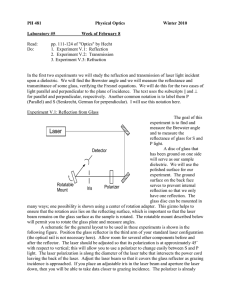
A list of some commonly used formulas in optics
... calculations, the incident electric field is broken into two plane-polarized components. The “wheel” in the pictures below denotes plane of incidence. The normal to the surface and all propagation vectors (ki, kr, kt) lie in this plane. ...
... calculations, the incident electric field is broken into two plane-polarized components. The “wheel” in the pictures below denotes plane of incidence. The normal to the surface and all propagation vectors (ki, kr, kt) lie in this plane. ...
20170327_AH_Interference
... waves travelling in air to have a constant phase relationship, they must have the same frequency and wavelength. At any given point, the phase difference between the two waves will be fixed. For us to see interference effects, we require two or more sources of coherent light waves. The best source o ...
... waves travelling in air to have a constant phase relationship, they must have the same frequency and wavelength. At any given point, the phase difference between the two waves will be fixed. For us to see interference effects, we require two or more sources of coherent light waves. The best source o ...
Chapter 8a Wave Optics
... Example 2: two microscope slides each 7.5cm long are in contact along one pair of edges while the other edges are held apart by a piece of paper 0.012mm thick. Calculate the spacing of interference fringes under illumination by light of 632nm wavelength at near normal incidence. Solution: let the a ...
... Example 2: two microscope slides each 7.5cm long are in contact along one pair of edges while the other edges are held apart by a piece of paper 0.012mm thick. Calculate the spacing of interference fringes under illumination by light of 632nm wavelength at near normal incidence. Solution: let the a ...
Digital holography of total internal reflection
... applications. Phase-shifting digital holography allows the elimination of zero-order and twinimage components even in an on-axis arrangement [5]. Optical scanning holography can generate holographic images of fluorescence [6]. Application of digital holography in microscopy is especially important, ...
... applications. Phase-shifting digital holography allows the elimination of zero-order and twinimage components even in an on-axis arrangement [5]. Optical scanning holography can generate holographic images of fluorescence [6]. Application of digital holography in microscopy is especially important, ...
Nanostructured Holograms for Broadband Manipulation of Vector
... working principle employs nanoscale optical resonators patterned at the interface at specific positions and with designed plasmonic resonances to engineer the scattering properties of the whole interface. The complexity in the design of each scattering element and the relatively narrow operating band ...
... working principle employs nanoscale optical resonators patterned at the interface at specific positions and with designed plasmonic resonances to engineer the scattering properties of the whole interface. The complexity in the design of each scattering element and the relatively narrow operating band ...
Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 076101 - APS Link Manager
... putational lens’’ (CL) [7–10]. Another approach is Fourier transform holography, where the scattering pattern from the sample is encoded by a reference wave. The interference pattern can then be uniquely inverted into a real space image, but the resolution is limited by the size of the reference str ...
... putational lens’’ (CL) [7–10]. Another approach is Fourier transform holography, where the scattering pattern from the sample is encoded by a reference wave. The interference pattern can then be uniquely inverted into a real space image, but the resolution is limited by the size of the reference str ...
Optical Micrometer
... for a series of angles of incidence in 10° steps. You should do this measurement with a smaller distance between the screen and the optical table, and again with a larger distance, having measured the distance L between your near and far points of observation. Measure the thickness of your plate "t" ...
... for a series of angles of incidence in 10° steps. You should do this measurement with a smaller distance between the screen and the optical table, and again with a larger distance, having measured the distance L between your near and far points of observation. Measure the thickness of your plate "t" ...
Three-Dimensional Imaging and Processing Using Computational
... reference beam interferes with the light diffracted by the 3-D object on the CCD detector. The intensity ratio between the two arms is chosen in a way that the camera collects approximately the same power from the light scattered by the object as from the reference wave. Similar to (1), the complex ...
... reference beam interferes with the light diffracted by the 3-D object on the CCD detector. The intensity ratio between the two arms is chosen in a way that the camera collects approximately the same power from the light scattered by the object as from the reference wave. Similar to (1), the complex ...
Lab Writeup Michelson(New)
... The image of M1 appears in line with M2 and may be either in front of or behind M2 (see Fig. 2). The complete theory, which must take into account the fact that the source is an extended source, shows that when M2, and the image of M1 are parallel, then monochromatic light produces an interference p ...
... The image of M1 appears in line with M2 and may be either in front of or behind M2 (see Fig. 2). The complete theory, which must take into account the fact that the source is an extended source, shows that when M2, and the image of M1 are parallel, then monochromatic light produces an interference p ...
[pdf]
... experimental images of absorbing and scattering objects in turbid media obtained by this approach. The method differs from least-squares techniques6 in that it is fast and noniterative. In addition to providing information about the position and shape of a hidden object or objects, projection images ...
... experimental images of absorbing and scattering objects in turbid media obtained by this approach. The method differs from least-squares techniques6 in that it is fast and noniterative. In addition to providing information about the position and shape of a hidden object or objects, projection images ...
Light Rays
... The optical centre is the centre of a lens. Light rays passing through it do not change direction. The principal axis is the line passing through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens. Rays parallel to the principal axis converge to or diverge from the focus or focal point of a lens. ...
... The optical centre is the centre of a lens. Light rays passing through it do not change direction. The principal axis is the line passing through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens. Rays parallel to the principal axis converge to or diverge from the focus or focal point of a lens. ...
Problem 2
... and the other one, denoted by Plate 2, is partially reflective ( but with a high reflectance). Suppose plane light waves are radiated from a source located near Plate 1, then such light waves are multiply reflected by the two plates inside the cavity. Since optically the Plate 2 is not ideally refle ...
... and the other one, denoted by Plate 2, is partially reflective ( but with a high reflectance). Suppose plane light waves are radiated from a source located near Plate 1, then such light waves are multiply reflected by the two plates inside the cavity. Since optically the Plate 2 is not ideally refle ...
Lithography - 123seminarsonly.com
... By scanning an area with the beam, the precursor gas will be decomposed into volatile and non-volatile components; the non-volatile component, such as tungsten, remains on the surface as a deposition. From nanometers to hundred of micrometers in length, tungsten metal deposition allows to put metal ...
... By scanning an area with the beam, the precursor gas will be decomposed into volatile and non-volatile components; the non-volatile component, such as tungsten, remains on the surface as a deposition. From nanometers to hundred of micrometers in length, tungsten metal deposition allows to put metal ...
setting up of a total internal reflection fluorescent microscope
... The green curve in Fig. 6b indicates the spectrum of Dichromatic beamsplitter (dichroic mirror) which is a specialized filter designed to efficiently reflect excitation wavelengths and pass emission wavelengths. These filters are always the interference type. Dichroic mirror is positioned in the lig ...
... The green curve in Fig. 6b indicates the spectrum of Dichromatic beamsplitter (dichroic mirror) which is a specialized filter designed to efficiently reflect excitation wavelengths and pass emission wavelengths. These filters are always the interference type. Dichroic mirror is positioned in the lig ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.













![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852293_1-2953858279e0bfa96bb28ed892089030-300x300.png)