Nitrogen Cycle
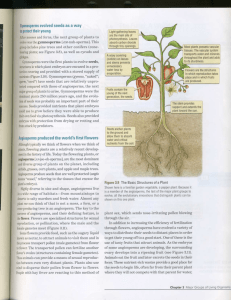
... carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen •Roots are used to acquire nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and sulfur • What has to happen before these elements can be absorbed by the roots? ...
... carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen •Roots are used to acquire nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and sulfur • What has to happen before these elements can be absorbed by the roots? ...
Growing instructions
... These Squash are very good to eat in soups or roasted in the oven but keep the biggest for the Show! GIANT TOMATO Tomatoes can be grown in a grow-bag, a pot or in the soil. Put in a sunny place out of the wind or, if you have one, in the greenhouse. As the plant grows it must be supported with stron ...
... These Squash are very good to eat in soups or roasted in the oven but keep the biggest for the Show! GIANT TOMATO Tomatoes can be grown in a grow-bag, a pot or in the soil. Put in a sunny place out of the wind or, if you have one, in the greenhouse. As the plant grows it must be supported with stron ...
Gymnosperms evolved seeds as a way to protect their young
... reproduction, or pollination, where the male and the female gametes meet (Figure 3 .11). Some flowers provide food, such as the sugary liquid known as nectar, to attract animals to visit them and in the process transport pollen (male gametes) from flower to flower. The transported pollen can fertili ...
... reproduction, or pollination, where the male and the female gametes meet (Figure 3 .11). Some flowers provide food, such as the sugary liquid known as nectar, to attract animals to visit them and in the process transport pollen (male gametes) from flower to flower. The transported pollen can fertili ...
Chapter 5: Elemental and Hydrologic Cycles
... becomes significant in anaerobic environments. 1. Carbon enters plants, algae, and cyanobacteria (and many chemoautotrophs) as CO2, which is incorporated into organic molecules by photosynthesis (or similar processes for carbon fixation). 2. Cell respiration by plants, by animals that eat plants, an ...
... becomes significant in anaerobic environments. 1. Carbon enters plants, algae, and cyanobacteria (and many chemoautotrophs) as CO2, which is incorporated into organic molecules by photosynthesis (or similar processes for carbon fixation). 2. Cell respiration by plants, by animals that eat plants, an ...
Don`t Let Winter Stop You from Gardening
... that have become the rage in Washington. This plant will easily reach 10 to 12 feet and deserves a prominent spot to spread out. Bright light and moderate moisture with regular fertilization will help this specimen grow into even the largest of spaces quite rapidly. If possible, move to a sheltered ...
... that have become the rage in Washington. This plant will easily reach 10 to 12 feet and deserves a prominent spot to spread out. Bright light and moderate moisture with regular fertilization will help this specimen grow into even the largest of spaces quite rapidly. If possible, move to a sheltered ...
Validation of coupled speciation-transport models to describe root
... The classical model for root uptake of solutes from the soil supposes a cylindrical root surrounded by soil through which the solute diffuses and is taken up in a Michaelis-Menten process. The conventional modeling of solute uptake does not consider biogeochemical interactions, e.g. root-induced che ...
... The classical model for root uptake of solutes from the soil supposes a cylindrical root surrounded by soil through which the solute diffuses and is taken up in a Michaelis-Menten process. The conventional modeling of solute uptake does not consider biogeochemical interactions, e.g. root-induced che ...
Vascular System PPT
... from the ground, through the root system, and up into the leaves, flower petals and fruits. ...
... from the ground, through the root system, and up into the leaves, flower petals and fruits. ...
SI 10/19/08 Exam 2 Review 1. Which of the following phylogenetic
... 1. Which of the following phylogenetic groups within the animal kingdom encompasses all the others in the list? A. rotifera B. deuterostomes C. bilateria D. arthropoda E. protostomes 2. Octopi are most closely related to which of the following organisms? A. clams B. jellyfish C. starfish D. earthwor ...
... 1. Which of the following phylogenetic groups within the animal kingdom encompasses all the others in the list? A. rotifera B. deuterostomes C. bilateria D. arthropoda E. protostomes 2. Octopi are most closely related to which of the following organisms? A. clams B. jellyfish C. starfish D. earthwor ...
Lecture 4
... Uniform removal of soil in thin layers from sloping land-resulting from sheet or overland flow occurring in thin layers. minute rilling takes place almost simultaneously with the first detachment and movement of soil particles. the constant meander and change of position of these microscopic rills. ...
... Uniform removal of soil in thin layers from sloping land-resulting from sheet or overland flow occurring in thin layers. minute rilling takes place almost simultaneously with the first detachment and movement of soil particles. the constant meander and change of position of these microscopic rills. ...
webinar presentation
... Adopted management and fertility practices that enhanced microbial activity Production of on farm Humus Compost™ from agricultural waste and intensive animal husbandry. Reduced the use of soluble fertilisers in cropping by 50%, added carbon to buffer any ...
... Adopted management and fertility practices that enhanced microbial activity Production of on farm Humus Compost™ from agricultural waste and intensive animal husbandry. Reduced the use of soluble fertilisers in cropping by 50%, added carbon to buffer any ...
Asexual Plant Propagation
... • You will be able to identify the areas on a plant from which cuttings may be taken. • You will be able to recognize materials, plants, and chemical hormones needed for successful plant propagation by cuttings. ...
... • You will be able to identify the areas on a plant from which cuttings may be taken. • You will be able to recognize materials, plants, and chemical hormones needed for successful plant propagation by cuttings. ...
Yuccah
... Yuccah is a natural-based wetting agent/soil penetrant derived from the Yucca schidigera plant. This unique desert plant produces natural surfactants to help it use water more efficiently. These surfactant compounds help plants survive the extreme heat, drought and soil salinity found in harsh clima ...
... Yuccah is a natural-based wetting agent/soil penetrant derived from the Yucca schidigera plant. This unique desert plant produces natural surfactants to help it use water more efficiently. These surfactant compounds help plants survive the extreme heat, drought and soil salinity found in harsh clima ...
Guide to Symptoms of Plant Nutrient Deficiencies
... may look like another (for instance, molybdenum is required by legumes to complete the nitrogen fixation process). ...
... may look like another (for instance, molybdenum is required by legumes to complete the nitrogen fixation process). ...
Presentation Title, Arial Regular 29pt Sub title, Arial Regular 24pt
... ‘Supercharging’ photosynthesis Plants have two major photosynthetic mechanisms: C3 and C4. Phenomics researchers want to replace the C3 pathway of rice with a more efficient C4 mechanism. C4 plants can concentrate carbon dioxide inside the leaf, and photosynthesise more efficiently than C3 plants, ...
... ‘Supercharging’ photosynthesis Plants have two major photosynthetic mechanisms: C3 and C4. Phenomics researchers want to replace the C3 pathway of rice with a more efficient C4 mechanism. C4 plants can concentrate carbon dioxide inside the leaf, and photosynthesise more efficiently than C3 plants, ...
Chapter 12: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Parasites
... Mycosis: Any fungal disease. Tend to be chronic because fungi grow slowly. Mycoses are classified into the following categories: ...
... Mycosis: Any fungal disease. Tend to be chronic because fungi grow slowly. Mycoses are classified into the following categories: ...
Controlled Experiment Quiz
... At the advice of her Biology teacher, the student re-designs the experiment. She puts aspirin in the soil of plant A only. She gives both plants the same amount of sunlight each day (12 hours). Plant B receives 0.5 liter of water daily, while plant A receives 1 liter of water daily to help dissolve ...
... At the advice of her Biology teacher, the student re-designs the experiment. She puts aspirin in the soil of plant A only. She gives both plants the same amount of sunlight each day (12 hours). Plant B receives 0.5 liter of water daily, while plant A receives 1 liter of water daily to help dissolve ...
Colorado Agri-science Curriculum Section: Plant & Soil
... The mesophilic microorganisms once again take over for the final phase of "curing" or maturation of the remaining organic matter. ...
... The mesophilic microorganisms once again take over for the final phase of "curing" or maturation of the remaining organic matter. ...
When are soils most likely to erode?
... plants in wet paper towels, wet gravel, wet cotton balls, and wet soil. Which question would be the best title for this ...
... plants in wet paper towels, wet gravel, wet cotton balls, and wet soil. Which question would be the best title for this ...
Chapter 2-section 3 geology notes
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
Plant Pathology 101 - UF/IFAS Extension Alachua County
... symptoms as stunting of plants, shortened internodes, inadequate development of roots, malformation of leaves, inadequate production of chlorophyll and other pigments, and failure of fruits and flowers to develop. Overdevelopment of tissues or organs. Examples include: galls on roots, stems, or leav ...
... symptoms as stunting of plants, shortened internodes, inadequate development of roots, malformation of leaves, inadequate production of chlorophyll and other pigments, and failure of fruits and flowers to develop. Overdevelopment of tissues or organs. Examples include: galls on roots, stems, or leav ...
NEW HORIZONS the next revolution in agriculture
... yy soil compaction which physically stop roots growing yy low fertility or nutrient deficient soils that limit root growth at depth, leaving soil moisture unused by crops or pastures at the end of a season yy saline sub-soils or soils with very high or very low pH levels which are hostile to root gr ...
... yy soil compaction which physically stop roots growing yy low fertility or nutrient deficient soils that limit root growth at depth, leaving soil moisture unused by crops or pastures at the end of a season yy saline sub-soils or soils with very high or very low pH levels which are hostile to root gr ...
SI 10/19/08 Exam 2 Review 1. Which of the following phylogenetic
... 1. Which of the following phylogenetic groups within the animal kingdom encompasses all the others in the list? A. rotifera B. deuterostomes C. bilateria D. arthropoda E. protostomes 2. Octopi are most closely related to which of the following organisms? A. clams B. jellyfish C. starfish D. earthwor ...
... 1. Which of the following phylogenetic groups within the animal kingdom encompasses all the others in the list? A. rotifera B. deuterostomes C. bilateria D. arthropoda E. protostomes 2. Octopi are most closely related to which of the following organisms? A. clams B. jellyfish C. starfish D. earthwor ...
Arbuscular mycorrhiza

An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (plural mycorrhizae or mycorrhizas, a.k.a. endomycorrhiza, AM fungi, or AMF) is a type of mycorrhiza in which the fungus penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant. (Not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza or ericoid mycorrhiza.)Arbuscular mycorrhizas are characterized by the formation of unique structures, arbuscules and vesicles by fungi of the phylum Glomeromycota. AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis played a crucial role in the initial colonisation of land by plants and in the evolution of the vascular plants.It has been said that it is quicker to list the plants that do not form mycorrhizae than those that do. This symbiosis is a highly evolved mutualistic relationship found between fungi and plants, the most prevalent plant symbiosis known, and AM is found in 80% of vascular plant families in existence today.The tremendous advances in research on mycorrhizal physiology and ecology over the past 40 years have led to a greater understanding of the multiple roles of AMF in the ecosystem. This knowledge is applicable to human endeavors of ecosystem management, ecosystem restoration, and agriculture.