 ns. Addition of water reduces the lifetime of the intermediate I but does not affect the other p ...
... Femtosecond absorption spectroscopy (left) reveals three kinetic processes. The excited state of NBA decays within 0.5 ps, an intermediate I has a lifetime of 70 ps and an intermediate II vanishes in ~ 2 ns. Addition of water reduces the lifetime of the intermediate I but does not affect the other p ...
Facts About Ultra Violet (UV) Lights
... more than once every 8 hours will diminish the longevity of the bulb. There are factors that will influence sensitivity of bacteria to UV. High humidity and low temperature will decrease its effectiveness. Temperatures of 36 degrees will reduce the efficiency to approximately 60%. ...
... more than once every 8 hours will diminish the longevity of the bulb. There are factors that will influence sensitivity of bacteria to UV. High humidity and low temperature will decrease its effectiveness. Temperatures of 36 degrees will reduce the efficiency to approximately 60%. ...
exam solutions
... function of the analyzer angle. The results are shown in the plots below. For each plot, identify the polarization state of the source and give a plausible argument as to why you have identified it as such. Elliptical polarization: The irradiance changes between two extrema at angles that correspond ...
... function of the analyzer angle. The results are shown in the plots below. For each plot, identify the polarization state of the source and give a plausible argument as to why you have identified it as such. Elliptical polarization: The irradiance changes between two extrema at angles that correspond ...
Assignment #2 - Rose
... in the z = 0 plane, with the beam waist radii w0x and w0y in the x and y-directions respectively. The contours of constant intensity are therefore ellipses instead of circles. Write expressions for the beam depth of focus, angular divergence, and radii of curvature in the x and y-directions, as func ...
... in the z = 0 plane, with the beam waist radii w0x and w0y in the x and y-directions respectively. The contours of constant intensity are therefore ellipses instead of circles. Write expressions for the beam depth of focus, angular divergence, and radii of curvature in the x and y-directions, as func ...
lecture 36 - waves in 3 dimensions, optical devices
... What do you want the wave’s amplitude to be? What frequency (or velocity) do you want the wave to have? What do you want the overall phase of the wave to be? ...
... What do you want the wave’s amplitude to be? What frequency (or velocity) do you want the wave to have? What do you want the overall phase of the wave to be? ...
Read more - Consumer Physics
... The simple model of springs and balls to describe molecules is quite useful to get some intuition about the vibrations of the molecules. There are, however, differences between molecules and the daily life springs and balls. Maybe the most striking difference is the quantum nature of the molecules v ...
... The simple model of springs and balls to describe molecules is quite useful to get some intuition about the vibrations of the molecules. There are, however, differences between molecules and the daily life springs and balls. Maybe the most striking difference is the quantum nature of the molecules v ...
1 Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves 2 Speed of an
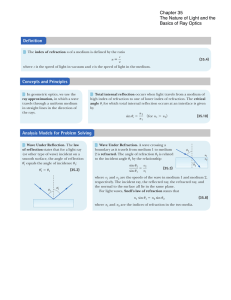
... 1. The incident, reflected, and refracted rays, and the normal to the surface, all lie in the same plane. 2. The angle of reflection Θr is equal to the angle of incidence Θa for all wavelengths and for any pair of substances; Θr = Θa . Law of reflection. 3. With qualifiers, the ratio of the sines of ...
... 1. The incident, reflected, and refracted rays, and the normal to the surface, all lie in the same plane. 2. The angle of reflection Θr is equal to the angle of incidence Θa for all wavelengths and for any pair of substances; Θr = Θa . Law of reflection. 3. With qualifiers, the ratio of the sines of ...
Youngs Double Slit
... Bring the slit up close to the eye and view the light source. What do you see? The interference pattern can only occur when the light diffracted by the two slits is coherent or in phase with each other. Coherence can be achieved with a laser, however Thomas Young performed this experiment in 1801 an ...
... Bring the slit up close to the eye and view the light source. What do you see? The interference pattern can only occur when the light diffracted by the two slits is coherent or in phase with each other. Coherence can be achieved with a laser, however Thomas Young performed this experiment in 1801 an ...
Luminescence spectroscopy
... of translation motion of the molecular fragments. Molecular Luminescence Spectroscopy Luminescence spectroscopy is a technique which studies the fluorescence, phosphorescence, and chemiluminescence of chemical systems. Fluorescence is light emission caused by irradiation with light (normally visible ...
... of translation motion of the molecular fragments. Molecular Luminescence Spectroscopy Luminescence spectroscopy is a technique which studies the fluorescence, phosphorescence, and chemiluminescence of chemical systems. Fluorescence is light emission caused by irradiation with light (normally visible ...
Unit 13: EM Radiation and Waves
... Electromagnetic Waves Since a changing electric field produces a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field produces an electric field, once sinusoidal fields are created they can propagate on their own. These propagating fields are called electromagnetic waves. ...
... Electromagnetic Waves Since a changing electric field produces a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field produces an electric field, once sinusoidal fields are created they can propagate on their own. These propagating fields are called electromagnetic waves. ...
Optical Fiber communication
... used in Fiber-optic communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than other forms of communication. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are also immune to electromagnetic interference. ...
... used in Fiber-optic communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than other forms of communication. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are also immune to electromagnetic interference. ...
Final Exam - Department of Physics and Astronomy : University of
... Yellow light (λ = 600 nm) is used to view an object under a microscope. The object lens diameter is 10.00 mm. (a) What is the limiting angle of resolution (i.e. angle of diffraction)? (b) Suppose it is possible to use visible light of any wavelength. What color should you choose to give the smallest ...
... Yellow light (λ = 600 nm) is used to view an object under a microscope. The object lens diameter is 10.00 mm. (a) What is the limiting angle of resolution (i.e. angle of diffraction)? (b) Suppose it is possible to use visible light of any wavelength. What color should you choose to give the smallest ...
Chapter 7 Components of Optical Instruments
... Main component - lasing medium, can be ruby, a semiconductor, solution of an organic dye, a gas(Ar. or Kr) ...
... Main component - lasing medium, can be ruby, a semiconductor, solution of an organic dye, a gas(Ar. or Kr) ...
File - Pragati fast updates
... Linearly, Circular and Elliptical polarization: Experimentally, it is found that the light exhibits the following three types of polarization. 1. Plane polarized light 2. Circularly polarized light 3. Elliptically polarized light. 1. Plane Polarized light: If the electric component of light passing ...
... Linearly, Circular and Elliptical polarization: Experimentally, it is found that the light exhibits the following three types of polarization. 1. Plane polarized light 2. Circularly polarized light 3. Elliptically polarized light. 1. Plane Polarized light: If the electric component of light passing ...
DESCRIPTION FOR THE GENERAL PUBLIC Luminescent materials
... DESCRIPTION FOR THE GENERAL PUBLIC Luminescent materials are defined as the materials revealing light emission cause by external stimuli. There are several types of luminescence differing in the source of light generation. For instance, photoluminescence is induced by the absorption of photons, whic ...
... DESCRIPTION FOR THE GENERAL PUBLIC Luminescent materials are defined as the materials revealing light emission cause by external stimuli. There are several types of luminescence differing in the source of light generation. For instance, photoluminescence is induced by the absorption of photons, whic ...
Efficient and fast optical phase conjugation orientation of angular momentum
... to form a grating. Recently, we observed four-wave mixing by use of CPT in a cryogenically cooled solid as well.5 However, for practical devices there are several problems with this double-L system. In the case of sodium, for example, the probe beam has to be detuned from one of the pump beams by ne ...
... to form a grating. Recently, we observed four-wave mixing by use of CPT in a cryogenically cooled solid as well.5 However, for practical devices there are several problems with this double-L system. In the case of sodium, for example, the probe beam has to be detuned from one of the pump beams by ne ...
Random Laser - Department of Physics
... electron can relax to a lower energy state. Two emission processes participate in this relaxation, which can be categorized as either radiative processes (such as CL) or non-radiative processes (such as phonon emission, capture by deep centers, or the Auger effect). In general, higher energy (higher ...
... electron can relax to a lower energy state. Two emission processes participate in this relaxation, which can be categorized as either radiative processes (such as CL) or non-radiative processes (such as phonon emission, capture by deep centers, or the Auger effect). In general, higher energy (higher ...