Lasers Essay Research Paper The light from
... bore there are mirrors. These mirrors must be held in precise alignment for the laser to work properly. In most HeNe lasers the mirrors are permanently attached or sealed onto the ends of the tube — sometimes referred to as hard seal technology. In higher power lasers the mirrors are usually not mou ...
... bore there are mirrors. These mirrors must be held in precise alignment for the laser to work properly. In most HeNe lasers the mirrors are permanently attached or sealed onto the ends of the tube — sometimes referred to as hard seal technology. In higher power lasers the mirrors are usually not mou ...
From a flat mirror, designer light — Harvard School of Engineering
... who was co-principal investigator for this work. "The reflected beam can bounce backward instead of forward. You can create negative refraction. There is a new angle of total internal reflection." Moreover, the frequency (color), amplitude (brightness), and polarization of the light can also be cont ...
... who was co-principal investigator for this work. "The reflected beam can bounce backward instead of forward. You can create negative refraction. There is a new angle of total internal reflection." Moreover, the frequency (color), amplitude (brightness), and polarization of the light can also be cont ...
HP unit 12 - wave optics student handout
... • When m = 0, it is the zeroth order maximum • When m = 1, it is called the first order maximum, etc ...
... • When m = 0, it is the zeroth order maximum • When m = 1, it is called the first order maximum, etc ...
HOLO TEXT
... holograms. The support materials for holographic emulsions are usually glass or some form of plastic. Frequently the laser light being used to construct a hologram will enter the supporting glass or plastic from the side of the material. Those rays that enter your cover glass from the side are often ...
... holograms. The support materials for holographic emulsions are usually glass or some form of plastic. Frequently the laser light being used to construct a hologram will enter the supporting glass or plastic from the side of the material. Those rays that enter your cover glass from the side are often ...
Triple Refraction_and_Total_Internal_Reflection
... When waves cross from slow to fast, they are refracted away from the normal. ...
... When waves cross from slow to fast, they are refracted away from the normal. ...
PhysicsTutor
... from the top surface of the film with light reflected from the film-glass interface. • The number of phase jumps is the same for recombining beams (air to soap and soap to glass). • Find the optical path length difference between the two beams, phase shift of 2. ...
... from the top surface of the film with light reflected from the film-glass interface. • The number of phase jumps is the same for recombining beams (air to soap and soap to glass). • Find the optical path length difference between the two beams, phase shift of 2. ...
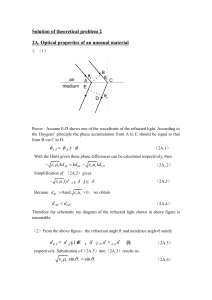
Solution of theoretical problem 2
... On the right side of above equation the first term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in air, the second term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in the unusual medium, while the third term accounts for the phas ...
... On the right side of above equation the first term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in air, the second term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in the unusual medium, while the third term accounts for the phas ...
Computer-generated holograms for three
... threedimensional (3-D) displays, sometimes called digitally synthetic holograms, are desired media for creating 3-D autostereoscopic images of virtual objects. However, the technology suffers from two problems: the necessity for extremely high spatial resolution to fabricate or display the holograms ...
... threedimensional (3-D) displays, sometimes called digitally synthetic holograms, are desired media for creating 3-D autostereoscopic images of virtual objects. However, the technology suffers from two problems: the necessity for extremely high spatial resolution to fabricate or display the holograms ...
Integral holography: white-light single-shot hologram
... pattern taken from any of the elemental images is employed in order to fix a common reference point for all the elemental images. Completely automatic cutting and centering methods may be possible and will be considered in our future research. In the experiment, we have chosen the common reference p ...
... pattern taken from any of the elemental images is employed in order to fix a common reference point for all the elemental images. Completely automatic cutting and centering methods may be possible and will be considered in our future research. In the experiment, we have chosen the common reference p ...
Physics 300 - WordPress.com
... Answer the multiple choice questions by placing the letter for the best answer on the line provided. Provide complete solutions to the questions on the back in the space provided. Do not use a separate piece of paper. 1-5. Definitions B • The number of oscillations per second is called… a. period b. ...
... Answer the multiple choice questions by placing the letter for the best answer on the line provided. Provide complete solutions to the questions on the back in the space provided. Do not use a separate piece of paper. 1-5. Definitions B • The number of oscillations per second is called… a. period b. ...
LBS-100 System
... contains the mounting frame, 1 wedge beam splitter and several attenuators. The exit end of the LBS-100 is standard C mount thread so all our cameras can be mounted to the frame. The wedge angle is 6.5 degrees to insure that the reflection from the rear side will not enter the camera. The optical el ...
... contains the mounting frame, 1 wedge beam splitter and several attenuators. The exit end of the LBS-100 is standard C mount thread so all our cameras can be mounted to the frame. The wedge angle is 6.5 degrees to insure that the reflection from the rear side will not enter the camera. The optical el ...
Midterm Exam
... b. Pick one of these stable resonators (choose numbers that satisfy the condition for part a) and solve for the mode of this cavity. Specifically, plot the spotsize, w(z), and the radius of curvature, R(z), of the mode everywhere in the cavity. c. Put a focusing lens immediately after the output cou ...
... b. Pick one of these stable resonators (choose numbers that satisfy the condition for part a) and solve for the mode of this cavity. Specifically, plot the spotsize, w(z), and the radius of curvature, R(z), of the mode everywhere in the cavity. c. Put a focusing lens immediately after the output cou ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.