Slide 1
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
ECEN 4616/5616 Optoelectronic Design
... away from the space telescope such that it blocks the light from the target star, but not from the star’s planets. A key element in this line of research is to find aperture shapes which have extremely small amounts of diffracted light on axis – that is, they create extremely dark shadows. ...
... away from the space telescope such that it blocks the light from the target star, but not from the star’s planets. A key element in this line of research is to find aperture shapes which have extremely small amounts of diffracted light on axis – that is, they create extremely dark shadows. ...
Exercise 13 Geometrical and Technical Optics WS 2013/2014
... A pure planoconvex lens with 100 mm focal length at d has a radius of curvature of: R n 1 f ' 51.68 mm In this case the aberrations for 40 mm beam diameter are (again first surface at z=-6 mm and second surface at z=0 mm): =587.6 nm: z_Focus: 92.981 mm, spot radius: 0.161 mm, P/V wave abe ...
... A pure planoconvex lens with 100 mm focal length at d has a radius of curvature of: R n 1 f ' 51.68 mm In this case the aberrations for 40 mm beam diameter are (again first surface at z=-6 mm and second surface at z=0 mm): =587.6 nm: z_Focus: 92.981 mm, spot radius: 0.161 mm, P/V wave abe ...
A method for characterizing longitudinal chromatic aberration of
... system, Fig. 1, the same optical fibre (SM450, Fibrecore Ltd, which is single moded at wavelengths greater than 450 nm) is used both to launch light into the microscope system and to detect the confocal signal. The reciprocal geometry is used so as to avoid unnecessary pinhole alignment difficulties ...
... system, Fig. 1, the same optical fibre (SM450, Fibrecore Ltd, which is single moded at wavelengths greater than 450 nm) is used both to launch light into the microscope system and to detect the confocal signal. The reciprocal geometry is used so as to avoid unnecessary pinhole alignment difficulties ...
Projecting Chromatic Aberrations
... The diagrams in Figure 1 were generated by the program RAYS, created with Layhey Fortran 90 14 by Phil Ryan in Dr. James L. Garner's PHY 3424 optics class at the University of North Florida. RAYS models non-paraxial rays and spherical thick lenses by calculating the angle of refraction for each ray ...
... The diagrams in Figure 1 were generated by the program RAYS, created with Layhey Fortran 90 14 by Phil Ryan in Dr. James L. Garner's PHY 3424 optics class at the University of North Florida. RAYS models non-paraxial rays and spherical thick lenses by calculating the angle of refraction for each ray ...
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
... that the microscope might reveal the “corpuscles” thought to be the elementary constituents of matter. When this proved not to be the case, interest in microscopy ebbed for almost two centuries. In the late nineteenth century, optical microscopy rebounded as mass-produced instruments with fewer dist ...
... that the microscope might reveal the “corpuscles” thought to be the elementary constituents of matter. When this proved not to be the case, interest in microscopy ebbed for almost two centuries. In the late nineteenth century, optical microscopy rebounded as mass-produced instruments with fewer dist ...
Intraocular Lenses
... plate is proportional to , so different colors focus at different distances from the zone plate. Ordinary refractive lenses have chromatic aberration as well, but much less pronounced than zone plates. For example: +10 D lens made of glass with an Abbe number of 30 (high dispersion) has CA ~ 0.3 D ...
... plate is proportional to , so different colors focus at different distances from the zone plate. Ordinary refractive lenses have chromatic aberration as well, but much less pronounced than zone plates. For example: +10 D lens made of glass with an Abbe number of 30 (high dispersion) has CA ~ 0.3 D ...
Lab 15 - College of San Mateo
... 4. Repeat step 2 with the lens at 60.0 cm. 5. Repeat step 2 with the lens at 55.0 cm. 6. Leave the long focus converging lens in place and place the screen at the 105.0 cm mark. Place the diverging lens between the converging lens and the screen. Move only the diverging lens until the image comes in ...
... 4. Repeat step 2 with the lens at 60.0 cm. 5. Repeat step 2 with the lens at 55.0 cm. 6. Leave the long focus converging lens in place and place the screen at the 105.0 cm mark. Place the diverging lens between the converging lens and the screen. Move only the diverging lens until the image comes in ...
Introduction to Mirrors and Lenses
... The size and location of an image formed by a lens can be found by using the information from these two rays which is shown in the illustration below. The following illustration depicts two rays, which are defined in the following text. A ray (1) parallel to the optical axis passes through the focal ...
... The size and location of an image formed by a lens can be found by using the information from these two rays which is shown in the illustration below. The following illustration depicts two rays, which are defined in the following text. A ray (1) parallel to the optical axis passes through the focal ...
Optical Term Definitions
... In an imaging system, depth of field refers to the distance in object space over which the system delivers an acceptably sharp image. The criteria for what is acceptably sharp is arbitrarily chosen by the user; depth of field increases with increasing f-number. For an imaging system, depth of focus ...
... In an imaging system, depth of field refers to the distance in object space over which the system delivers an acceptably sharp image. The criteria for what is acceptably sharp is arbitrarily chosen by the user; depth of field increases with increasing f-number. For an imaging system, depth of focus ...
Non-invasive ophthalmic imaging of adult zebrafish eye using
... mean retinal thickness and effective refractive index of the crystalline lens. Keywords: Eyes, non-invasive ophthalmic imaging, optical coherence tomography, zebrafish. USE of optical techniques for biomedical imaging is a topic of considerable current interest. This is motivated by the potential of ...
... mean retinal thickness and effective refractive index of the crystalline lens. Keywords: Eyes, non-invasive ophthalmic imaging, optical coherence tomography, zebrafish. USE of optical techniques for biomedical imaging is a topic of considerable current interest. This is motivated by the potential of ...
Following the path of light: recovering and
... Holography is an imaging technique that does not require lenses as is based on the registration on a photographic plate of the interference pattern produced by the light field diffracted by the object and a reference field.4 To register the interference, holography requires the use of laser light, that ...
... Holography is an imaging technique that does not require lenses as is based on the registration on a photographic plate of the interference pattern produced by the light field diffracted by the object and a reference field.4 To register the interference, holography requires the use of laser light, that ...
1 - Hodge Hill College
... 1.17 Explain refraction in terms of change of speed of radiation 1.18 Investigate the critical angle for perspex/air or glass/air or water/air boundaries 1.19 Investigate TIR between different media 1.20 Explain how TIR is used in optical fibres 1.21 Explain uses of optical fibres in endoscopes ...
... 1.17 Explain refraction in terms of change of speed of radiation 1.18 Investigate the critical angle for perspex/air or glass/air or water/air boundaries 1.19 Investigate TIR between different media 1.20 Explain how TIR is used in optical fibres 1.21 Explain uses of optical fibres in endoscopes ...
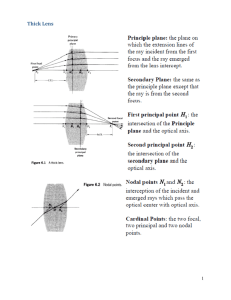
Thick Lens 1
... All modern astronomical telescopes have this basic configuration because it is much more practical to fabricate large mirrors than lenses. The size of the large main mirror (the entrance pupil) sets the diffraction limit. Also, a larger entrance pupil gathers more light, so that faint objects can be ...
... All modern astronomical telescopes have this basic configuration because it is much more practical to fabricate large mirrors than lenses. The size of the large main mirror (the entrance pupil) sets the diffraction limit. Also, a larger entrance pupil gathers more light, so that faint objects can be ...
Light - PhysicsDCS
... The angle of incidence ,i, is always equal to the angle of reflection, r. The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal all lie on the same plane. ...
... The angle of incidence ,i, is always equal to the angle of reflection, r. The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal all lie on the same plane. ...
Exposure and Imaging
... – The best lenses used in projection lithography have NA = 0.3 - 0.4 – A lens with NA = 0.50 is a f/1.00 lens: its focal length and effective diameter are the same! – The largest NA lenses ever made were a NA = 0.54 and a NA = 0.60 by Nikon. ...
... – The best lenses used in projection lithography have NA = 0.3 - 0.4 – A lens with NA = 0.50 is a f/1.00 lens: its focal length and effective diameter are the same! – The largest NA lenses ever made were a NA = 0.54 and a NA = 0.60 by Nikon. ...
[pdf]
... experimental images of absorbing and scattering objects in turbid media obtained by this approach. The method differs from least-squares techniques6 in that it is fast and noniterative. In addition to providing information about the position and shape of a hidden object or objects, projection images ...
... experimental images of absorbing and scattering objects in turbid media obtained by this approach. The method differs from least-squares techniques6 in that it is fast and noniterative. In addition to providing information about the position and shape of a hidden object or objects, projection images ...
Mirrors and Lenses
... The image in a plane mirror appears to be behind the mirror. The rays of light diverge at the location of the image. When the rays diverge, the image is called a virtual image. ...
... The image in a plane mirror appears to be behind the mirror. The rays of light diverge at the location of the image. When the rays diverge, the image is called a virtual image. ...
Concave Lenses and Mirrors
... In this part of the experimental tutorial you will determine the focal length of a converging lens then observe the change when the same lens is used in conjunction with a diverging lens. Measuring this change accurately will enable you to calculate the focal length of the diverging lens. Select a ...
... In this part of the experimental tutorial you will determine the focal length of a converging lens then observe the change when the same lens is used in conjunction with a diverging lens. Measuring this change accurately will enable you to calculate the focal length of the diverging lens. Select a ...
Answers - mackenziekim
... 10. A person's vision in one eye is corrected using a lens with a power of 5.2 d. Is the eye nearsighted or farsighted? 11. To direct parallel light rays through the slide, the light source of a projector is located at the centre of curvature of the converging mirror and at the principal focus of th ...
... 10. A person's vision in one eye is corrected using a lens with a power of 5.2 d. Is the eye nearsighted or farsighted? 11. To direct parallel light rays through the slide, the light source of a projector is located at the centre of curvature of the converging mirror and at the principal focus of th ...
Biology 3235: Resolution and magnification of a light microscopes
... shorter wavelengths of light also provide for greater resolution; smaller details can be resolved with blue light (λ = 480 nm) than with red light (λ = 650 nm). The NA of dry lenses is limited by the refractive index of air, and the phenomenon of internal reflection, to less than 1.0. By using oil b ...
... shorter wavelengths of light also provide for greater resolution; smaller details can be resolved with blue light (λ = 480 nm) than with red light (λ = 650 nm). The NA of dry lenses is limited by the refractive index of air, and the phenomenon of internal reflection, to less than 1.0. By using oil b ...
Optical Microscopy and 4 Pi Microscopy
... • Samples shown in natural color • Magnifications are 100 – 1000X. ...
... • Samples shown in natural color • Magnifications are 100 – 1000X. ...
Correcting chromatic aberrations using a diffraction grating in a
... In 1800 Thomas Young demonstrated interference patterns in light [3]. He shone monochromatic light at two screens. The first had one narrow slit in it, which had the effect of only letting light from a small part of the source through, and resulted in the transmitted light being fairly coherent. The ...
... In 1800 Thomas Young demonstrated interference patterns in light [3]. He shone monochromatic light at two screens. The first had one narrow slit in it, which had the effect of only letting light from a small part of the source through, and resulted in the transmitted light being fairly coherent. The ...
Optics
... Focal length can change the feeling of a shot. Depth of field can change a character’s size as they move within the frame and represent a character’s size relative to other characters within the frame. Wide Angle lenses provide greater depth of field, so action can be staged in depth. Teleph ...
... Focal length can change the feeling of a shot. Depth of field can change a character’s size as they move within the frame and represent a character’s size relative to other characters within the frame. Wide Angle lenses provide greater depth of field, so action can be staged in depth. Teleph ...
Inleiding Optica 2010
... (1) parallel—focal point (2) focal point—parallel (3) center of curavature—same Image at point of intersection P′ Concave: real (for objects outside focal point) Convex: virtual ...
... (1) parallel—focal point (2) focal point—parallel (3) center of curavature—same Image at point of intersection P′ Concave: real (for objects outside focal point) Convex: virtual ...
Superlens

A practical superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but there are constraints and obstacles involved in realizing each of them.












![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852293_1-2953858279e0bfa96bb28ed892089030-300x300.png)