Convex Lenses and Mirrors
... Part 4: Using a convex mirror on the optical bench (15 mins) In this part you will maintain the object position as in Part 2 and use the same lens as before. Then you will form an image using a convex mirror and determine its radius of curvature. Place the lens on the optical bench near the object ...
... Part 4: Using a convex mirror on the optical bench (15 mins) In this part you will maintain the object position as in Part 2 and use the same lens as before. Then you will form an image using a convex mirror and determine its radius of curvature. Place the lens on the optical bench near the object ...
Physics 44
... a) Turn the optical track so that it points toward a distant, bright object with the objective lens at the end of the track toward the bright object. b) Move a clean white sheet of paper back and forth along the axis of the objective lens on the side of the lens opposite the bright object (that is, ...
... a) Turn the optical track so that it points toward a distant, bright object with the objective lens at the end of the track toward the bright object. b) Move a clean white sheet of paper back and forth along the axis of the objective lens on the side of the lens opposite the bright object (that is, ...
Exam 3 Solutions
... It makes no matter that this is negative! Just go ahead and plug it into the equation again to infer where the second image forms. The result is i2 = 5 cm, which means the image is 5 c ...
... It makes no matter that this is negative! Just go ahead and plug it into the equation again to infer where the second image forms. The result is i2 = 5 cm, which means the image is 5 c ...
Presentation
... The lens is placed in front of the eye and is synchronized to the graphic display such that each depth region in the simulated scene is presented when the lens is in the appropriate state. In this way, they construct a temporally multiplexed image with correct focus cues. ...
... The lens is placed in front of the eye and is synchronized to the graphic display such that each depth region in the simulated scene is presented when the lens is in the appropriate state. In this way, they construct a temporally multiplexed image with correct focus cues. ...
Partially coherent image formation with x
... an x-ray CCD camera. Because zone plates are diffraction optics, they have a strong chromatic error, and the image quality depends on the monochromaticity of the image-forming light. To provide the required monochromaticity, a pinhole is put in close proximity to the sample plane. This pinhole toget ...
... an x-ray CCD camera. Because zone plates are diffraction optics, they have a strong chromatic error, and the image quality depends on the monochromaticity of the image-forming light. To provide the required monochromaticity, a pinhole is put in close proximity to the sample plane. This pinhole toget ...
All-dielectric subwavelength metasurface focusing lens
... manufactured with relaxed tolerance, compared to precision diffractive structures. The objective was to create a sub-wavelength, fine-patterned meta-surface as a phase mask with a smooth radial dependence of phase increment on transmission, avoiding 2π phase steps. Quasi-parabolic radial gradients o ...
... manufactured with relaxed tolerance, compared to precision diffractive structures. The objective was to create a sub-wavelength, fine-patterned meta-surface as a phase mask with a smooth radial dependence of phase increment on transmission, avoiding 2π phase steps. Quasi-parabolic radial gradients o ...
Viewing Microstructures of Materials using the Optical Microscope
... controlled by a voltage adjustment. The range of useful magnification for an objective/eyepiece combination is defined by the numerical aperture, or the measure of the microscope’s ability to gather light and resolve fine specimen detail. The numerical aperture is determined by the acceptance angle ...
... controlled by a voltage adjustment. The range of useful magnification for an objective/eyepiece combination is defined by the numerical aperture, or the measure of the microscope’s ability to gather light and resolve fine specimen detail. The numerical aperture is determined by the acceptance angle ...
MICROSCOPY
... computer. The camera is usually fitted with a light source, although extra sources (such as a fibreoptic light) can be used to highlight features of interest in the object. They also offer a large depth of field, a great advantage at high magnifications. ...
... computer. The camera is usually fitted with a light source, although extra sources (such as a fibreoptic light) can be used to highlight features of interest in the object. They also offer a large depth of field, a great advantage at high magnifications. ...
Chapter 10: Simple Harmonic Motion
... illuminates a single slit 0.750 mm in width. (a) At what distance from the slit should a screen be located if the first minimum in the diffraction pattern is to be 0.850 mm from the center of the principal maximum? (b) What is the width of the central maximum? ...
... illuminates a single slit 0.750 mm in width. (a) At what distance from the slit should a screen be located if the first minimum in the diffraction pattern is to be 0.850 mm from the center of the principal maximum? (b) What is the width of the central maximum? ...
An Optical ‘‘Janus’’ Device for Integrated Photonics By Xiang Zhang*
... medium and thus allow to design novel devices for microwave and optical frequencies such as invisibility cloaks,[6–10] light concentrators,[11–15] beam manipulators,[16–19] object transformers,[20,21] and even electromagnetic wormholes and blackholes.[15,22,23] On the other hand, transformation opti ...
... medium and thus allow to design novel devices for microwave and optical frequencies such as invisibility cloaks,[6–10] light concentrators,[11–15] beam manipulators,[16–19] object transformers,[20,21] and even electromagnetic wormholes and blackholes.[15,22,23] On the other hand, transformation opti ...
TOPS Optical Bench Finding Focal Length of Lenses and
... Procedure to determine the focal length of the 50mm mirror: 1. Replace the 150mm lens with the 50mm mirror. Mount the mirror on the right side of the component holder with the writing facing to the right. 2. Put the mirror at the 22cm mark. 3. Remove the viewing screen from its component holder 4. T ...
... Procedure to determine the focal length of the 50mm mirror: 1. Replace the 150mm lens with the 50mm mirror. Mount the mirror on the right side of the component holder with the writing facing to the right. 2. Put the mirror at the 22cm mark. 3. Remove the viewing screen from its component holder 4. T ...
Multiple wavelength diffractive imaging - X
... obtain an estimated full width at half-maximum for the resolution function of !165! 5" nm. If the resolution, *, is determined by the relationship * = 0.94% / NA !Sparrow criterion", where NA is the numerical aperture of the detector, then the observed resolution is consistent with an effective wave ...
... obtain an estimated full width at half-maximum for the resolution function of !165! 5" nm. If the resolution, *, is determined by the relationship * = 0.94% / NA !Sparrow criterion", where NA is the numerical aperture of the detector, then the observed resolution is consistent with an effective wave ...
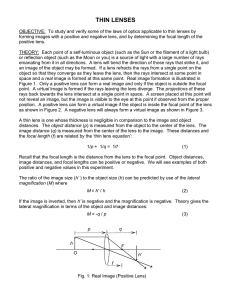
Thin Lenses
... form a real or virtual image if the object is at its focal point. Now move the lens closer so that the object is inside the focal point. Confirm that a real image cannot be formed on the screen at any position. But if you now look through the lens at the object with your eye, you should see a magnif ...
... form a real or virtual image if the object is at its focal point. Now move the lens closer so that the object is inside the focal point. Confirm that a real image cannot be formed on the screen at any position. But if you now look through the lens at the object with your eye, you should see a magnif ...
Chapter 3: Telescopes
... radio telescopes as if it came from a single dish. • Resolution will be that of dish whose diameter = largest separation between dishes. ...
... radio telescopes as if it came from a single dish. • Resolution will be that of dish whose diameter = largest separation between dishes. ...
A high resolution ion microscope for cold atoms
... method. The destruction can be suppressed when using the related method of phase contrast imaging, allowing to image the same cloud several times [6], yet at a reduced contrast. For non-destructive imaging of dilute samples with single atom sensitivity, fluorescence imaging is typically used. In gen ...
... method. The destruction can be suppressed when using the related method of phase contrast imaging, allowing to image the same cloud several times [6], yet at a reduced contrast. For non-destructive imaging of dilute samples with single atom sensitivity, fluorescence imaging is typically used. In gen ...
Lithography In the Top
... – ArF – 193 nM – Shorter wavelength than so-called “deep UV” peak of 248nM – F2 Laser – Low output but at 157nM ...
... – ArF – 193 nM – Shorter wavelength than so-called “deep UV” peak of 248nM – F2 Laser – Low output but at 157nM ...
Measurement of the 4Pi-confocal point spread function proves 75
... by focusing elements. An objective lens focuses light by concentrating a segment of a spherical wave front into an object point. The intensity in the focal region is distributed around the focal point forming a focal volume, which is described by the point spread function (PSF). The extent of the PS ...
... by focusing elements. An objective lens focuses light by concentrating a segment of a spherical wave front into an object point. The intensity in the focal region is distributed around the focal point forming a focal volume, which is described by the point spread function (PSF). The extent of the PS ...
Applied physics viva
... A2. The distance between the optical centre of the lens and its focus is called focal length. Q3. On what factors does the focal length of a lens depend? A3. Focal length depends upon: Radii of curvature of the surfaces. (i)Refractive index of the medium of lens. (ii)Colour of rays and (iii)Media of ...
... A2. The distance between the optical centre of the lens and its focus is called focal length. Q3. On what factors does the focal length of a lens depend? A3. Focal length depends upon: Radii of curvature of the surfaces. (i)Refractive index of the medium of lens. (ii)Colour of rays and (iii)Media of ...
Microscopes
... • Uses electrons to image the sample • Electromagnets act as lenses (though very weak) • Electron λ ~ 0.0055 nm • Thus resolutions of < 1 nm • WONDERFUL RESOLUTION BUT: ...
... • Uses electrons to image the sample • Electromagnets act as lenses (though very weak) • Electron λ ~ 0.0055 nm • Thus resolutions of < 1 nm • WONDERFUL RESOLUTION BUT: ...
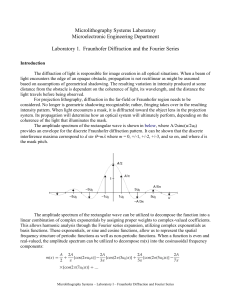
MLSystems Lab 1 - Fourier v4 - RIT
... These discrete coefficients are the diffraction orders of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern that are produced when a diffraction grating is illuminated by coherent illumination. These coefficients, represented as terms in the harmonic decomposition of m(x) correspond to the discrete orders seen in ...
... These discrete coefficients are the diffraction orders of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern that are produced when a diffraction grating is illuminated by coherent illumination. These coefficients, represented as terms in the harmonic decomposition of m(x) correspond to the discrete orders seen in ...
Equipment list: Description Supplier Model Optical test bench
... Horiba-Jobin-Yvon Uvisel/460 Spectroscopic Ellipsometer ...
... Horiba-Jobin-Yvon Uvisel/460 Spectroscopic Ellipsometer ...
PDF Link
... clear dip in intensity) when imaged by a specific microscope. The same point sources in the same locations will not be resolved by the same microscope (that is, will appear as only one large spot) if the sources are instead emitting light that is coherent and in-phase. However, the two sources becom ...
... clear dip in intensity) when imaged by a specific microscope. The same point sources in the same locations will not be resolved by the same microscope (that is, will appear as only one large spot) if the sources are instead emitting light that is coherent and in-phase. However, the two sources becom ...
The Fresnel Biprism
... points showing the imaginary sources could be seen on the screen. The distance between the imaginary sources was found to be a = 0.06 ± 0.02cm. There is no real way to compare this answer to a reference source as each optical system tends to be different in one way or another however this number was ...
... points showing the imaginary sources could be seen on the screen. The distance between the imaginary sources was found to be a = 0.06 ± 0.02cm. There is no real way to compare this answer to a reference source as each optical system tends to be different in one way or another however this number was ...
Physics 323 Lecture Notes Part I: Optics
... by two pebbles dropped at the same time exhibit this nicely: Where two crests overlap, the waves reinforce each other, but where a crest and a trough coincide, the two waves actually cancel. This is illustrated in Figure 1.2. If light is a wave, two sources emitting waves in a synchronized fashion1 ...
... by two pebbles dropped at the same time exhibit this nicely: Where two crests overlap, the waves reinforce each other, but where a crest and a trough coincide, the two waves actually cancel. This is illustrated in Figure 1.2. If light is a wave, two sources emitting waves in a synchronized fashion1 ...
Superlens

A practical superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but there are constraints and obstacles involved in realizing each of them.