Electromagnetic Waves - University of Toronto Physics
... 2. The fields E and B are perpendicular to each other in a manner such that E × B is in the direction of energy propagation. 3. The wave travels in vacuum at speed c. 4. E = cB at any point on the wave. ...
... 2. The fields E and B are perpendicular to each other in a manner such that E × B is in the direction of energy propagation. 3. The wave travels in vacuum at speed c. 4. E = cB at any point on the wave. ...
Document
... If e-’s are in quantized energy states, then DE of states can have only certain values. This explains sharp line spectra. E = -C ...
... If e-’s are in quantized energy states, then DE of states can have only certain values. This explains sharp line spectra. E = -C ...
Document
... ('particles' of light) must bounce back and forth until they can escape at the correct frequency. A red laser would produce light with a wavelength around 700nm, so the main lasing unit must be at least 350nm. This is much larger than the 32nm features that are being etched on silicon today. Because ...
... ('particles' of light) must bounce back and forth until they can escape at the correct frequency. A red laser would produce light with a wavelength around 700nm, so the main lasing unit must be at least 350nm. This is much larger than the 32nm features that are being etched on silicon today. Because ...
An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption
... Chemical deviations from Beer’s law are caused by shifts in the position of a chemical or physical equilibrium involving the absorbing species. A common example of this behavior is found with acid/base indicators. Deviations arising from chemical factors can only be observed when concentrations are ...
... Chemical deviations from Beer’s law are caused by shifts in the position of a chemical or physical equilibrium involving the absorbing species. A common example of this behavior is found with acid/base indicators. Deviations arising from chemical factors can only be observed when concentrations are ...
Beam Splitters A beam splitter is a device that`s used to divide an
... A mirror is a smooth surface that can reflect enough light to serve a useful purpose. Mirrors have been used since man first saw his image in a calm pool of water. They have progressed from the great silver-blackened hall mirrors of the eighteenth century to where, today, they are used to reflect li ...
... A mirror is a smooth surface that can reflect enough light to serve a useful purpose. Mirrors have been used since man first saw his image in a calm pool of water. They have progressed from the great silver-blackened hall mirrors of the eighteenth century to where, today, they are used to reflect li ...
Resolution questions with solutions
... central maximum around X; correct overall shape (only two secondary maxima need be shown); secondary maxima much less intense than the central maximum; ...
... central maximum around X; correct overall shape (only two secondary maxima need be shown); secondary maxima much less intense than the central maximum; ...
The Nature of Light
... The apparent magnitude of a star is given by m = -2.5log(Fobs). Greater magnitude refers to dimmer stars. An m1 star is brighter than an m6 star by 100 times. The brightest star (Sirius A) in the sky is -1.4 in magnitude. Ex.6a: the intrinsic luminosity of the Sun is 3.8x1026 W, and its radiant flux ...
... The apparent magnitude of a star is given by m = -2.5log(Fobs). Greater magnitude refers to dimmer stars. An m1 star is brighter than an m6 star by 100 times. The brightest star (Sirius A) in the sky is -1.4 in magnitude. Ex.6a: the intrinsic luminosity of the Sun is 3.8x1026 W, and its radiant flux ...
Instrumental Methods of Analysis
... • Deuterating convenient way to confirm presence of particular type of bond, since frequency shift is relatively large and predictable. Chem 422 ...
... • Deuterating convenient way to confirm presence of particular type of bond, since frequency shift is relatively large and predictable. Chem 422 ...
Molecular Term Symbols
... The Franck-Condon factor shows, the probability of a vibrationalelectronic transition is governed by the overlap between the final and initial vibrational wave functions at fixed internuclear distances. Moreover, in the simplest sense, we can take the initial states to be ground molecular electronic ...
... The Franck-Condon factor shows, the probability of a vibrationalelectronic transition is governed by the overlap between the final and initial vibrational wave functions at fixed internuclear distances. Moreover, in the simplest sense, we can take the initial states to be ground molecular electronic ...
Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom
... Schrodinger's equation lets us calculate the probability that an electron is at a particular point in space. The region of space an e– is most likely to be found is called an atomic orbital. The atomic orbital is often represented as an electron density cloud around the nucleus. The density cloud is ...
... Schrodinger's equation lets us calculate the probability that an electron is at a particular point in space. The region of space an e– is most likely to be found is called an atomic orbital. The atomic orbital is often represented as an electron density cloud around the nucleus. The density cloud is ...
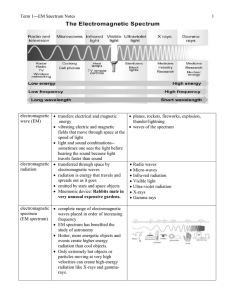
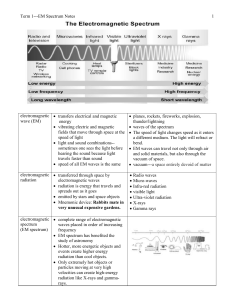
EM Spectrum Notes - Biloxi Public Schools
... Term 1---EM Spectrum Notes blue shift objects moving towards Earth shorter wavelength ...
... Term 1---EM Spectrum Notes blue shift objects moving towards Earth shorter wavelength ...
Chapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... classic wave theory attributed this effect to the light energy being transferred to the electron according to this theory, if the wavelength of light is made shorter, or the light waves intensity made brighter, more electrons should be ejected ...
... classic wave theory attributed this effect to the light energy being transferred to the electron according to this theory, if the wavelength of light is made shorter, or the light waves intensity made brighter, more electrons should be ejected ...
Spectroscopic methods for biology and medicine
... Detection of particles other than photons Spectroscopic or spectrometric information can be gained from the interaction of the sample with particles other than photons. Electrons have a much shorter deBroglie wavelength than X-Ray photons and can be used for absorption or diffraction experiments wit ...
... Detection of particles other than photons Spectroscopic or spectrometric information can be gained from the interaction of the sample with particles other than photons. Electrons have a much shorter deBroglie wavelength than X-Ray photons and can be used for absorption or diffraction experiments wit ...
Why The Sky Is Blue
... intensity as a function of angle from the sun, polarization of the light, dust is typically not small compared to the wavelengths of light, and so Rayleigh scattering is not occurring, etc. Rayleigh scattering applies to more than just light; it works for sound as well under the right circumstances. ...
... intensity as a function of angle from the sun, polarization of the light, dust is typically not small compared to the wavelengths of light, and so Rayleigh scattering is not occurring, etc. Rayleigh scattering applies to more than just light; it works for sound as well under the right circumstances. ...