13 - Cengage Learning
... • Childhood Disintegrative Disorder: Characterized by significant regression in several areas of functioning following at least 2 years of normal development. Affected areas may include language and communication skills, social skills, motor skills, and bowel or bladder control ...
... • Childhood Disintegrative Disorder: Characterized by significant regression in several areas of functioning following at least 2 years of normal development. Affected areas may include language and communication skills, social skills, motor skills, and bowel or bladder control ...
Personality Disorder
... Psychoanalysts blame an inadequate resolution to the Oedipal complex for personality disorders, stating that this results in a poorly developed superego. Cognitive-learning theorists see personality disorders as a set of learned behavior that has become maladaptive— bad habits learned early on i ...
... Psychoanalysts blame an inadequate resolution to the Oedipal complex for personality disorders, stating that this results in a poorly developed superego. Cognitive-learning theorists see personality disorders as a set of learned behavior that has become maladaptive— bad habits learned early on i ...
Learning
... thought, feeling or behavior that disrupt an individual’s sense of well-being or social/occupational functioning • Psycho – Involves the brain and personality ...
... thought, feeling or behavior that disrupt an individual’s sense of well-being or social/occupational functioning • Psycho – Involves the brain and personality ...
Sign and Symptoms
... catatonic posturing Voluntary assumption of an inappropriate or bizarre posture, generally maintained for long periods of time. May switch unexpectedly with catatonic excitement. catatonic rigidity Fixed and sustained motoric position that is resistant to change. P.275 catatonic stupor Stupor in whi ...
... catatonic posturing Voluntary assumption of an inappropriate or bizarre posture, generally maintained for long periods of time. May switch unexpectedly with catatonic excitement. catatonic rigidity Fixed and sustained motoric position that is resistant to change. P.275 catatonic stupor Stupor in whi ...
Co-Occurring Disorders
... Definitions 1 • Dual Diagnosis (DD) was an early term used for the presence of a mental disorder and a SADO • DD has been used interchangeably with Co-occurring disorders and co-morbidity. • But DSM IV TR also uses co-morbidity to describe two mental disorders in the same person • And DSM IV TR doe ...
... Definitions 1 • Dual Diagnosis (DD) was an early term used for the presence of a mental disorder and a SADO • DD has been used interchangeably with Co-occurring disorders and co-morbidity. • But DSM IV TR also uses co-morbidity to describe two mental disorders in the same person • And DSM IV TR doe ...
General Psychology - K-Dub
... didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop… The clothes hung… two fingers apart… I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house… I had constant anxiety… I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
... didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop… The clothes hung… two fingers apart… I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house… I had constant anxiety… I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
Chapter 27 SEVERE PSYCHIATRIC ILLNESS IN THE MILITARY
... to wait to see if the symptoms persist over time; it is estimated that 25% of these cases will resolve.3 Unfortunately for many patients, both brief psychotic disorder and schizophreniform disorder may serve only as place markers in the timeline of new onset schizophrenia, most commonly a chronic an ...
... to wait to see if the symptoms persist over time; it is estimated that 25% of these cases will resolve.3 Unfortunately for many patients, both brief psychotic disorder and schizophreniform disorder may serve only as place markers in the timeline of new onset schizophrenia, most commonly a chronic an ...
Co-occurring addiction and mental disorders
... Bipolar vs Sub induced sytmptoms Types of substance Addiction vs Psych behavioral problems Denial ...
... Bipolar vs Sub induced sytmptoms Types of substance Addiction vs Psych behavioral problems Denial ...
Abnormal psychology: concepts of normality
... behaviour is referred to as psychopathology—that is, psychological (or mental) illness that is based on the observed symptoms of a patient. The term “mental disorder” is used in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders published by the American Psychiatric Association (called DSM-IV ...
... behaviour is referred to as psychopathology—that is, psychological (or mental) illness that is based on the observed symptoms of a patient. The term “mental disorder” is used in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders published by the American Psychiatric Association (called DSM-IV ...
Menstrual Cycle in Schizophrenic Patients: Review with a Case
... enough response to the antipsychotic treatment in menstrual psychosis (27). In the scope of these characteristics, we considered that our patient, who was followed-up because of a diagnosis of schizophrenia and treated with antipsychotic therapy for the past two decades, should be diagnosed schizoph ...
... enough response to the antipsychotic treatment in menstrual psychosis (27). In the scope of these characteristics, we considered that our patient, who was followed-up because of a diagnosis of schizophrenia and treated with antipsychotic therapy for the past two decades, should be diagnosed schizoph ...
Clinical Psychology II - Therapies The Big Picture
... • On Being Sane in Insane Places - A study of how being perceived as insane colours other people’s perception of you. ...
... • On Being Sane in Insane Places - A study of how being perceived as insane colours other people’s perception of you. ...
Mental Illness for Individuals with IDD
... supports. The solution must fit the problem! *Fosters empathy and allows us to be more patient when a client is exhibiting challenging behaviors. *Enables us to help our clients understand their experiences. *Makes us better advocates for our clients with doctors, case managers, psychiatrists, behav ...
... supports. The solution must fit the problem! *Fosters empathy and allows us to be more patient when a client is exhibiting challenging behaviors. *Enables us to help our clients understand their experiences. *Makes us better advocates for our clients with doctors, case managers, psychiatrists, behav ...
resource - Primary and Integrated Mental Health Care
... • Assess for most common risk factors: high levels of distress, well formed plans (suicide note), hopelessness, distressing psychotic symptoms (command hallucinations), pain or chronic illness, lack of social supports (young single male/unemployed), substance misuse • Listen to your “gut feeling” an ...
... • Assess for most common risk factors: high levels of distress, well formed plans (suicide note), hopelessness, distressing psychotic symptoms (command hallucinations), pain or chronic illness, lack of social supports (young single male/unemployed), substance misuse • Listen to your “gut feeling” an ...
Progress Tracker
... (Note that examples were added to criterion to facilitate application across life span [child, adolescent, adult]). 4) Several inattentive or hyperactive/impulsive symptoms are present in two or more settings (eg, at home, school, or work; with friends or relatives; in other activities). 5) There ...
... (Note that examples were added to criterion to facilitate application across life span [child, adolescent, adult]). 4) Several inattentive or hyperactive/impulsive symptoms are present in two or more settings (eg, at home, school, or work; with friends or relatives; in other activities). 5) There ...
Attribution bias and social anxiety in schizophrenia
... delusions but showed no differences related to comorbid SAD. Although it has been suggested that people with persecutory delusions show increased biases in general (Bentall et al., 1994; Kinderman and Bentall, 1997; Martin and Penn, 2002), the results here suggest that different biases are rather li ...
... delusions but showed no differences related to comorbid SAD. Although it has been suggested that people with persecutory delusions show increased biases in general (Bentall et al., 1994; Kinderman and Bentall, 1997; Martin and Penn, 2002), the results here suggest that different biases are rather li ...
Psychological Disorders
... and presents a better prognosis for recovery with no recurrance. This is not true for gradual onset schizophrenia. IV. Long-term outcome studies regarding schizophrenia indicate that recovery may be more rapid in developing countries than in the U.S., Europe, or Russia. This may be due to greater ac ...
... and presents a better prognosis for recovery with no recurrance. This is not true for gradual onset schizophrenia. IV. Long-term outcome studies regarding schizophrenia indicate that recovery may be more rapid in developing countries than in the U.S., Europe, or Russia. This may be due to greater ac ...
Disruptive insights in psychiatry - Journal of Clinical Investigation
... patients unable to work or function during an episode. In contrast to many other disabling, chronic illnesses, mental disorders begin early in life. There are, of course, mental disorders that we associate with childhood, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and ASD. But even for ...
... patients unable to work or function during an episode. In contrast to many other disabling, chronic illnesses, mental disorders begin early in life. There are, of course, mental disorders that we associate with childhood, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and ASD. But even for ...
Chapter 22
... or early in adulthood, usually before the age of 30. Although the disorder has been diagnosed in children, approximately 75% of persons diagnosed as having schizophrenia develop the clinical symptoms between the ages of 16 and 25. ...
... or early in adulthood, usually before the age of 30. Although the disorder has been diagnosed in children, approximately 75% of persons diagnosed as having schizophrenia develop the clinical symptoms between the ages of 16 and 25. ...
Classification of Mental Disorders
... Not all AOD workers are able to formally diagnose the presence or absence of mental health disorders ...
... Not all AOD workers are able to formally diagnose the presence or absence of mental health disorders ...
Revisiting unitary psychosis, from nosotaxis to
... be in these assessments, the real difficulty lies in the fact that most of the time the resemblance is in the clinical core and not in the periphery, as we will discuss later with regard to bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. In this regard, it is very likely that there is more overlapping between d ...
... be in these assessments, the real difficulty lies in the fact that most of the time the resemblance is in the clinical core and not in the periphery, as we will discuss later with regard to bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. In this regard, it is very likely that there is more overlapping between d ...
Workbook Assignment 4 Chapters 12 and 13 to correspond with
... Why did Dr Anderson talk to the wall? (this is part of a lecture and can only be answered after Dr Anderson has given this lecture). ...
... Why did Dr Anderson talk to the wall? (this is part of a lecture and can only be answered after Dr Anderson has given this lecture). ...
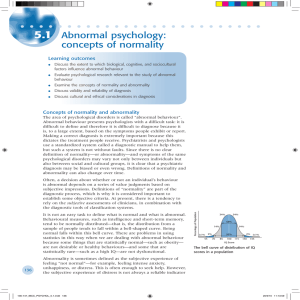
Abnormal Psychology: Concepts of Normality
... DSM-III for anxiety disorders. Two clinicians separately diagnosed 267 individuals seeking treatment for anxiety and stress disorders. They found high reliability for obsessive compulsive disorder (.80), but very low reliability for assessing generalized anxiety disorder, (.57), mainly due to proble ...
... DSM-III for anxiety disorders. Two clinicians separately diagnosed 267 individuals seeking treatment for anxiety and stress disorders. They found high reliability for obsessive compulsive disorder (.80), but very low reliability for assessing generalized anxiety disorder, (.57), mainly due to proble ...
PSYCHOSIS
... to medical conditions, substance intox or w/d, or focal brain lesions • Functional/Primary= psychoses originating from psychiatric illness (Schizophrenia, Major Depression, Bipolar Dis or Schizoaffective Disorder) ...
... to medical conditions, substance intox or w/d, or focal brain lesions • Functional/Primary= psychoses originating from psychiatric illness (Schizophrenia, Major Depression, Bipolar Dis or Schizoaffective Disorder) ...